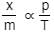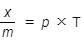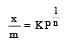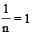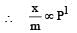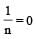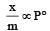31 Year NEET Previous Year Questions: Surface Chemistry (Old NCERT) - NEET MCQ
16 Questions MCQ Test Chemistry Class 12 - 31 Year NEET Previous Year Questions: Surface Chemistry (Old NCERT)
For adsorption of a gas on a solid, the plot of log x/m vs log P is linear with slope equal to (n being whole number) [1994,2006]
During dialysis [1996]
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
The ability of an ion to bring about coagulation of a given colloid depends upon [1997]
At the critical micelle concentration (CMC) the surfactant molecules [1998]
Hardy- Schulzerule explains the effect of electrolytes on the coagulation of colloidal solution. According to this rule, coagulation power of cations follow the order [1999]
Which is used for ending charge on colloidal solution? [2000]
Pure water can be obtained from sea water by[2001]
Which is not correct regarding the adsorption of a gas on surface of solid? [2001]
Position of non-polar and polar part in micelle is[2002]
According to the adsorption theory of catalysis, the speed of the reaction increases because- [2003]
Which of the following forms cationic micelles above certain concentration [2004]
Which one of the following forms micelles in aqueous solution above certain concentration? [2005]
The Langmuir adsorption isotherm is deduced using the assumption [2007]
If x is amount of adsorbate and m is amount of adsorbent, which of the following relations is not related to adsorption process ? [2011]
In Freundlich Adsorption isotherm, the value of 1/n is:[2012]
The protecting power of lyophilic colloidal sol is expressed in terms of : [2012]
|
108 videos|286 docs|123 tests
|


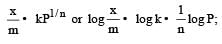
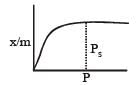
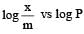 is linear with slope
is linear with slope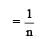
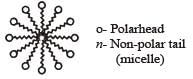
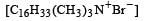 is a cationic micelle
is a cationic micelle