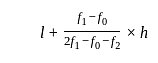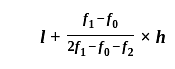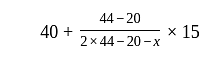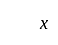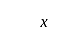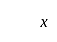APSET Paper 2 Mock Test - 3 (Commerce) - AP TET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test APSET Mock Test Series 2025 - APSET Paper 2 Mock Test - 3 (Commerce)
The RBI prints all the currency notes except the _______ currency note.
"The life expectancy of people in Kerala is more than that of Tamil Nadu." This statement is an example of:
Which of the following is not a category of non-performing assets?
Which of the following will be charged to GST?
(I) Electricity
(II) Sale of Property
(III) Petrol
(IV) Alcohol liquor for human consumption
The black box model in marketing relates to:
Which of the following does NOT come under the purview of 'paper taxes'?
In regression model, assumptions of error term are:
(A) Zero-mean assumption
(B) Constant-variance assumption
(C) Dependence assumption
(D) Independence assumption
(E) Normality assumption
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
Which of the following is true about GST?
I. GST applies different rates to same products.
II. The tax has become a subject of national unrest.
III. Some loopholes have been exploited to dupe government.
Identify the correct statement from the following.
The Regression Coefficient is independent of the change of
(A) Scale only
(B) Origin only
(C) Both Scale and Origin
(D) Neither Scale nor Origin
Choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below:
Reserve Bank of India controls the activities of which of the following banks in India:
(i) Commercial Banks
(ii) Cooperative Banks
(iii) Foreign Banks
(iv) Rural Banks
Codes:
Which of the following may be an ethics code?
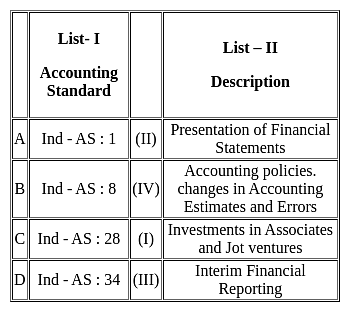
Match List I with List II:
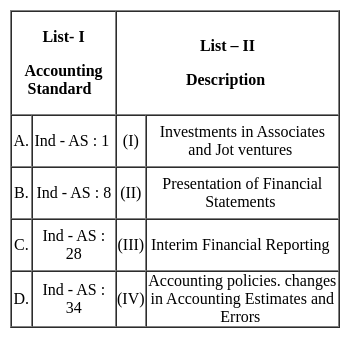
Choose the correct answer from the options given below -
Assertion (A): Weighted average cost of capital should be used as a hurdle rate for accepting or rejecting a capital budgeting proposal.
Reason (R): It is because by financing in the proportions specified and accepting the project, yielding more than the weighted average required return, the firm is able to increase the market price of its stock.
A perfectly elastic supply curve means:
i. A horizontal supply curve
ii. Price Elasticity of Supply = Infinity
Anil retired from XYZ Ltd. after 28 years of service and received a gratuity of Rs.12 lakh. His last drawn salary (basic + DA) was Rs. 1,00,000 per month. If Anil is not covered by the Payment of Gratuity Act, 1972, the exemption under sec 10(10) in respect of gratuity is:
Which of the following relationship is true?
When goods in the domestic market are sold at a high price and in the foreign market at a low price, it is a situation of:
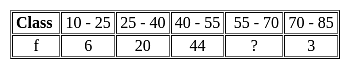
If the mode of the above distribution is 48.6, then the missing frequency will be
|
60 tests
|