Assertion & Reason Test: Aldehydes, Ketones & Carboxylic Acids - NEET MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test Topic-wise MCQ Tests for NEET - Assertion & Reason Test: Aldehydes, Ketones & Carboxylic Acids
Directions: In the following questions, A statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as.
Assertion (A): Oxidation of ketones is easier than aldehydes.
Reason (R): C–C bond of ketones is stronger than C–H bond of aldehydes.
Directions: In the following questions, A statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as.
Assertion (A): Aromatic aldehydes and formaldehyde undergo Cannizzaro reaction.
Reason (R): Aromatic aldehydes are almost as reactive as formaldehyde.
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Directions: In the following questions, A statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as.
Assertion (A): Benzoic acid does not undergo Friedel-craft’s reaction.
Reaction (R): The carboxyl group is activating and undergo electrophilic substitution reaction.
Directions: In the following questions, A statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as.
Assertion (A): Aromatic carboxylic groups do not undergo Friedel- Crafts reaction.
Reason (R): Carboxyl group is deactivating and the catalyst aluminium chloride gets bonded to the carboxyl group.
Directions: In the following questions, A statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as.
Assertion (A): Benzaldehyde is less reactive than ethanal towards nucleophilic addition reactions.
Reason (R): Ethanal is more sterically hindered.
Directions: In the following questions, A statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as.
Assertion (A): Aldehydes and ketones, both react with Tollen’s reagent to form silver mirror.
Reason (R): Both aldehydes and ketones contain a carbonyl group.
Directions: In the following questions, A statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as.
Assertion (A): Compounds containing —CHO group are easily oxidised to corresponding carboxylic acids.
Reason (R): Carboxylic acids can be reduced to alcohols by treatment with LiAlH4.
Directions: In the following questions, A statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as.
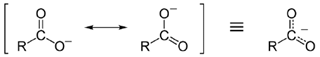
Assertion (A): Carboxylic acids are more acidic than phenols.
Reason (R): Phenols are ortho and para directing.
Directions: These questions consist of two statements, each printed as Assertion and Reason. While answering these questions, you are required to choose any one of the following four responses.
Assertion : The boiling points of aldehydes and ketones are higher than hydrocarbons and ethers of comparable molecular masses.
Reason : There is a weak molecular association in aldehydes and ketones arising out of the dipole-dipole interactions.
Directions: These questions consist of two statements, each printed as Assertion and Reason. While answering these questions, you are required to choose any one of the following four responses.
Assertion : Compounds containing –CHO group are easily oxidised to corresponding carboxylic acids.
Reason : Carboxylic acids can be reduced to alcohols by treatment with LiAlH4
|
9 docs|1272 tests
|