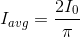BITSAT Practice Test - 14 - JEE MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test BITSAT Mock Tests Series & Past Year Papers 2025 - BITSAT Practice Test - 14
A circular coil, of radius R, carries a current I. The expression for the magnetic field due to this coil at its centre is
The acceleration of a particle increases linearly with time t as 6t. If the initial velocity of the particle is zero and the particle starts from the origin, then the distance travelled by the particle in time t will be
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
A ray of light travels from a medium of refractive index n1 to a medium of refractive index n2. If angle of incidence is i and the angle of refraction is r. Then sini/sinr is equal to
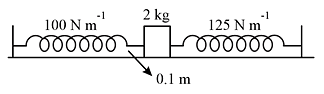
A block of mass, m = 2 kg is attached to two unstretched springs of force constant, k1 = 100 N m−1 and k2 = 125 N m−1. The block is displaced towards the left through a distance of 10 cm and released. Find the speed of the block as it passes through the mean position.
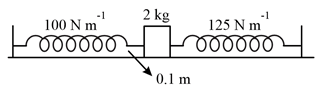
A toy car of mass 5 kg moves up a ramp under the influence of force F plotted against displacement x. The maximum height attained by the car is given by,
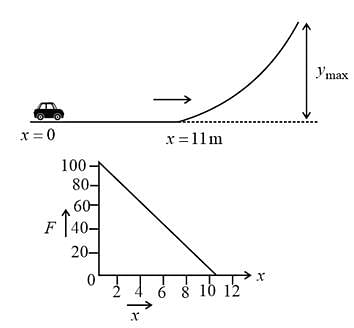
The graph which represents the relation between the total resistance R of a multi-range moving coil voltmeter and its full-scale deflection V is
The mass of a proton is 1836 times more than the mass of an electron. If a subatomic particle of mass (m′) 207 times the mass of an electron is captured by the nucleus, then what will happen to the first ionization potential of H?
A particle executes linear simple harmonic motion with an amplitude of 3 cm. When the particle is at 2 cm from the mean position, the magnitude of its velocity is equal to that of its acceleration. Then its time period in seconds is
In a biprism experiment with sodium light, bands of width 0.0195 cm are observed at 100 cm from slit. On introducing a convex lens 30 cm away from the slit between biprism and screen, two images of the slit are seen 0.7 cm apart at 100 cm distance from the slit. Calculate the wavelength of sodium light.
Two masses of M and 4M are moving with equal kinetic energy. The ratio of their linear momentum is
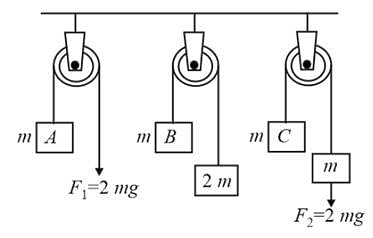
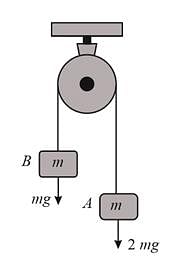
In the figure, the blocks A, B and C each of mass m have acceleration a1, a2 and a3, respectively. F1 and F2 are external forces of magnitude 2mg and mg respectively. Then
A whistle of frequency 540 Hz rotates in a horizontal circle of radius 2 m at an angular speed of 15 rad s−1. The highest frequency heard by a listener at rest at large distance with respect to the centre of circle (velocity of sound in air = 330 m s−1)
Consider two observers moving with respect to each other at a speed v along a straight line. They observe a block of mass moving over a distance l on a rough surface. The following quantities will be same as observed by the two observers
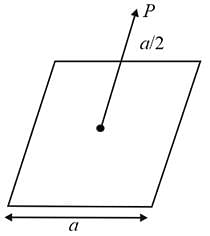
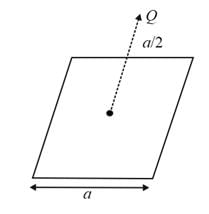
A charge Q is placed at a distance a/2 above the centre of a square surface of side length a. The electric flux through the square surface due to the charge would be?
Find the elongation of the steel and brass wire in the fig. unloaded length of steel wire = 1.5 m, unloaded length of brass wire 0.3 cm, diameter of each wire = 0.3 cm. Young's modulus for steel = 20 × 1010 Pa and that for brass = 9.0 × 1010 Pa.

If a = 18√v (where 'a' and 'v' are acceleration and velocity at any instant, respectively), then the acceleration when the time t = 1 second is
The following figure is part of a horizontally stretched net. Section 'AB' is stretched with a force of 10 N. The tensions in the sections 'BC' and 'BF', respectively, are

A cricket ball of mass 200 gms moving with a velocity of 20 m/sec is brought to rest by a player in 0.1 sec. The average force applied by the player is
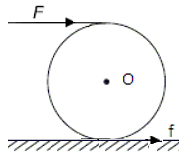
A hollow sphere of mass M and radius R is initially at rest on a horizontal rough surface. It moves under the action of a constant horizontal force F as shown in the figure.
The frictional force between the sphere and the surface is
A body of mass m is raised to a height h above the surface of Earth of mass M and radius R until its gravitational potential energy increases by 1/3 mgR. The value of h is
A capillary tube of radius r is immersed in water and water rises in it to a height h. The mass of water in the capillary tube is 5 g. Another capillary tube of radius 2r is immersed in water. The mass of water, that will rise in this tube, is
Two harmonic motions are represented by the equations y1 = 10 sin and y2 = 5
. Their amplitudes are in the ratio of
When sounded together, a column of air and a tuning fork produce 4 beats per second. The tuning fork gives the lower note. The temperature of air is 15°C. When the temperature falls to 10°C, the two produce 3 beats per second. Find the frequency of the fork.
A 2 μF, capacitor C1 is charged to a voltage 100 V and a 4 μF capacitor C2 is charged to a voltage 50 V. The capacitors are then connected in parallel. What is the loss of energy due to parallel connection?
The following figure shows a spherical Gaussian surface and a charge distribution (magnitude of all the given point charges is different). When calculating the flux of electric field through the Gaussian surface, the electric field will be due to
The length of a wire of a potentiometer is 100 cm and the emf of its stand and cell is E volt. It is employed to measure the emf of a battery whose internal resistance is 0.5 W. If the balance point is obtained at l = 30 cm from the positive end, then the emf of the battery is
A wire of length L metres carrying a current I amperes is bent in the form of a circle. The magnitude of the magnetic moment is
In a series circuit, L, C and R are connected with an alternating voltage source of frequency f. The current leads the voltage by 45o. The value of C is
When a thin transparent plate of thickness t and refractive index m is placed in the path of one of the two interfering waves of light, then the path difference changes by
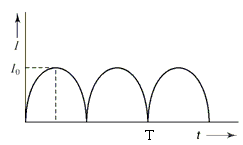
The output current (I) versus time (t) curve of a rectifier is shown in the figure. The average value of the output current in this case is
|
2 videos|17 docs|85 tests
|
|
2 videos|17 docs|85 tests
|



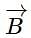 at the centre is perpendicular to the plane of the circular coil and directed inwards.
at the centre is perpendicular to the plane of the circular coil and directed inwards.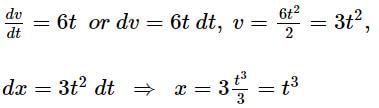
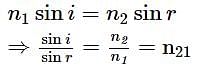
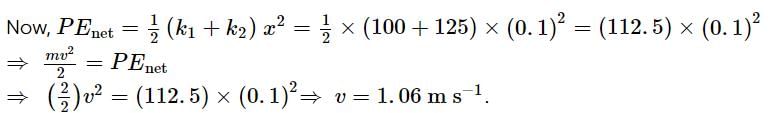

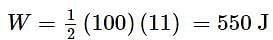

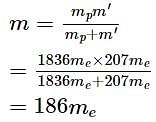
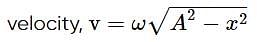
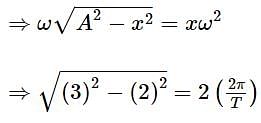
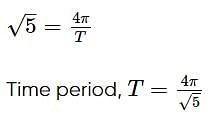
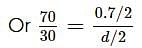
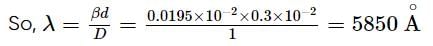

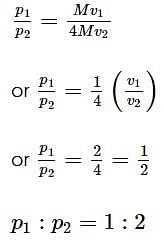


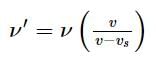
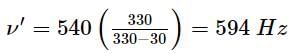
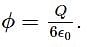





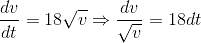


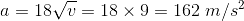



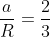 MRa
MRa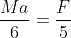 .
.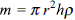
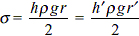
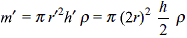
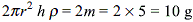
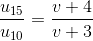
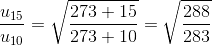 …(2)
…(2)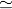 110 Hz
110 Hz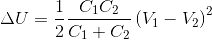
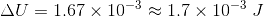
 V/cm
V/cm , l = 30 cm
, l = 30 cm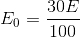
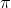 r2I, where r is the radius of the circular loop.
r2I, where r is the radius of the circular loop.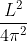
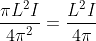
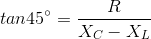
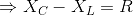
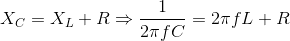
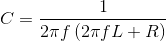

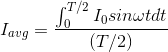
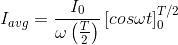
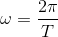 .
.