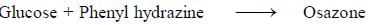Carbohydrates MCQ - Biotechnology Engineering (BT) MCQ
21 Questions MCQ Test Mock Test Series of IIT JAM Biotechnology 2025 - Carbohydrates MCQ
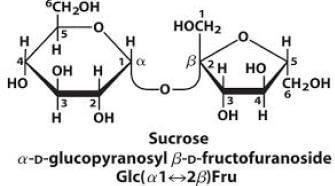
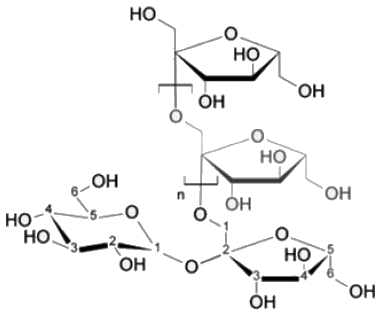
Sucrose, also known as table sugar is one of the most commonly used carbohydrate as a sweetener. It is a disaccharide made up of glucose and fructose. The kind of linkage that is found in sucrose is
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Which of the following carbohydrates would be the most abundant in the diet of strict vegetarians?
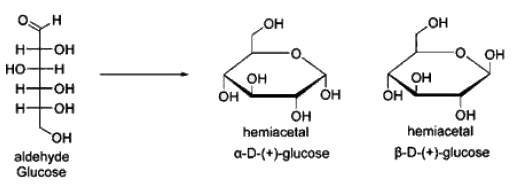
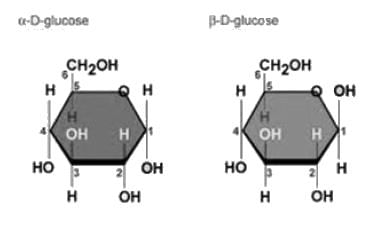
Which of the following anomeric form of Glucose is present in Starch
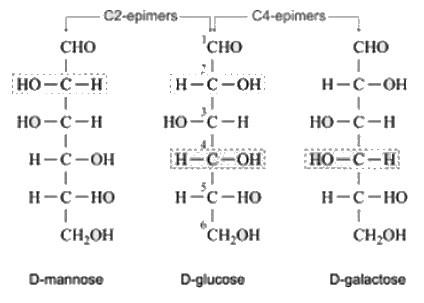
Which of the following is the correct combination of C-2 epimer and C-4 epimer of Glucose respectively.
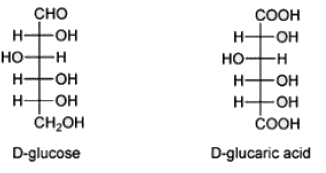
Which of the following is formed if glucose is oxidized at both C1 and C6 positions.
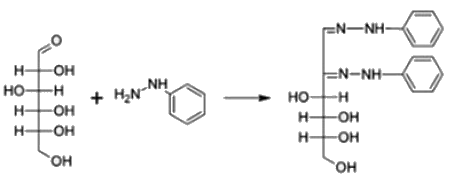
Osazone are formed by a chemical reaction between carbohydrates containing a free aldehyde or keto group and
This sugar is extracted from the roots of Dahelia and many other tuberous plants and useful in the determination of Glomerular filteration rate of kidneys.
On adding iodine to three different tubes labelled A, B and C, the colour of A turned blue, colour of B turned reddish violet and colour of C remained red (colour of iodine), Provided that all the tubes contained carbohydrates which of the following is true.
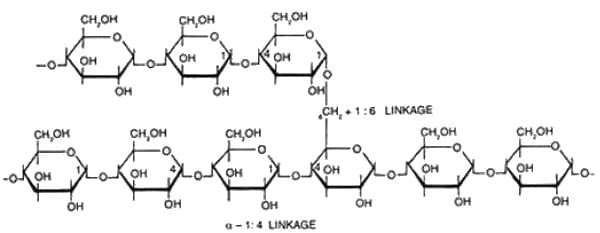
Which of the following polysachharides are heteropolysachharides.
Which of the following statement s are true about carbohydrates
If the number of asymmetric carbon atoms in a sugar are 3, the total number of stereoisomers will be 8. Let us assume that one of the structure is named as pintose, then the number of Diasteromers pintose will have are_________________
During a mutarotation experiment, the net optical activity at any given time point was observed as +100o. The absolute optical activity of alpha anomer is +112.2º and beta anomer is +18.7º. The percentage of alpha anomers at that time will be ___________
The net optical rotation of a solution containing 20% sucrose hydrolyzed into glucose and fructose during the process of sugar inversion is _____________
Given – Optical activity of Glucose = + 52.7, Fructose = –92.0 and Sucrose = + 66.7).
The stems of bamboo, a tropical grass, can grow at the phenomenal rate of 0.3 m/day under optimal conditions. It is given that the stems are composed almost entirely of cellulose fibers oriented in the direction of growth. Each D-glucose unit contributes ~0.5 nm to the length of a cellulose molecule. The number of sugar residues per second that must be added enzymatically to growing cellulose chains to account for the growth rate is ______________


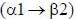 fructose linkage.
fructose linkage.