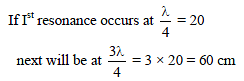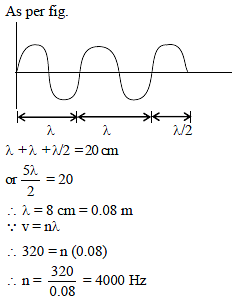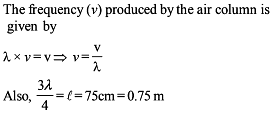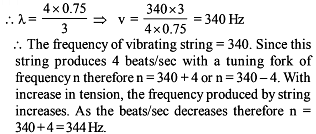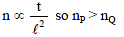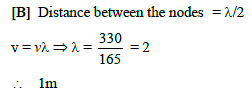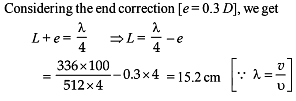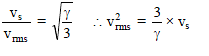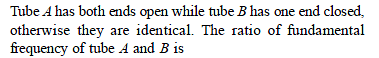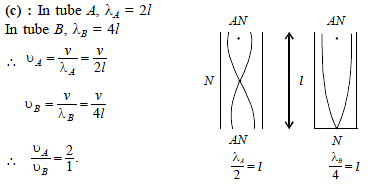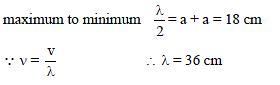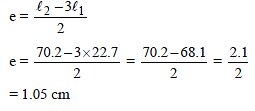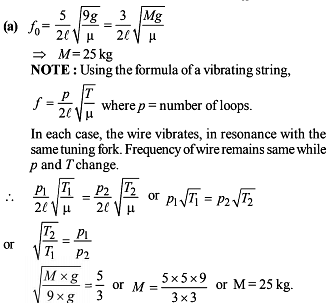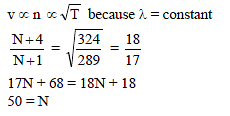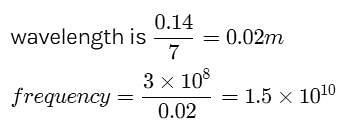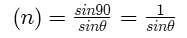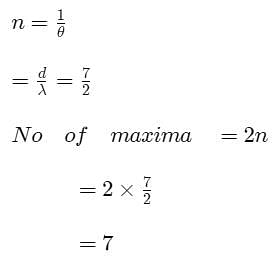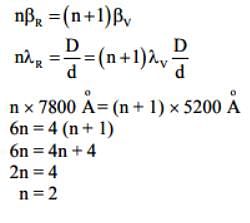Chapter Test: Waves - 2 - JEE MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test Physics for JEE Main & Advanced - Chapter Test: Waves - 2
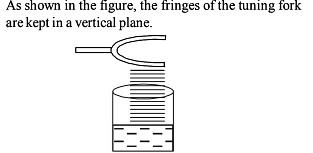
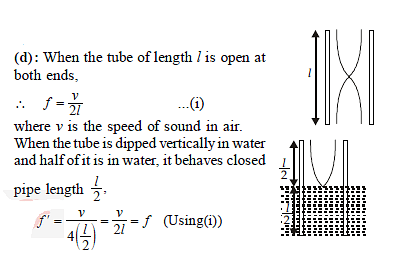
In a resonance column experiment, the first resonance is obtained when the level of the water in the tube is at 20 cm from the open end. Resonance will also be obtained when the water level is at a distance of -
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
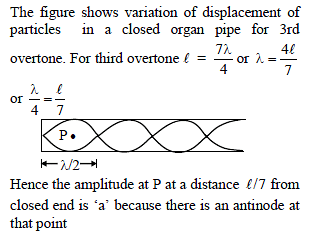
For the wave shown in figure, the wavelength and frequency, if its speed is 320 m/sec, are -
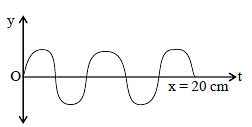
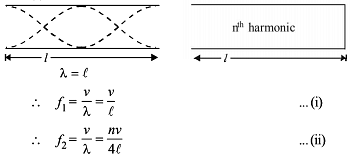
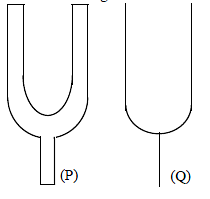
Which relation is giving the correct information for the shown tuning forks –
Stationary waves are set up in air column. Velocity of sound in air is 330 m/s and frequency is 165 Hz. Then distance between the nodes is -
The velocity of sound in air is 330 m/s. The r.m.s. velocity of air molecules (γ = 1.4) is approximately equal to -
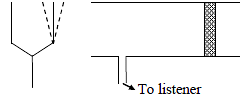
A tuning fork of frequency n is sounded at the open end of a long cylindrical tube having a side opening and fitted with a movable reflecting piston. On moving the piston through 9 cm, the intensity of sound heard by the listener changes from maximum to minimum. If speed of sound is 360 m/s, value of n is
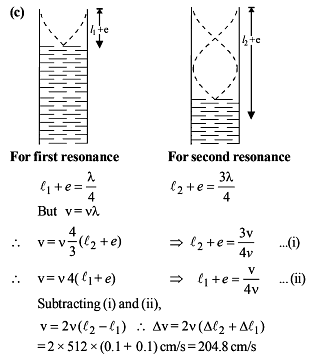
In a resonance pipe the first and second resonance are obtained at lengths 22.7 cm and 70.2 cm respectively. What will be the end correction -
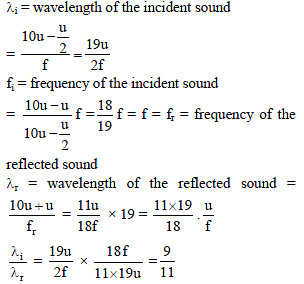
A wall is moving with velocity u and a source of sound moves with velocity u/2 in the same direction as shown in the figure. Assuming that the sound travels with velocity 10u. The ratio of incident sound wavelength on the wall to the reflected sound wavelength by the wall, is equal to -
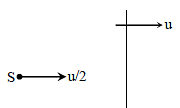
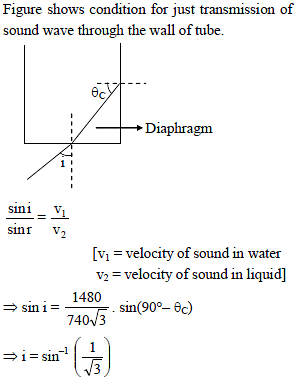
One end of a thin metal tube is closed by thin diaphragm of latex and the tube is lower in water with closed end downward. The tube is filled with a liquid 'x'. A plane progressive wave inside water hits the diaphragm making an angle 'θ' with its normal. Assuming Snell's law to hold true for sound. Maximum angle 'θ' for which sound is not transmitted through the walls of tube is (velocity of sound in liquid x = 740√3 m/s and in water = 1480 m/s)
The frequency of a car horn is f. What frequency is observed if both the car and the observer are at rest, but a wind is blowing from the car toward the observer ?
A tuning fork and an air column in resonance tube whose temperature is 51°C produces 4 beats in 1 second when sounded together. When the temperature of the air column decreases, the number of beats per second decreases. When the temperature remains 16°C, only 1 beat per second is produced. Then the
frequency of the tuning fork is -
Plane microwaves from a transmitter are directed normally towards a plane reflector. A detector moves along the normal to the reflector. Between positions of 14 successive maxima, the detector travels a distance 0.14 m. If the velocity of light is 3 × 108 m/s, find the frequency of the transmitter.
In YDSE how many maxima can be obtained on the screen if wavelength of light used is 200nm and d = 700 nm.
In Young's double slit experiment, the wavelength of red light is 7800 Å and that of blue light is 5200 Å. The value of n for which nth bright band due to red light coincides with (n + 1)th bright band due to blue light, is
If the Young's double slit experiment is performed with white light, then which of the following is not true
|
289 videos|635 docs|179 tests
|
|
289 videos|635 docs|179 tests
|