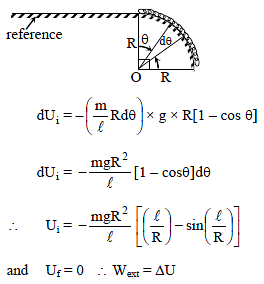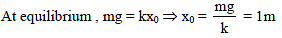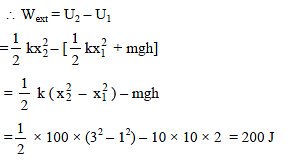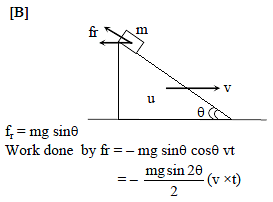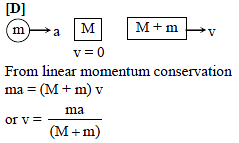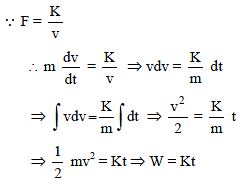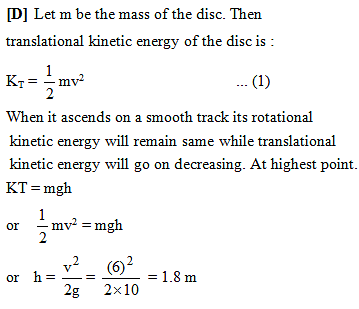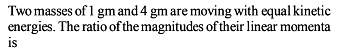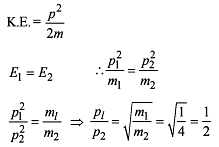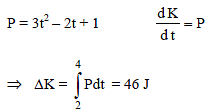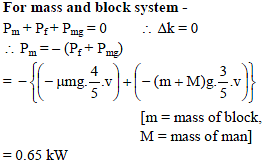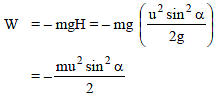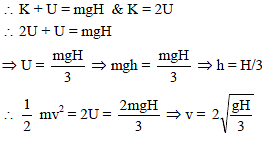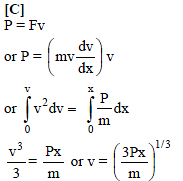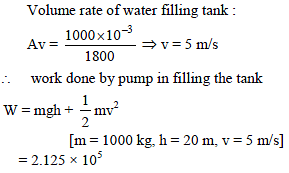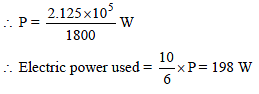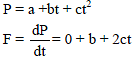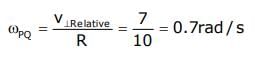Chapter Test: Work, Energy & Power - 2 - JEE MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test Physics for JEE Main & Advanced - Chapter Test: Work, Energy & Power - 2
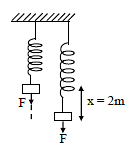
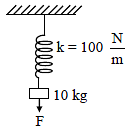
A vertical spring of force constant 100 N/m is attached with a hanging mass of 10 kg. Now an external force is applied on the mass so that the spring is stretched by additional 2 m. The work done by the force F is : (g = 10m/s2)

| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
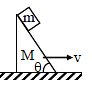
A block of mass m is stationary with respect to wedge of mass M moving with uniform speed v on horizontal surface. Find the work done by friction force on the block in t second -
A bullet of mass m and velocity a is fired into a large block of wood of mass M. The final velocity of the system is -
Assertion : The work done by all forces on a system equals to the change in kinetic energy of that system. This statement is true even if non-conservative forces act on the system.
Reason : The total work done by internal forces may be positive.
Force acting on a particle moving in a straight line varies with the velocity of the particle as F = K/v . Here K is constant. The work done by this force in time t is -
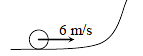
A disc of radius 0.1 m rolls without sliding on a horizontal surface with a velocity of 6 m/s. It then ascends a smooth continuous track as shown in figure. The height upto which it will ascend is : (g = 10 m/s2)
Power applied to a particle varies with time as P = (3t2 – 2t + 1) watts, where t is time in seconds. Then the change in kinetic energy between time t = 2s to t = 4s is-
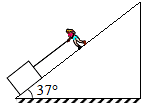
A man of mass 50 kg is moving up an inclined plane pull a block of mass 25 kg with constant speed 1 m/s. Friction coefficient between block and plane is 0.5. Assuming that man doesn’t slips. Power delivered by man –
A particle of mass m is projected at an angle α to the horizontal with an initial velocity v0. The work done by gravity during the time it reaches its highest point is -
A particle of mass m = 9 × 10–31 kg moving towards the wall of a vessel at a velocity of v = 600 ms–1 strikes it at an angle of 60° to the normal and rebounds at the same angle at the same speed. The impulse of the force experienced by the wall during the impact is -
A particle is released from a height H. At certain height its kinetic energy is two times its potential energy. Height and speed of particle at that instant are -
The speed v reached by a car of mass m, driven with constant power P, is given by -
A overhead tank of capacity 1000 liter has to be filled in 1/2 hour using water pump. Tank is kept at a height 10 m above ground and water level is 10 m below ground. The opening of inlet pipe inside tank is 1.11 cm2. Assuming the efficiency of motor to be 60%, the electric power used is (Neglect viscosity) -
The linear momentum of a particle varies with time t as :
p = a + bt + ct2
Which of the following statements is correct ?
A spot light S rotates in a horizontal plane with a constant angular velocity of 0.1 rad/s. The spot of light p moves along the wall at a distance 3 m. What is the velocity of the spot P when q = 45° ?
Two moving particle P and Q are 10 m apart at a certain instant. The velocity of P is 8m/s making an angle 30° with the line joining P and Q and that of Q is 6m/s making an angle 30° with PQ as shown in the figure. Then angular velocity of P with respect to Q is
The magnitude of displacement of a particle moving in a circle of radius a with constant angular speed w varies with time t as
A particle moves along an arc of a circle of radius R. Its velocity depends on the distance covered as v = a, where a is a constant then the angle a between the vector of the total acceleration and the vector of velocity as a function of s will be
A particle with constant total energy E moves in one dimension in a region where the potential energy is U(x). The speed of the particle is zero where
|
289 videos|635 docs|179 tests
|
|
289 videos|635 docs|179 tests
|