Economics Mock Test- 5 - Class 9 MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - Economics Mock Test- 5
Vulnerability to poverty is determined by the options for finding an alternative living in terms of
In which of the following countries did poverty actually rise from 1981 to 2001?
For making comparisons between developing countries, which uniform standard (per person per day) for the poverty line is used in terms of minimum availability?
What was the concept of white revolution is associated with?
Who is a person who puts together land, labour and capital?
The persons who are not working by choice are covered under
Which of the following places of Jharkhand witnessed starvation death recently?
Which are the two places in Orissa where starvation deaths are reported?
In which of the following years was the food grain stock with the FCI the maximum?
A farmer who works on a piece of 1 hectare of land is treated as
As per Planning Commission, minimum daily intake of calories for determining poverty line for rural area is
In which of the following fields is disguised unemployment found?
At what price, the government purchases the food grain for making buffer stock?
Assertion (A) : Caste system is prevalent in Indian society.
Reason (R) : Social exclusion reduces poverty.
Out of the total cultivated areas in the country, how much area is irrigated today:
Read the text given below and answer the following questions:
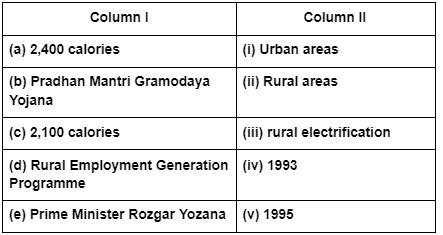
Poverty in India also has another aspect or dimension. The proportion of poor people is not the same in every state. States like Madhya Pradesh, Assam, Uttar Pradesh, Bihar and Orissa had above all India poverty levels. Bihar and Orissa continue to be the two poorest states with poverty ratios. There has been a substantial reduction in global poverty. Poverty declined substantially in China and Southeast Asian countries as a result of rapid economic growth and massive investments in human resource development. There were a number of causes for the widespread poverty in India. One historical reason is the low level of economic development under the British colonial administration. The policies of the colonial government ruined traditional handicrafts and discouraged development of industries like textiles. Removal of poverty has been one of the major objectives of Indian developmental strategy. In these circumstances, there is a clear need for targeted anti-poverty programmes. Although there are so many schemes which are formulated to affect poverty directly or indirectly. These anti-poverty programmes are Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act, Prime Minister Rozgar Yozana, Rural Employment Generation Programme, Swarnajayanti Gram Swarozgar Yojana, Pradhan Mantri Gramodaya Yojana, etc.
Q. What was ruined by the policies of the colonial government?