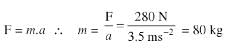Force And Laws Of Motion - Olympiad Level MCQ, Class 9 Science - Class 9 MCQ
25 Questions MCQ Test - Force And Laws Of Motion - Olympiad Level MCQ, Class 9 Science
A batsman hits a cricket ball, which then rolls on a level ground. After covering a short distance, the ball comes to rest. The ball slows down to stop because:
The force of freely falling body is directly proportional to:
The principle of conservation of linear momentum states that in a system it :
Action-reaction forces:
A porter is carrying a weight of 200 N on his head. If the force exerted on his head is taken as action, then the reaction force is exerted by :
Which of the following are vector quantities:
Two bodies collide at the same time. Which of the following is conserved?
Impulse is equal to :
A rocket works on the principle of:
When a speeding car takes a sharp turn, the persons sitting in it experience outward pull. This happens due to:
The ratio of force and acceleration of a moving body is the measure of its:
When you kick a stone, you get hurt. Due to which property this happens?
A car accelerates on a horizontal road due to the force exerted by
Impulse has same unit as that of:
By Newton's second law, the physical quantity which can be calculated, if we know the magnitude of force on a given mass is :
A body is moving with a constant momentum. The motion of the body is :
A cracker at rest explodes into two equal parts. These parts will move in :
A batsman has a choice to use heavy or light bat, while facing a fast bowler. He will prefer:
A vehicle has a mass of 1500 kg. If the vehicle is to be stopped with a negative acceleration of 1.7 ms–2, the force of friction between the vehicle and road is :
A man while running at a constant acceleration of 3.5 ms–2, develops a force of 280 N. The mass of man is:
The mass of an aeroplane is 2.5 t. Its engine develops a force of 8750 N before taking off. The acceleration of the aeroplane at the time of take off is :
A horse while running at a constant velocity of 15 ms–1, develops a momentum of 3000 Ns. The mass of horse is:
A truck starts from rest and rolls down the hill with a constant acceleration. It travels 400 m in 20 s. If the mass of truck is 7 metric tonnes, the force acting on it is:
A bullet of mass 0.01 kg is fired from a rifle. The bullet takes 0.003 s to move through the barrel and leaves with a velocity of 300 ms–1. The acceleration acting on the bullet is :
A 8000 kg engine pulls a train of 5 wagons, each of 2000 kg along a horizontal track. If the engine exerts a force of 40,000 N and track offers a friction of 5000 N, then net accelerating force acting on the system is: