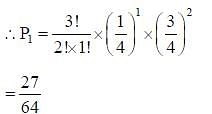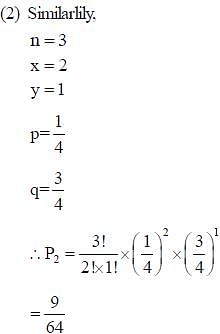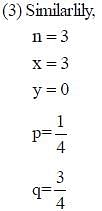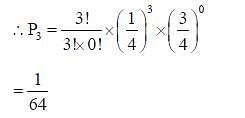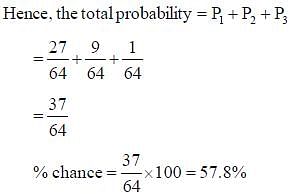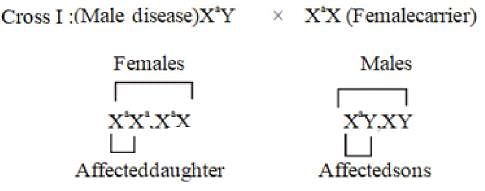Genetics MCQ 2 - Biotechnology Engineering (BT) MCQ
21 Questions MCQ Test Mock Test Series of IIT JAM Biotechnology 2025 - Genetics MCQ 2
Suppose a mouse with a black coat breeds with an albino mouse and all of their offspring have a grey coat phenotype. What then does the gene for coat color in mice appear to be an example of?
What fraction of the offspring will express one of the two dominant alleles, but not both in a cross of AaBb x AaBb?
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Which of the following is true for two genes undergoing independent assortment?
Color blindness is an X-linked recessive trait. If a carrier mother and a color blind father have two children, then what is the probability that both the children will be male and both of them would be color blind?
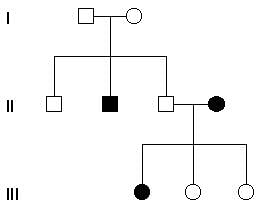
Which inheritance pattern does the following trait represents and the possible genotype of the father in the 2nd generation in the given pedigree chart?
The brown allele for hair color (B) is dominant over the blond allele (b). If two brown-haired parents produce a child that is blonde haired, what is the approximate probability that at least one out of the next three children they produce will also have blonde hair?
Which of the following is not a true for an ideal population under the Hardy-Weinberg Equilibrium?
A plant of the genotype AaBb is selfed. The two genes are linked and are 50 map units apart. What proportion of the progeny will have the genotype aabb?
Humans with Phenylketonuria develop light colored hair because of reduced hair pigmentation. This condition is an example of :
Crossing two Drosophila flies with two different mutations yields almost all progeny with wild type traits. With this information, we can conclude that:
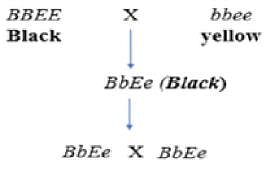
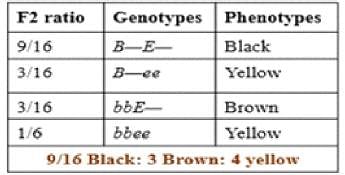
A black Labrador homozygous for the dominant alleles (BBEE) is crossed with a yellow Labrador homozygous for the recessive alleles (bbee). On inter-crossing the F1, the F2 progeny was obtained in the following ratio, 9 Black : 3 Brown : 4 Yellow.This is an example of
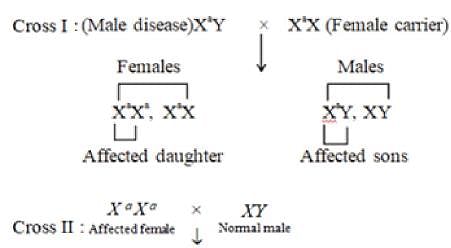
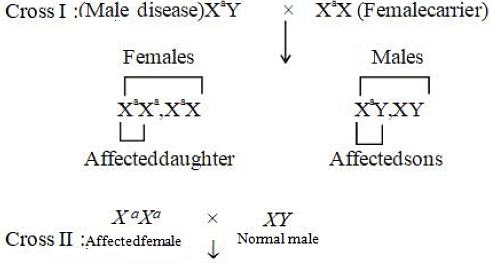
On basis of statements given below the mode of inheritance is
• Mostly males are sufferer of disease
• All male child developed from affected mother are diseased
• Female develope disease only when her father is diseased and mother is carrier
Which of the following is correct for a species that has a chromosome number 2n = 20?
Two heterozygous individuals having the genotype AaBb are crossed with each other. The probability of having a baby with genotype AaBb is _______ (Answer upto two decimal points)
The probability of having a hemophilic baby if the mother is the carrier and the father is unaffected by this X-linked recessive disease will be _______ (Answer upto two decimal points)
In a flock of sheep, 9% of the population has black wool and 91% has white wool. The percent of population is heterozygous for this trait if black wool is recessive and the population is in Hardy Weinberg Equilibrium will be ________% (Answer in integer)
Albinism is a recessive condition in humans. If 85% of a population is albino, then the allele frequency of the dominant allele will be (Answer upto three decimal points) __________