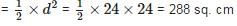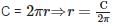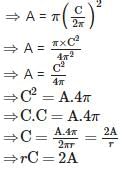HSSC TGT Math Mock Test - 7 - HSSC PGT/TGT MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test HSSC TGT Mock Test Series 2025 - HSSC TGT Math Mock Test - 7
What is the aim of all energy conservation techniques?
Which of the following district of Haryana state is having famous Humayun Mosque?
Bir Bara Ban Wildlife Sanctuary is situated in which district of Haryana?
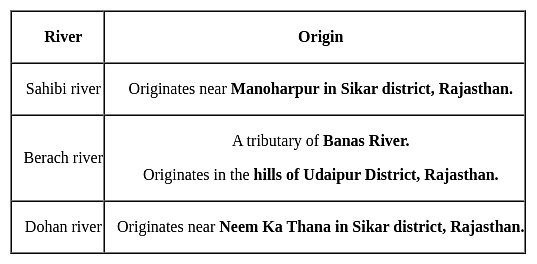
Which river is believed to have originated from the Har-ki-Dun glacier in West Garhwal of Haryana ?
Statement A:- Maturation is a developmental process.
Statement B:- Maturation and learning work together to promote the development of an individual.
Choose the correct option.
Ten eggs are drawn successively with replacement from a lot containing 10% defective eggs. The probability that there is at least one defective egg is:
Tangents to the curve y = x3 at the points (1, 1) and (– 1, – 1) are
If the coefficient of variation between x and y is 0.28, covariance between x and y is 7.6, and the variance of x is 9, then the S.D. of the y series is
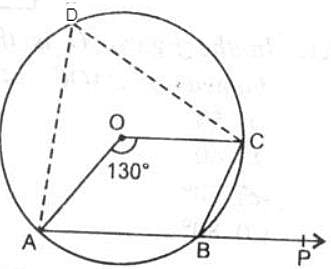
Arc ABC subtends an angle of 130o at the centre O of the circle. AB is extended to P. Then ∠CBP equals :
The area of the square that can be inscribed in a circle of radius 12 cm is
The transformation ‘orthogonal projection on X-axis’ is given by the matrix
. ……. about a central value ‘a’ is the mean of the absolute values of the deviations of the observations from ‘a’.
The conditional probability of an event E, given the occurrence of the event F is given by
If A1 and A2 be the two A.M.s between two numbers a and b, then (2A1 – A2) (2A2 – A1) is equal to :
The equation of parabola whose focus is (– 3, 0) and directrix x + 5 = 0 is:
If the area of a circle is ‘A’, radius of the circle is ‘r’ and its circumference is ‘C’, then
If 2 cos(A + B) = 1, and 2 sin(A –B) = 1 then the values of A and B are
If a and b are the position vectors of two points A and B and C is a point on AB produced such that AC = 3AB, then position vector of C will be