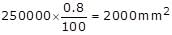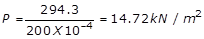JKSSB JE Civil Mock Test - 3 - Civil Engineering (CE) MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - JKSSB JE Civil Mock Test - 3
The maximum spacing of shear reinforcement (as vertical stirrups) measured along the axis of a reinforced concrete beam of width 300 mm and effective depth 500 mm, with a span 6 m is:
Consider the following statements:
- Bitumen is more resistant to water than tar.
- Bitumen is a petroleum product and tar is produced by destructive distillation of coal or wood.
Which of the above statements is(are) correct?
For a 5° Non-transitioned curve on narrow gauge track, the safe speed as per Martin formula is
Which one of the following is not a self-reading staff?
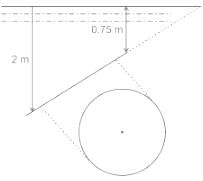
A circular plate 1.5 m diameter is submerged in water with its greatest and least depths below the surface being 2 m and 0.75 m respectively. What is the approximate total pressure on one face of the plate?
In a flow field, the streamlines and equipotential lines
You are provided with a sample of soil. You have to determine the water content of the given sample. Which of the following method cannot be help in the given scenario?
What will be the cant deficiency (cm), if maximum safe speed on a 5 Degree curve of a broad gauge track is 110 km/h and average speed of train is 85 km/h?
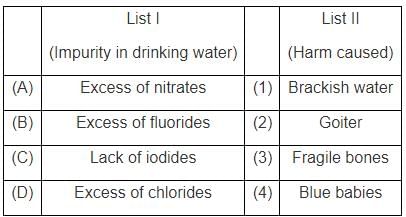
Match List – I with List – II and select the correct answer using the code given below the Lists:
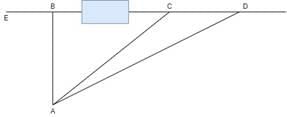
In the figure given below, survey line EB passes through an obstacle. The ∠BAC and ∠BAD are 30o and 45o respectively. If AB is 90 m, what will be the length of AC, AD and obstructed portion BC respectively, such that CD is in line with EB produced?
Which of the following statements is correct about corrections applied to length measured by a tape?
If the diameter of the most economical circular section is 5 m, then maximum velocity occurs when the depth of flow is,
What will be the minimum required area of longitudinal reinforcement in a short axially loaded square column (Fe 415 steel and M20 concrete), if its gross cross-sectional area is 250000 mm2?
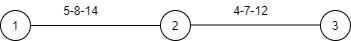
If event '1' is the initial event, earliest expected time for event '2' in the given network will be,
Maximum surface width of cracks allowed by IS 456:2000 for a structural member located in tidal zone, will be,
What will be the minimum stress in a section (20 cm x 25 cm) of a column carrying a load of 30 kN in a plane bisecting 25 cm side, at an eccentricity of 10 cm from the geometric axis of the section?
Which of the following is/are relevant to theodolite traversing?
- Centring
- Face left
- Face right
50 g of soil sample was oven dried at 106oC. What will be the water content of the sample if the weight of the sample after oven drying is 36 g?
Water that remains in the soil after permanent wilting point is reached, is called,
What will be the pressure exerted by a penguin of weight 30kg walking on snow with a total foot implant area of 200 cm2?
There is no need of cross-drainage work for a canal aligned along a natural watershed because,
In which of the following methods of calculating depreciation, a property loses its value at a fixed percentage of its value at the beginning of every year.
If perfect conditions prevail, the shortest possible time required to complete an activity, is called,
What will be the additional length required for a bar (of diameter 'd') which is cranked or bent up at both ends at 30º?




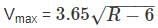 [For transitioned curve]
[For transitioned curve]
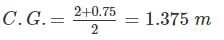
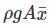
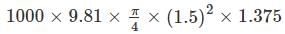
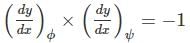
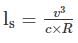
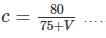 c value should be between 0.5 to 0.8
c value should be between 0.5 to 0.8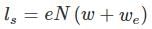
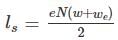
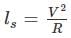 for Hilly terrain and
for Hilly terrain and 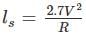 for Plain and Rolling terrain.
for Plain and Rolling terrain.