KTET Paper 2: Child Development and Pedagogy Test - 7 (Science and Mathematics) - KTET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test KTET Mock Test Series 2024 - KTET Paper 2: Child Development and Pedagogy Test - 7 (Science and Mathematics)
The conclusion 'Children can learn violent behaviour depicted in movies' may be derived on the basis of the work done by which of the following psychologists?
Which of the following is NOT a characteristic of socially disadvantaged students?
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Which IQ range is called trainable IQ level of mentally retarded children?
Do children acquire language because they are genetically predisposed to do so or because parents intensively teach them from an early age? This question essentially highlights
Arrange the following stages of cognitive development as recommended by Piaget:
(A) Sensorimotor stage
(B) Concrete operational stage
(C) Pre-operational stage
(D) Formal operational stage
Choose the correct answer from the options given below :
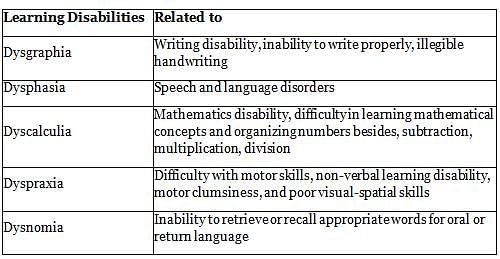
A child’s notebook shows errors in writing like reverse images, mirror imaging, etc. Such a child is showing signs of:
Motivation begins with needs that exist in all of us. The need that the student would tend to fulfil first pertains to
For ensuring and improving class discipline, the teacher should
Bani doesn't speak much at home, but speaks a lot in school. It shows:
Which of the following statements is correct?
Progressive education:
Which sequence depicts the correct hierarchical order of learning outcomes of affective domain in Bloom’s taxonomy?
A certificate is given to children when they read a specific number of books. In the long run, this strategy might not work since
NCF 2005 recommends that:
In a heterogeneous and mixed ability class, a teacher should:
Which of the following statements is not true ?
What type of questions asked by a teacher are convergent questions?
School-based assessment was introduced to:
Which of the following is NOT the tool for Formative Assessment in scholastic domain?
The son of a doctor becomes an expert doctor. It is an example of:
Which of the following is a teacher-related factor affecting learning?
Which of the following will be the most appropriate to maximise learning?
The problem-solving strategy in which one begins from the goal and moves back sequentially to figure out the solution, is called -
Teachers blame learning problems in students based on:
Which of the following are the external factors affecting the interest of students in a classroom?
____ is usually high ability or aptitude in one or more areas to the point where special educated services are necessary.
What should be the amendments in teacher preparation in classroom management?
Do children acquire language because they are genetically predisposed to do so or because parents intensively teach them from an early age? This question essentially highlights
Arrange the following stages of cognitive development as recommended by Piaget:
(A) Sensorimotor stage
(B) Concrete operational stage
(C) Pre-operational stage
(D) Formal operational stage
Choose the correct answer from the options given below :
Kohlberg's idea of moral development has levels.
|
100 tests
|