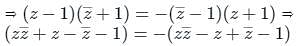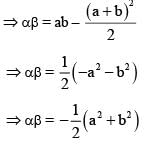KVS PGT Mathematics Mock Test - 8 - KVS PGT/TGT/PRT MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test KVS PGT Exam Mock Test Series 2024 - KVS PGT Mathematics Mock Test - 8
The following sentence has been broken into four parts with an error in one part. Identify that part and mark it as your answer. If there are no errors in any of the given parts, mark option 4 or ‘No error’ as your answer.
Q. The student, whom you (1)/ expected to win the prize, (2)/ had lost miserably.(3)/ No error (4).
Directions: Improve the bracketed part of the sentence.
Q. The Finance Minister presented data on the large sums of money (deposit into) some bank accounts, causing problems in the economy.
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
What is the cardinality of the set of odd positive integers less than 10?
The area bounded by the curves y = √x, 2y+3 = x and the x- axis in the first quadrant is
Find the unit vector in the direction of vector where P and Q are the points (1, 2, 3) and (4, 5, 6), respectively
General solution of a given differential equation
The number of ways in which three different rings can be worn in four fingers with at most one in each finger, are
If A is a non singular matrix of order 3 , then |adj(A3)| =
In the rule method, the null set is represented by:
A pendulum 36 cm long oscillates through an angle of 10 degrees. Find the length of the path described by its extremity.
If z is a complex number such that 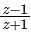 is purely imaginary, then what is |z| equal to ?
is purely imaginary, then what is |z| equal to ?
The figures 4, 5, 6, 7, 8 are written in every possible order. The number of numbers greater than 56000 is
Equation of common tangent of parabola y2 = 8x and x2 + y = 0 is
The sum of 40 A.M.’s between two number is 120. The sum of 50 A.M.’s between them is equal to
The expansion [x + (x3 - 1)1/2]5 + [x + (x3 - 1)1/2]5 is a polynomial of degree
If the roots of the equation are equal in magnitude but opposite in sign, then their product is :



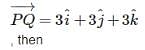
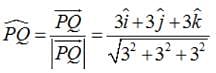
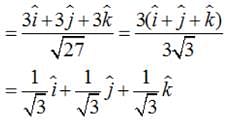
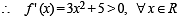
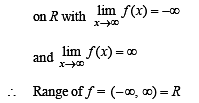
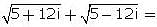

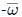
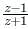 is purely imaginary,
is purely imaginary,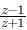 = a + ib, then a = 0
= a + ib, then a = 0