Kinetics - Nuclear - Surface - Photochemistry - Chemistry MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test Mock Test Series for IIT JAM Chemistry - Kinetics - Nuclear - Surface - Photochemistry
Activation energy for decomposition of H2O2 is 76 kJ/mol at 298K and the decomposition is very slow. When a little iodide is added, the activation energy decreases to 57kJ/mol. Hence, rate coefficient increases by a factor of
The rate of radioactive disintegration ..........with time:
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
For opposing reaction, A + B ↔ C + D, Ea = 100 kJ/mol and A = 1010 M-1s-1. The equilibrium concentration of A, B, C, D are 1, 2, 5, 4 M resp., at 700K. The values of k1 and k-1 at this temp are-
If 0.001M of a substance quenches the efficiency of fluorescence by 20%, the value of Stern-Volmer constant in M-1 is
Decomposition of ammonia on tungsten at 850oC has a rate constant value of 0.10 Torr sec-1. If the initial pressure of ammonia is 100 Torr, the pressure of ammonia at t = 200 sec is
The value of the rate constant for the gas phase reaction, 2NO2 + F2 → 2NO2F is 38 dm3 mol–1 s–1 at 300 K. The order of the reaction is:
A reaction follows second order rate law, 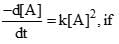
The specific rate constant of decomposition of a compound is represented by
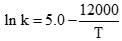
The activation energy of decomposition for this compound at 300 K is:
The fluorescence life time of a molecule in solution is 10 ns. If the fluorescence quantum yield is 0.1, the rate constant of fluorescence decay is:
For the reaction shown below,

The value of k1 is 1 × 10–4 s–1. If the reaction starts from X, the ratio of the concentrations of Y and Z at any given time during the course of the reaction is found to be  The value of k2 is:
The value of k2 is:
For an adsorbant-adsorbate system obeying the Langmuir adsorption isotherm, K = 0.48 bar-1 and P = 0.16 bar-1. At what pressure will 50% of the surface be covered?
The reaction, 2NO(g) + O2(g) → 2NO2(O) proceeds via the following steps:
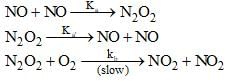
The rate of this reaction is equal to
The decomposition of N2O5 according to following reaction is first order
2 N2O5 → 4 NO2(g) + O2 (g). After 30 minutes from the start of decomposition in a closed vessel the total pressure developed is found to be 250 mm of Hg and on complete decomposition the total pressure is 500 mm of Hg. Calculate rate constant of the reaction.
1 g of 90Sr gets converted to 0.953 g after 2 yr. The half-life of 90Sr, and the amount of 90Sr remaining after 5 yr are:
A graph is plotted between log10K and 1/T in which straight line BC has no slope and tan(ᴓ) = -1/2.303 and intercept on y-axis is 5. What is activation energy?
In a reaction, A + B → Product, rate is doubled when the concentration of B is doubled, and rate increases by a factor of 8 when the concentrations of both the reactants (Aand B) are doubled, rate law for the reaction can be written as
when the rate of the reaction is equal to the rate constant, the order of the reaction is
The inversion of cane sugar proceeds with half-life of 500 minutes at pH 5 for any concentration of sugar. However if pH = 6, the half-life changes to 50 minute. The rate law expression for the sugar inversion can be written as:
The reaction, A(g) + 2B(g) → C(g) + D(g) is an elementary process. In an experiment, the initial partial pressure of A and B are PA = 0.60 and PB = 0.80 atm. When PC = 0.2 atm the rate of reaction relative to the initial rate is:
For an enzyme catalyzed reaction, a Lineweaver-Burk plot gave the slope value = 40 s and intercept = 4 (mmoldm-3s-1)-1. If initial concentration of enzyme is 2.5× 10-9 moldm-3, catalytic efficiency is 10x. Calculate the value of ‘x’.
At 273 K, N2 is adsorbed on mica surface. A plot of 1/V vs 1/P (V in m3 and P in Torr) gives a straight line with slope equal to 2.0 × 10–5 torr m–3 and an intercept Vm equal to 4 × 10–8 m3. The adsorption coefficient and number of molecules of N2 forming monolayer, resp., are:
Physiosorbed particles undergo desorption at 270C with an activation energy of 16.628 kJ/mol. Assuming first order process and a frequency factor of 1012 Hz, the average residence time (in sec) of particles on the surface is
A monoatomic gas, X absorbed on a surface, Langmuir, A plot of the fraction of surface coverage, q against the concentration of the gas [X], for very low concentration of the gas, is described by the equation:
Which of the following transformations is not correct?
Which ones of the following reactions are artificial radioactive decay?
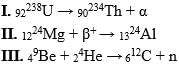
A, B, C and D elements form compounds AC, A2D and BD. If AC and A2D are radioactive and BD is not radioactive compound, find the following radioactive compounds-
(I) A2 (II) A2C (III) C2D (IV) BC
A substance absorbs 2.0 x 1016 quanta or radiations per second and 0.002 mole of it reacts in 1200 seconds. What is the quantum yield or the reaction (N = 6.02 x 1023)?
Which regions of the light radiations of the visible ultraviolet lying between – wavelength are chiefly concerned in bringing about photochemical reactions?
A closed vessel with rigid walls contain 1 mol of 92U238 and 1 mol of air at 298K. Considering complete decay of 92U238 to 82U206, the ratio of the final pressure to the initial pressure of the system at 298K is____?
The periodic table consists of 18 groups. An isotope of copper, on bombardment with protons, undergoes a nuclear reaction yielding element X as shown below. To which group, element X belongs in periodic table? 29Cu63 + 1H1 → X + 2 1H1 + α + 6 0n1
|
2 docs|25 tests
|

















