Legal Studies: CUET Mock Test - 4 - CUET Humanities MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test Legal Studies Practice Tests: CUET Preparation - Legal Studies: CUET Mock Test - 4
According to the Preamble of Indian Constitution, what does India as a 'Sovereign State' imply?
- It implies that India is neither a dependency nor a dominion of other nations, there is no other authority above it and it is both internally and externally free to conduct its own affairs.
- Extra constitutional declaration like continuation of full membership of Commonwealth of Nations does not affect Indian's Sovereignty.
- It implies that India can acquire a foreign territory, but cannot cede its territory in favour of a foreign state.
Directions: The question is based on the reasoning and arguments, or facts and principles set out in the passage. Some of these principles may not be true in the real or legal sense, yet you must conclusively assume that they are true for the purpose. Please answer the question on the basis of what is stated or implied in the passage. Do not rely on any principle of law other than the ones supplied to you, and do not assume any facts other than those supplied to you when answering the question. Please choose the option that most accurately and comprehensively answers the question.
Assault is typically defined as an intentional act that puts another individual in apprehension of immediate harm. Assault thus criminalises the threat of harm itself, rather than requiring that actual harm has occurred. For this reason, it is sometimes also known as attempted battery. Since assault is an intentional act, it cannot be committed by accident. This means that a perpetrator must have intended to cause fear in another person, or that he or she acted in a way that was knowingly dangerous, even if a specific individual was not targeted. Assault does not require that the victim feared is subjected to severe bodily harm or death. Any reasonable fear is sufficient.
Assault also requires that an act be taken in furtherance of the threat of harm. This could be any variety of acts, including approaching someone with raised fists, scaring someone with a weapon, or attempting to push an individual into a crowded street. However, some sort of act is required. Simply stating a threat is not enough to create an assault unless the words are accompanied by an additional action that creates a fear of harm.
Battery is, in many ways, the completion of an assault. Battery is defined as an intentional offensive or harmful touching of another person that is done without his or her consent. Since an assault is the threatening of harm, and a battery is the actual act of harm, the two crimes are often charged together. As with assault, battery requires that the perpetrator intended to commit the act.
The act of battery does not require that the victim is severely injured or traumatised. Any type of touching that the victim considers harmful or offensive can be sufficient. For example, if a woman pours a mug of hot water on someone else, this could be a battery. To go even further, a classic case of a battery that does not result in pain or injury is when the perpetrator spits on the victim. However, a defendant will not be held liable for contact that is deemed offensive only because the victim is abnormally sensitive. The standard of offensiveness is determined from the perspective of an ordinary individual.
When the conduct of a defendant is particularly egregious, he or she may be charged with the elevated crime of aggravated assault or battery. This can vary by state, but it is generally meant to criminalise conduct that society finds particularly offensive. Thus, for instance, aggravated assault may apply to circumstances when a deadly weapon, such as a gun, is used, or when the victim is particularly vulnerable, such as a pregnant woman or an elderly individual. In some states, if the harm done to the victim is particularly severe and causes serious and lasting injury, the assault or battery will be charged as aggravated. If the perpetrator's actions could have caused death, the defendant will face a charge of attempted murder and manslaughter.
[Extracted, with edits and revisions, from Assault and Battery, blog by justia]
Q. A man has a reputation of being a mean and violent drunk person. While walking down a street, he approached a woman. Can it be called an assault if the woman was intimidated by this act?
Assault is typically defined as an intentional act that puts another individual in apprehension of immediate harm. Assault thus criminalises the threat of harm itself, rather than requiring that actual harm has occurred. For this reason, it is sometimes also known as attempted battery. Since assault is an intentional act, it cannot be committed by accident. This means that a perpetrator must have intended to cause fear in another person, or that he or she acted in a way that was knowingly dangerous, even if a specific individual was not targeted. Assault does not require that the victim feared is subjected to severe bodily harm or death. Any reasonable fear is sufficient.
Assault also requires that an act be taken in furtherance of the threat of harm. This could be any variety of acts, including approaching someone with raised fists, scaring someone with a weapon, or attempting to push an individual into a crowded street. However, some sort of act is required. Simply stating a threat is not enough to create an assault unless the words are accompanied by an additional action that creates a fear of harm.
Battery is, in many ways, the completion of an assault. Battery is defined as an intentional offensive or harmful touching of another person that is done without his or her consent. Since an assault is the threatening of harm, and a battery is the actual act of harm, the two crimes are often charged together. As with assault, battery requires that the perpetrator intended to commit the act.
The act of battery does not require that the victim is severely injured or traumatised. Any type of touching that the victim considers harmful or offensive can be sufficient. For example, if a woman pours a mug of hot water on someone else, this could be a battery. To go even further, a classic case of a battery that does not result in pain or injury is when the perpetrator spits on the victim. However, a defendant will not be held liable for contact that is deemed offensive only because the victim is abnormally sensitive. The standard of offensiveness is determined from the perspective of an ordinary individual.
When the conduct of a defendant is particularly egregious, he or she may be charged with the elevated crime of aggravated assault or battery. This can vary by state, but it is generally meant to criminalise conduct that society finds particularly offensive. Thus, for instance, aggravated assault may apply to circumstances when a deadly weapon, such as a gun, is used, or when the victim is particularly vulnerable, such as a pregnant woman or an elderly individual. In some states, if the harm done to the victim is particularly severe and causes serious and lasting injury, the assault or battery will be charged as aggravated. If the perpetrator's actions could have caused death, the defendant will face a charge of attempted murder and manslaughter.
[Extracted, with edits and revisions, from Assault and Battery, blog by justia]
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Directions: The question is based on the reasoning and arguments, or facts and principles set out in the passage. Some of these principles may not be true in the real or legal sense, yet you must conclusively assume that they are true for the purpose. Please answer the question on the basis of what is stated or implied in the passage. Do not rely on any principle of law other than the ones supplied to you, and do not assume any facts other than those supplied to you when answering the question. Please choose the option that most accurately and comprehensively answers the question.
Assault is typically defined as an intentional act that puts another individual in apprehension of immediate harm. Assault thus criminalises the threat of harm itself, rather than requiring that actual harm has occurred. For this reason, it is sometimes also known as attempted battery. Since assault is an intentional act, it cannot be committed by accident. This means that a perpetrator must have intended to cause fear in another person, or that he or she acted in a way that was knowingly dangerous, even if a specific individual was not targeted. Assault does not require that the victim feared is subjected to severe bodily harm or death. Any reasonable fear is sufficient.
Assault also requires that an act be taken in furtherance of the threat of harm. This could be any variety of acts, including approaching someone with raised fists, scaring someone with a weapon, or attempting to push an individual into a crowded street. However, some sort of act is required. Simply stating a threat is not enough to create an assault unless the words are accompanied by an additional action that creates a fear of harm.
Battery is, in many ways, the completion of an assault. Battery is defined as an intentional offensive or harmful touching of another person that is done without his or her consent. Since an assault is the threatening of harm, and a battery is the actual act of harm, the two crimes are often charged together. As with assault, battery requires that the perpetrator intended to commit the act.
The act of battery does not require that the victim is severely injured or traumatised. Any type of touching that the victim considers harmful or offensive can be sufficient. For example, if a woman pours a mug of hot water on someone else, this could be a battery. To go even further, a classic case of a battery that does not result in pain or injury is when the perpetrator spits on the victim. However, a defendant will not be held liable for contact that is deemed offensive only because the victim is abnormally sensitive. The standard of offensiveness is determined from the perspective of an ordinary individual.
When the conduct of a defendant is particularly egregious, he or she may be charged with the elevated crime of aggravated assault or battery. This can vary by state, but it is generally meant to criminalise conduct that society finds particularly offensive. Thus, for instance, aggravated assault may apply to circumstances when a deadly weapon, such as a gun, is used, or when the victim is particularly vulnerable, such as a pregnant woman or an elderly individual. In some states, if the harm done to the victim is particularly severe and causes serious and lasting injury, the assault or battery will be charged as aggravated. If the perpetrator's actions could have caused death, the defendant will face a charge of attempted murder and manslaughter.
[Extracted, with edits and revisions, from Assault and Battery, blog by justia]
Q. A man was very sensitive to touching as he suffered from an extremely rare illness. One day, he was caught up in a fight with his co-worker and the co-worker just touched him; as a consequence of which he ended in the hospital. As per the passage, decide.
Assault is typically defined as an intentional act that puts another individual in apprehension of immediate harm. Assault thus criminalises the threat of harm itself, rather than requiring that actual harm has occurred. For this reason, it is sometimes also known as attempted battery. Since assault is an intentional act, it cannot be committed by accident. This means that a perpetrator must have intended to cause fear in another person, or that he or she acted in a way that was knowingly dangerous, even if a specific individual was not targeted. Assault does not require that the victim feared is subjected to severe bodily harm or death. Any reasonable fear is sufficient.
Assault also requires that an act be taken in furtherance of the threat of harm. This could be any variety of acts, including approaching someone with raised fists, scaring someone with a weapon, or attempting to push an individual into a crowded street. However, some sort of act is required. Simply stating a threat is not enough to create an assault unless the words are accompanied by an additional action that creates a fear of harm.
Battery is, in many ways, the completion of an assault. Battery is defined as an intentional offensive or harmful touching of another person that is done without his or her consent. Since an assault is the threatening of harm, and a battery is the actual act of harm, the two crimes are often charged together. As with assault, battery requires that the perpetrator intended to commit the act.
The act of battery does not require that the victim is severely injured or traumatised. Any type of touching that the victim considers harmful or offensive can be sufficient. For example, if a woman pours a mug of hot water on someone else, this could be a battery. To go even further, a classic case of a battery that does not result in pain or injury is when the perpetrator spits on the victim. However, a defendant will not be held liable for contact that is deemed offensive only because the victim is abnormally sensitive. The standard of offensiveness is determined from the perspective of an ordinary individual.
When the conduct of a defendant is particularly egregious, he or she may be charged with the elevated crime of aggravated assault or battery. This can vary by state, but it is generally meant to criminalise conduct that society finds particularly offensive. Thus, for instance, aggravated assault may apply to circumstances when a deadly weapon, such as a gun, is used, or when the victim is particularly vulnerable, such as a pregnant woman or an elderly individual. In some states, if the harm done to the victim is particularly severe and causes serious and lasting injury, the assault or battery will be charged as aggravated. If the perpetrator's actions could have caused death, the defendant will face a charge of attempted murder and manslaughter.
[Extracted, with edits and revisions, from Assault and Battery, blog by justia]
Directions: The question is based on the reasoning and arguments, or facts and principles set out in the passage. Some of these principles may not be true in the real or legal sense, yet you must conclusively assume that they are true for the purpose. Please answer the question on the basis of what is stated or implied in the passage. Do not rely on any principle of law other than the ones supplied to you, and do not assume any facts other than those supplied to you when answering the question. Please choose the option that most accurately and comprehensively answers the question.
Assault is typically defined as an intentional act that puts another individual in apprehension of immediate harm. Assault thus criminalises the threat of harm itself, rather than requiring that actual harm has occurred. For this reason, it is sometimes also known as attempted battery. Since assault is an intentional act, it cannot be committed by accident. This means that a perpetrator must have intended to cause fear in another person, or that he or she acted in a way that was knowingly dangerous, even if a specific individual was not targeted. Assault does not require that the victim feared is subjected to severe bodily harm or death. Any reasonable fear is sufficient.
Assault also requires that an act be taken in furtherance of the threat of harm. This could be any variety of acts, including approaching someone with raised fists, scaring someone with a weapon, or attempting to push an individual into a crowded street. However, some sort of act is required. Simply stating a threat is not enough to create an assault unless the words are accompanied by an additional action that creates a fear of harm.
Battery is, in many ways, the completion of an assault. Battery is defined as an intentional offensive or harmful touching of another person that is done without his or her consent. Since an assault is the threatening of harm, and a battery is the actual act of harm, the two crimes are often charged together. As with assault, battery requires that the perpetrator intended to commit the act.
The act of battery does not require that the victim is severely injured or traumatised. Any type of touching that the victim considers harmful or offensive can be sufficient. For example, if a woman pours a mug of hot water on someone else, this could be a battery. To go even further, a classic case of a battery that does not result in pain or injury is when the perpetrator spits on the victim. However, a defendant will not be held liable for contact that is deemed offensive only because the victim is abnormally sensitive. The standard of offensiveness is determined from the perspective of an ordinary individual.
When the conduct of a defendant is particularly egregious, he or she may be charged with the elevated crime of aggravated assault or battery. This can vary by state, but it is generally meant to criminalise conduct that society finds particularly offensive. Thus, for instance, aggravated assault may apply to circumstances when a deadly weapon, such as a gun, is used, or when the victim is particularly vulnerable, such as a pregnant woman or an elderly individual. In some states, if the harm done to the victim is particularly severe and causes serious and lasting injury, the assault or battery will be charged as aggravated. If the perpetrator's actions could have caused death, the defendant will face a charge of attempted murder and manslaughter.
[Extracted, with edits and revisions, from Assault and Battery, blog by justia]
Q. A shoots B with a gun. B is taken to the hospital. B remains critical for a couple of days but after that, he recovers. What offences have A committed?
According to which article of the International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights are rights such as the right to life, freedom of thought, prohibition of slavery, etc. said to be non-derogable?
Directions: Consider the following statements of Assertion (A) and Reason (R), and choose the correct option accordingly.
Assertion (A): Writ jurisdiction of the Supreme Court is exclusive.
Reason (R): The Supreme Court has original jurisdiction in terms of issuing writs, i.e. a citizen can go directly to the Supreme Court and not by way of appeal.
An agreement not supported by consideration is called which of the following?
Directions: Consider the following statements of Assertion (A) and Reason (R), and choose the correct option accordingly.
Assertion (A): In an adversarial system, the parties in a legal proceeding develop their own theory of the case and gather evidence to support their claims.
Reason (R): In an adversarial system, cross examination is an effective way to test the credibility of the witnesses presented.
Which of the following is/are the function(s) of Central authority?
The Law Society of ____________ determines fitness of character for admission.
Which of the following doctrines requires that only the parties to the contract can enforce it?
'You must not use a steam hammer to crack a nut if a nut cracker would do.' This statement refers to which doctrine of Administrative Law?
Which case gave primacy to the Executive in making judicial appointments?
The concept of Public Interest Litigation, which has become quite popular in India, originated in
Which of the following US states have unified bars?
Which of the following functions are performed by the Bar Council of India?
Match the following events with their respective years of occurrence.
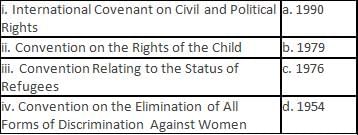
Directions: The question contains two statements, one labelled as Assertion (A) and the other as Reason (R). Examine whether the statements are correct and related to each other with the help of the codes given below:
Assertion (A): Directive principles of state policy are not enforceable in a court of law.
Reason (R): Directive principles are only moral obligations.
Which of the following statements is/are correct with regard to International Court of Justice?
Statement I: International Court of Justice does not have advisory jurisdiction.
Statement II: International Court of Justice is the primary source of dispute resolution with regard to domestic and international disputes.
Directions: The question is based on the reasoning and arguments, or facts and principles set out in the passage. Some of these principles may not be true in the real or legal sense, yet you must conclusively assume that they are true for the purpose. Please answer the question on the basis of what is stated or implied in the passage. Do not rely on any principle of law other than the ones supplied to you, and do not assume any facts other than those supplied to you when answering the question. Please choose the option that most accurately and comprehensively answers the question.
Assault is typically defined as an intentional act that puts another individual in apprehension of immediate harm. Assault thus criminalises the threat of harm itself, rather than requiring that actual harm has occurred. For this reason, it is sometimes also known as attempted battery. Since assault is an intentional act, it cannot be committed by accident. This means that a perpetrator must have intended to cause fear in another person, or that he or she acted in a way that was knowingly dangerous, even if a specific individual was not targeted. Assault does not require that the victim feared is subjected to severe bodily harm or death. Any reasonable fear is sufficient.
Assault also requires that an act be taken in furtherance of the threat of harm. This could be any variety of acts, including approaching someone with raised fists, scaring someone with a weapon, or attempting to push an individual into a crowded street. However, some sort of act is required. Simply stating a threat is not enough to create an assault unless the words are accompanied by an additional action that creates a fear of harm.
Battery is, in many ways, the completion of an assault. Battery is defined as an intentional offensive or harmful touching of another person that is done without his or her consent. Since an assault is the threatening of harm, and a battery is the actual act of harm, the two crimes are often charged together. As with assault, battery requires that the perpetrator intended to commit the act.
The act of battery does not require that the victim is severely injured or traumatised. Any type of touching that the victim considers harmful or offensive can be sufficient. For example, if a woman pours a mug of hot water on someone else, this could be a battery. To go even further, a classic case of a battery that does not result in pain or injury is when the perpetrator spits on the victim. However, a defendant will not be held liable for contact that is deemed offensive only because the victim is abnormally sensitive. The standard of offensiveness is determined from the perspective of an ordinary individual.
When the conduct of a defendant is particularly egregious, he or she may be charged with the elevated crime of aggravated assault or battery. This can vary by state, but it is generally meant to criminalise conduct that society finds particularly offensive. Thus, for instance, aggravated assault may apply to circumstances when a deadly weapon, such as a gun, is used, or when the victim is particularly vulnerable, such as a pregnant woman or an elderly individual. In some states, if the harm done to the victim is particularly severe and causes serious and lasting injury, the assault or battery will be charged as aggravated. If the perpetrator's actions could have caused death, the defendant will face a charge of attempted murder and manslaughter.
[Extracted, with edits and revisions, from Assault and Battery, blog by justia]
Q. A man hits a shopper with his grocery cart while in the supermarket as the market was overcrowded. Can this be regarded as battery?
Directions: The question is based on the reasoning and arguments, or facts and principles set out in the passage. Some of these principles may not be true in the real or legal sense, yet you must conclusively assume that they are true for the purpose. Please answer the question on the basis of what is stated or implied in the passage. Do not rely on any principle of law other than the ones supplied to you, and do not assume any facts other than those supplied to you when answering the question. Please choose the option that most accurately and comprehensively answers the question.
Assault is typically defined as an intentional act that puts another individual in apprehension of immediate harm. Assault thus criminalises the threat of harm itself, rather than requiring that actual harm has occurred. For this reason, it is sometimes also known as attempted battery. Since assault is an intentional act, it cannot be committed by accident. This means that a perpetrator must have intended to cause fear in another person, or that he or she acted in a way that was knowingly dangerous, even if a specific individual was not targeted. Assault does not require that the victim feared is subjected to severe bodily harm or death. Any reasonable fear is sufficient.
Assault also requires that an act be taken in furtherance of the threat of harm. This could be any variety of acts, including approaching someone with raised fists, scaring someone with a weapon, or attempting to push an individual into a crowded street. However, some sort of act is required. Simply stating a threat is not enough to create an assault unless the words are accompanied by an additional action that creates a fear of harm.
Battery is, in many ways, the completion of an assault. Battery is defined as an intentional offensive or harmful touching of another person that is done without his or her consent. Since an assault is the threatening of harm, and a battery is the actual act of harm, the two crimes are often charged together. As with assault, battery requires that the perpetrator intended to commit the act.
The act of battery does not require that the victim is severely injured or traumatised. Any type of touching that the victim considers harmful or offensive can be sufficient. For example, if a woman pours a mug of hot water on someone else, this could be a battery. To go even further, a classic case of a battery that does not result in pain or injury is when the perpetrator spits on the victim. However, a defendant will not be held liable for contact that is deemed offensive only because the victim is abnormally sensitive. The standard of offensiveness is determined from the perspective of an ordinary individual.
When the conduct of a defendant is particularly egregious, he or she may be charged with the elevated crime of aggravated assault or battery. This can vary by state, but it is generally meant to criminalise conduct that society finds particularly offensive. Thus, for instance, aggravated assault may apply to circumstances when a deadly weapon, such as a gun, is used, or when the victim is particularly vulnerable, such as a pregnant woman or an elderly individual. In some states, if the harm done to the victim is particularly severe and causes serious and lasting injury, the assault or battery will be charged as aggravated. If the perpetrator's actions could have caused death, the defendant will face a charge of attempted murder and manslaughter.
[Extracted, with edits and revisions, from Assault and Battery, blog by justia]
Q. A hits B with an iron rod. This leads to B's leg being fractured. What can be the charge against A?
Dinesh Kumar, a practicing advocate engaged in the following activities as part of his professional duties:
a. Accepted the brief from his client
b. Asked for contingency fee from the client
c. Met the opposite party directly
d. Maintained client confidentiality
Which of the above activities amounts to a breach of professional duties by the advocate?
Directions: Identify the false statement(s) about the Attorney General of India.
Statements:
- Attorney General is appointed in India for the period which the President feels suitable.
- Article 76 of the Constitution gives a right to the Attorney General of India to speak in both the houses of the Parliament.
- The person who is appointed as Attorney General of India should be a distinguished jurist.
Who is the ex-officio chairman of Taluk Legal Services Committee?
In which year were the provisions related to dual system of practitioners in the Bombay and Calcutta High Courts deleted?
Which of the following statements is/are incorrect?
Statement I: An advocate is duty bound to not act in an illegal manner towards the opposite party.
Statement II: An advocate is duty bound to represent clients in all circumstances.
ABC International Ltd. and XYZ Pvt. Ltd. have a dispute over the production process which involved intricate trade secrets. The most suited alternative dispute resolution mechanism that can protect the trade secrets while resolving the dispute is:
The authority to issue writs for the enforcement of Fundamental Rights in India is vested with












