MAH-CET MBA Mock Test- 4 - CAT MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test Additional Study Material for CAT - MAH-CET MBA Mock Test- 4
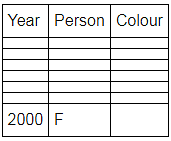
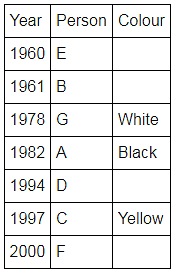
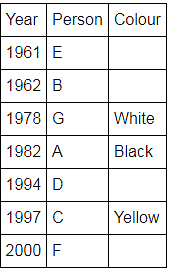
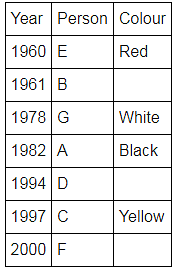
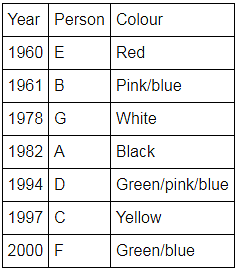
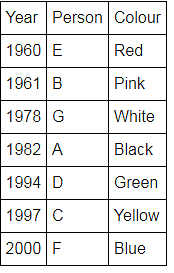
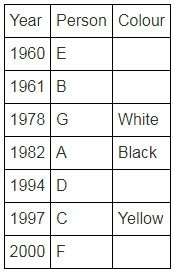
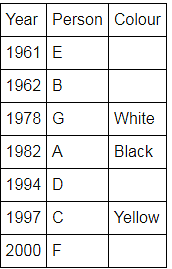
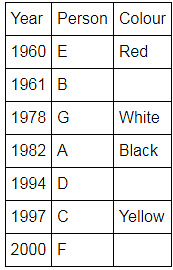
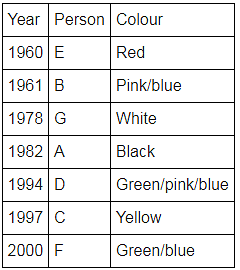
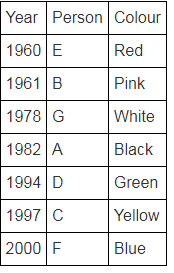
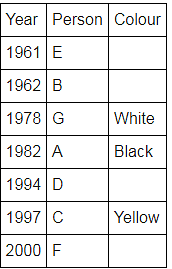
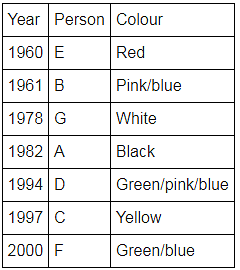
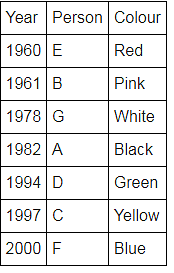
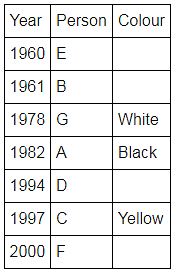
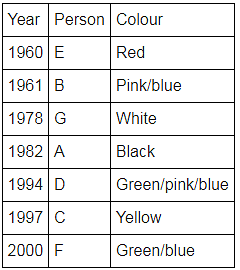
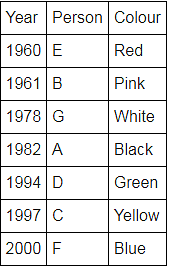
Directions: Seven people A, B, C, D, E, F and G are born in different years and like different colours - red, blue, pink, yellow, green, black and white not necessarily in same order.
B and E are born in consecutive years (B being younger), one of them been born in 1961.
The one who likes black is born in 1982 and is 4 years younger than the one who likes white.
The difference between present ages of A and D is 10 less than the difference between present ages of G and F. (A and G are elder than D and F respectively)
G is born in 1978.
F is born in 2000 and is youngest and doesn't like pink.
C likes yellow and is born three years after D was born, who is 6 years elder than F and 34 years younger to one who likes red colour.
The second eldest person doesn't like green.
The no. of people elder than the one who likes pink are 1 more than the no. of people younger than one who likes blue.
Who likes blue colour?
B and E are born in consecutive years (B being younger), one of them been born in 1961.
The one who likes black is born in 1982 and is 4 years younger than the one who likes white.
The difference between present ages of A and D is 10 less than the difference between present ages of G and F. (A and G are elder than D and F respectively)
G is born in 1978.
F is born in 2000 and is youngest and doesn't like pink.
C likes yellow and is born three years after D was born, who is 6 years elder than F and 34 years younger to one who likes red colour.
The second eldest person doesn't like green.
The no. of people elder than the one who likes pink are 1 more than the no. of people younger than one who likes blue.
Directions: A machine is programmed in such a manner that when some elements are provided, it gives output in the following pattern. Observe the pattern and answer accordingly.
INPUT: strongest 57 12 outrage biggest enormous 38 31 78 unanimous rigorous 91
Step I: strongest 57 12 outrage biggest unanimous 78 enormous 38 31 rigorous 91
Step II: strongest 57 12 outrage unanimous biggest 78 31 enormous 38 rigorous 91
Step III: strongest 12 outrage unanimous biggest enormous 78 31 38 57 rigorous 91
Step IV: strongest outrage unanimous biggest enormous rigorous 78 31 38 57 12 91
Step V: strongest unanimous biggest enormous rigorous outrage 78 31 38 57 12 91
Step VI: unanimous biggest enormous rigorous outrage strongest 78 31 38 57 12 91
Step VI is the final step of the input. Based on the above pattern, answer accordingly.
INPUT: 77 34 longest brigadier evaporation 12 91 pace intelligence 19 88 around
How many elements are there between evaporation and 19 in Step V?
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Directions: A machine is programmed in such a manner that when some elements are provided, it gives output in the following pattern. Observe the pattern and answer accordingly.
INPUT: strongest 57 12 outrage biggest enormous 38 31 78 unanimous rigorous 91
Step I: strongest 57 12 outrage biggest unanimous 78 enormous 38 31 rigorous 91
Step II: strongest 57 12 outrage unanimous biggest 78 31 enormous 38 rigorous 91
Step III: strongest 12 outrage unanimous biggest enormous 78 31 38 57 rigorous 91
Step IV: strongest outrage unanimous biggest enormous rigorous 78 31 38 57 12 91
Step V: strongest unanimous biggest enormous rigorous outrage 78 31 38 57 12 91
Step VI: unanimous biggest enormous rigorous outrage strongest 78 31 38 57 12 91
Step VI is the final step of the input. Based on the above pattern, answer accordingly.
INPUT: 77 34 longest brigadier evaporation 12 91 pace intelligence 19 88 around
What is the place of brigadier from the right end in Step III?
Directions: A machine is programmed in such a manner that when some elements are provided, it gives output in the following pattern. Observe the pattern and answer accordingly.
INPUT: strongest 57 12 outrage biggest enormous 38 31 78 unanimous rigorous 91
Step I: strongest 57 12 outrage biggest unanimous 78 enormous 38 31 rigorous 91
Step II: strongest 57 12 outrage unanimous biggest 78 31 enormous 38 rigorous 91
Step III: strongest 12 outrage unanimous biggest enormous 78 31 38 57 rigorous 91
Step IV: strongest outrage unanimous biggest enormous rigorous 78 31 38 57 12 91
Step V: strongest unanimous biggest enormous rigorous outrage 78 31 38 57 12 91
Step VI: unanimous biggest enormous rigorous outrage strongest 78 31 38 57 12 91
Step VI is the final step of the input. Based on the above pattern, answer accordingly.
INPUT: 77 34 longest brigadier evaporation 12 91 pace intelligence 19 88 around
Which step will be penultimate step for the given input?
Directions: A machine is programmed in such a manner that when some elements are provided, it gives output in the following pattern. Observe the pattern and answer accordingly.
INPUT: strongest 57 12 outrage biggest enormous 38 31 78 unanimous rigorous 91
Step I: strongest 57 12 outrage biggest unanimous 78 enormous 38 31 rigorous 91
Step II: strongest 57 12 outrage unanimous biggest 78 31 enormous 38 rigorous 91
Step III: strongest 12 outrage unanimous biggest enormous 78 31 38 57 rigorous 91
Step IV: strongest outrage unanimous biggest enormous rigorous 78 31 38 57 12 91
Step V: strongest unanimous biggest enormous rigorous outrage 78 31 38 57 12 91
Step VI: unanimous biggest enormous rigorous outrage strongest 78 31 38 57 12 91
Step VI is the final step of the input. Based on the above pattern, answer accordingly.
INPUT: 77 34 longest brigadier evaporation 12 91 pace intelligence 19 88 around
Which step is the following output, 'brigadier intelligence pace evaporation longest 88 19 34 77 12 91 around'?
Directions: A machine is programmed in such a manner that when some elements are provided, it gives output in the following pattern. Observe the pattern and answer accordingly.
INPUT: strongest 57 12 outrage biggest enormous 38 31 78 unanimous rigorous 91
Step I: strongest 57 12 outrage biggest unanimous 78 enormous 38 31 rigorous 91
Step II: strongest 57 12 outrage unanimous biggest 78 31 enormous 38 rigorous 91
Step III: strongest 12 outrage unanimous biggest enormous 78 31 38 57 rigorous 91
Step IV: strongest outrage unanimous biggest enormous rigorous 78 31 38 57 12 91
Step V: strongest unanimous biggest enormous rigorous outrage 78 31 38 57 12 91
Step VI: unanimous biggest enormous rigorous outrage strongest 78 31 38 57 12 91
Step VI is the final step of the input. Based on the above pattern, answer accordingly.
INPUT: 77 34 longest brigadier evaporation 12 91 pace intelligence 19 88 around
Which element is second to the left of the element which is third from the right end in Step V?
Direction: In each of the following questions, two statements I and II are given. There may be cause and effect relationships between the two statements. These two statements may be the effect of same cause or independent causes. These statements may be independent causes without having any relationship. Read both the statements in each question and mark your answer accordingly.
Statement I: The food prices touched an all time high during this weekend.
Statement II: Many shops were raided and adulterated food items were seized.
Direction: In each question below is given a statement followed by two courses of action numbered I and II. You have to assume everything in the statement to be true, then decided which of the two suggested courses of action logically follows for pursuing.
Statement: The Minister said that the teachers are still not familiarized with the need, importance and meaning of population education in the higher education system. They are not even clearly aware about their role and responsibilities in the population education programme.
Courses of action:
I. Population education programme should be included in the College action Curriculum.
II. Orientation programme should be conducted for teachers on Population education.
Direction: In each question below is given a statement followed by two courses of action numbered I and II. You have to assume everything in the statement to be true, then decided which of the two suggested courses of action logically follows for pursuing.
Statement: Financial stringency prevented the State Government from paying salaries to its employees since April this year.
Courses of action:
I. The State Government should immediately curtail the staff strength at least by 30%.
II. The State Government should reduce wasteful expenditure and arrange to pay the salaries of its employees.
Direction: In the following question, the symbol @, ©, *, $ and # are used with the following meaning:
‘P @ Q’ means ‘P is neither smaller than nor equal to Q’.
‘P © Q’ means ‘P is not smaller than Q’.
‘P * Q’ means ‘P is not greater than Q’.
‘P $ Q’ means’ P is neither smaller than nor greater than Q’.
‘P # Q’ means ‘P is neither greater than nor equal to Q’.
Now in the following question, assuming the given statements to be true, find which of the two conclusions I and II have given below them is/are definitely true?
Statements : Z#N, F©N, F*K
Conclusion :
I. K $ N
II. K @ Z
Direction: In the following question, the symbol @, ©, *, $ and # are used with the following meaning:
‘P @ Q’ means ‘P is neither smaller than nor equal to Q’.
‘P © Q’ means ‘P is not smaller than Q’.
‘P * Q’ means ‘P is not greater than Q’.
‘P $ Q’ means’ P is neither smaller than nor greater than Q’.
‘P # Q’ means ‘P is neither greater than nor equal to Q’.
Now in the following question, assuming the given statements to be true, find which of the two conclusions I and II have given below them is/are definitely true?
Statements : D $ T, T©M, M # K
Conclusions :
I. M $ D
II. D@ M
Direction: In the following question, the symbol @, ©, *, $ and # are used with the following meaning:
‘P @ Q’ means ‘P is neither smaller than nor equal to Q’.
‘P © Q’ means ‘P is not smaller than Q’.
‘P * Q’ means ‘P is not greater than Q’.
‘P $ Q’ means’ P is neither smaller than nor greater than Q’.
‘P # Q’ means ‘P is neither greater than nor equal to Q’.
Now in the following question, assuming the given statements to be true, find which of the two conclusions I and II have given below them is/are definitely true?
Statements: W©A, B*A, B@M
Conclusions:
I. B # W
II. W $ B
Direction: In the following question, the symbol @, ©, *, $ and # are used with the following meaning:
‘P @ Q’ means ‘P is neither smaller than nor equal to Q’.
‘P © Q’ means ‘P is not smaller than Q’.
‘P * Q’ means ‘P is not greater than Q’.
‘P $ Q’ means’ P is neither smaller than nor greater than Q’.
‘P # Q’ means ‘P is neither greater than nor equal to Q’.
Now in the following question, assuming the given statements to be true, find which of the two conclusions I and II have given below them is/are definitely true?
Statements: J * M, M $ N, N # T
Conclusions:
I. T @ J
II. T $ J
Direction: In the following question, the symbol @, ©, *, $ and # are used with the following meaning:
‘P @ Q’ means ‘P is neither smaller than nor equal to Q’.
‘P © Q’ means ‘P is not smaller than Q’.
‘P * Q’ means ‘P is not greater than Q’.
‘P $ Q’ means’ P is neither smaller than nor greater than Q’.
‘P # Q’ means ‘P is neither greater than nor equal to Q’.
Now in the following question, assuming the given statements to be true, find which of the two conclusions I and II have given below them is/are definitely true?
Statements: V * F, F @ R, R © G
Conclusions:
I. G # V
II. G@ V
Direction: In each question below is given a statement followed by two courses of action numbered I and II. You have to assume everything in the statement to be true, then decided which of the two suggested courses of action logically follows for pursuing.
Statement: One of the problems facing the food processing industry is the irregular supply of raw material. The producers of raw material are not getting a reasonable price.
Courses of action:
I. The government should regulate the supply of raw material to other industries also.
II. The government should announce an attractive package to ensure regular supply of raw material for food processing industry.
Direction: In each question below is given a statement followed by two courses of action numbered I and II. You have to assume everything in the statement to be true, then decided which of the two suggested courses of action logically follows for pursuing.
Statement: The office In charge of a Company had a hunch that some money was missing from the safe.
Courses of action:
I. He should get it recounted with the help of the staff and Check it with the balance sheet.
II. He should inform the police.
In a certain language, ‘cot tip mot’ means ‘singing is appreciable’; ‘mot baj min’ means ‘dancing is good’ and ‘tip nop baj’ means ‘singing and dancing’. Which of the following means ‘good’ in that code language?
Direction: In each of the question given below, there are two statements followed by two conclusions numbered 1 and 2. You have to take the given statements to be true even if they seem to be at variance with commonly known facts and then decide which of the given conclusions logically follow (s) from the given statements.
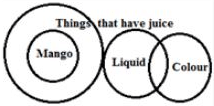
Statements:
(a) All mangoes have juices
(b) No juice has colour
(c) Some colours have liquid.
Conclusions:
I. Some mangoes have colour.
II. At least some juices have liquid.
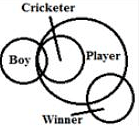
Direction: In each of the question given below, there are two statements followed by two conclusions numbered 1 and 2. You have to take the given statements to be true even if they seem to be at variance with commonly known facts and then decide which of the given conclusions logically follow (s) from the given statements.
Statements:
(a) Some boys are cricketers.
(b) All cricketers are players.
(c) Some players are winners.
Conclusions:
I. Some winners are cricketers.
II. Some players are boys.
Direction: In each of the question given below, there are two statements followed by two conclusions numbered 1 and 2. You have to take the given statements to be true even if they seem to be at variance with commonly known facts and then decide which of the given conclusions logically follow (s) from the given statements.
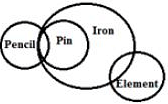
Statements:
(a) Some pencil are pins
(b) all pins are iron.
(c) Some iron is element.
Conclusion:
I. Some element is pins.
II. No iron is pencil
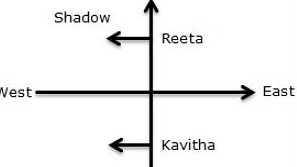
One morning after sunrise, Reeta and Kavita were talking to each other face to face at Tilak Square. If Kavita’s shadow was exactly to the right to Reeta, which direction was Kavita facing?
If A+B means B is the father of A, A*B means A is the son of B, A-B means B is the daughter of A, A÷B means B is the mother of A. Then in which of the following given options, A is the maternal uncle of E?
If A-B means B is the husband of A, A*B means A is the brother of B, A+B means B is the son of A, A÷B means B is the father of A. Then in which of the following given options, E is the cousin of A?
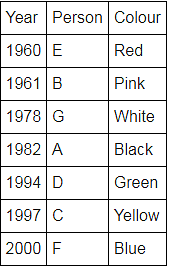
Directions: Seven people A, B, C, D, E, F and G are born in different years and like different colours - red, blue, pink, yellow, green, black and white not necessarily in same order.
B and E are born in consecutive years (B being younger), one of them been born in 1961.
The one who likes black is born in 1982 and is 4 years younger than the one who likes white.
The difference between present ages of A and D is 10 less than the difference between present ages of G and F. (A and G are elder than D and F respectively)
G is born in 1978.
F is born in 2000 and is youngest and doesn't like pink.
C likes yellow and is born three years after D was born, who is 6 years elder than F and 34 years younger to one who likes red colour.
The second eldest person doesn't like green.
The no. of people elder than the one who likes pink are 1 more than the no. of people younger than one who likes blue.
Who is the eldest person?
Directions: Seven people A, B, C, D, E, F and G are born in different years and like different colours - red, blue, pink, yellow, green, black and white not necessarily in same order.
B and E are born in consecutive years (B being younger), one of them been born in 1961.
The one who likes black is born in 1982 and is 4 years younger than the one who likes white.
The difference between present ages of A and D is 10 less than the difference between present ages of G and F. (A and G are elder than D and F respectively)
G is born in 1978.
F is born in 2000 and is youngest and doesn't like pink.
C likes yellow and is born three years after D was born, who is 6 years elder than F and 34 years younger to one who likes red colour.
The second eldest person doesn't like green.
The no. of people elder than the one who likes pink are 1 more than the no. of people younger than one who likes blue.
What is the difference between the present ages of E and F.
Directions: Seven people A, B, C, D, E, F and G are born in different years and like different colours - red, blue, pink, yellow, green, black and white not necessarily in same order.
B and E are born in consecutive years (B being younger), one of them been born in 1961.
The one who likes black is born in 1982 and is 4 years younger than the one who likes white.
The difference between present ages of A and D is 10 less than the difference between present ages of G and F. (A and G are elder than D and F respectively)
G is born in 1978.
F is born in 2000 and is youngest and doesn't like pink.
C likes yellow and is born three years after D was born, who is 6 years elder than F and 34 years younger to one who likes red colour.
The second eldest person doesn't like green.
The no. of people elder than the one who likes pink are 1 more than the no. of people younger than one who likes blue.
A is born in _____ and likes _____ colour.
Directions: Seven people A, B, C, D, E, F and G are born in different years and like different colours - red, blue, pink, yellow, green, black and white not necessarily in same order.
B and E are born in consecutive years (B being younger), one of them been born in 1961.
The one who likes black is born in 1982 and is 4 years younger than the one who likes white.
The difference between present ages of A and D is 10 less than the difference between present ages of G and F. (A and G are elder than D and F respectively)
G is born in 1978.
F is born in 2000 and is youngest and doesn't like pink.
C likes yellow and is born three years after D was born, who is 6 years elder than F and 34 years younger to one who likes red colour.
The second eldest person doesn't like green.
The no. of people elder than the one who likes pink are 1 more than the no. of people younger than one who likes blue.
When is B born?
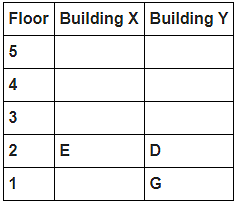
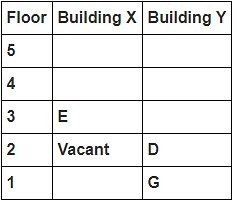
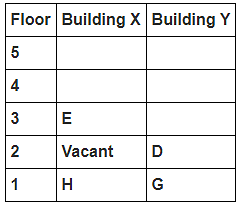
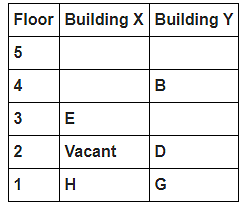
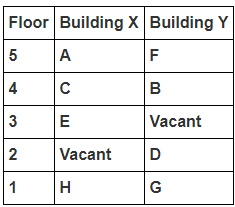
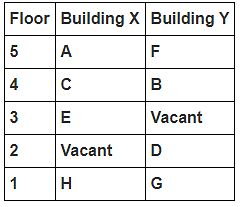
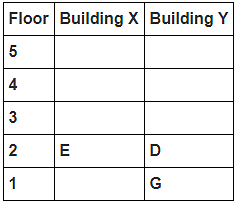
Directions : Study the following information carefully and answer the questions given below:
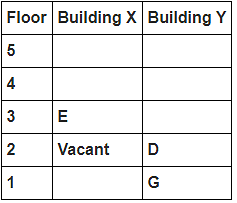
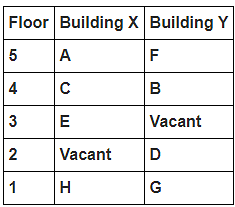
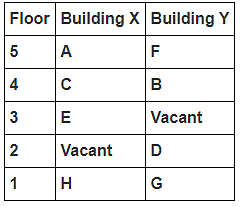
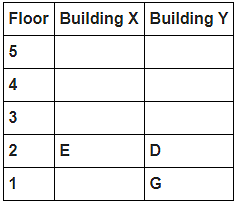
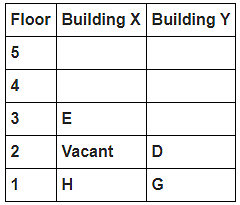
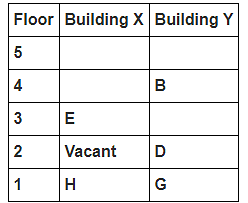
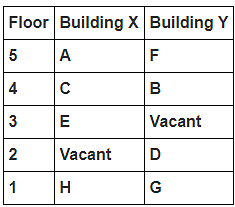
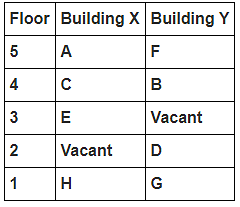
8 persons A, B, C, D, E, F, G and H live in 2 different buildings Building X and Building Y. Both buildings have 5 floors each with ground floor numbered 1; floor above it numbered 2 and so on until topmost is numbered 5. One of the floors are vacant in each building. Only one person lives on each floor of the building X and building Y. No same number of floors are vacant. Only one person lives below E. At least one person lives between F and G. Number of persons above D is one more than the person below D. D lives in building Y. No one lives between F and B. G lives one of the floors below B. D lives immediately above G. No one lives between E and H and they both lives on odd numbered floor. F and A lives on the same numbered floor. C lives below A. 1st floor is not vacant in any of the building. B's and E's floor numbers are not same.
How many persons live between C and H?
Directions : Study the following information carefully and answer the questions given below:
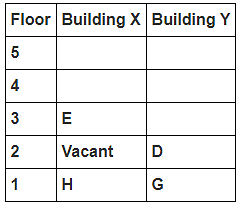
8 persons A, B, C, D, E, F, G and H live in 2 different buildings Building X and Building Y. Both buildings have 5 floors each with ground floor numbered 1; floor above it numbered 2 and so on until topmost is numbered 5. One of the floors are vacant in each building. Only one person lives on each floor of the building X and building Y. No same number of floors are vacant. Only one person lives below E. At least one person lives between F and G. Number of persons above D is one more than the person below D. D lives in building Y. No one lives between F and B. G lives one of the floors below B. D lives immediately above G. No one lives between E and H and they both lives on odd numbered floor. F and A lives on the same numbered floor. C lives below A. 1st floor is not vacant in any of the building. B's and E's floor numbers are not same.
Who among the following does not belongs to the group?
Directions : Study the following information carefully and answer the questions given below:
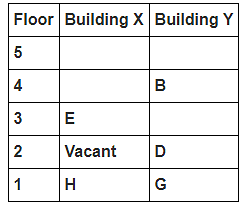
8 persons A, B, C, D, E, F, G and H live in 2 different buildings Building X and Building Y. Both buildings have 5 floors each with ground floor numbered 1; floor above it numbered 2 and so on until topmost is numbered 5. One of the floors are vacant in each building. Only one person lives on each floor of the building X and building Y. No same number of floors are vacant. Only one person lives below E. At least one person lives between F and G. Number of persons above D is one more than the person below D. D lives in building Y. No one lives between F and B. G lives one of the floors below B. D lives immediately above G. No one lives between E and H and they both lives on odd numbered floor. F and A lives on the same numbered floor. C lives below A. 1st floor is not vacant in any of the building. B's and E's floor numbers are not same.
Which of the following is true regarding B?
|
5 videos|378 docs|164 tests
|
|
5 videos|378 docs|164 tests
|