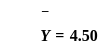MH SET Paper 2 Mock Test - 5 (Geography) - MAHA TET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test MH SET Mock Test Series 2024 - MH SET Paper 2 Mock Test - 5 (Geography)
Which of the following industrial region is famous for IT industries in India?
Which of the following is NOT a reason for generation of ocean currents?
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Which of the following rivers is NOT a tributary of Ganga?
With reference to the Tropical Cyclones, consider the following statements:
1. Cyclone forming over land has an effect over a large area.
2. If a cyclone stays at a place, rains may continue for a longer duration than average.
3. Temperature of ocean water must be higher than approx 27oC for the formation of cyclones.
How many of the statements given above are correct?
Assertion (A): The River Ganga has a deep but narrow channel at Rishikesh.
Reason (R) : Lateral cutting occurs at the youthful stage in rivers.
Select the correct answer from options given below:
i. The index has indicators like development vulnerabilities, exclusions etc.
ii. They compare country performances.
iii. They are not easy to interpret.
iv. It summarizes multi-dimensional realities.
a) L.C . King’s theory is based on the arid topography as well as the semi-arid regions of South Africa.
b) He mentioned that the profile of an ideal hillslope must consist of summit, scarp, slope and pediments.
c) According to King, the African landscape consisted of scarps which have steep slopes and varied in angle from 15-30 degree.
d) He also did explain the presence of Yardangs and Zuegen as prime features of the African Landscape.
Which of the following options are correct?
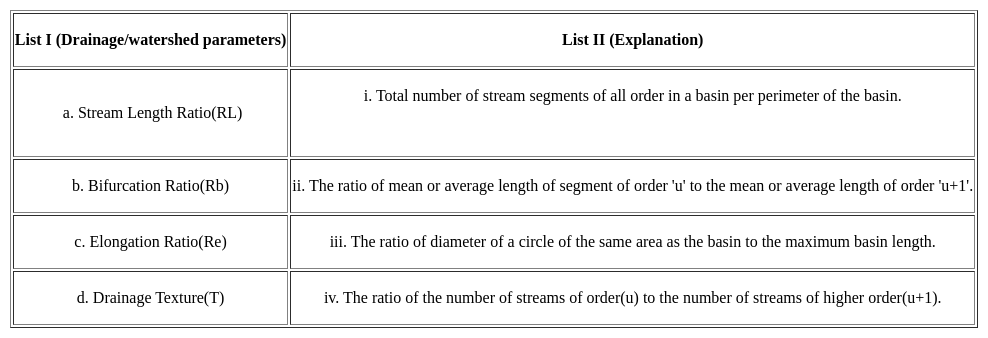
In the Remote Sensing, Classification processes can be done using the following methods:
Which of the following statement is correct about Fusion in remote sensing image interpretation?
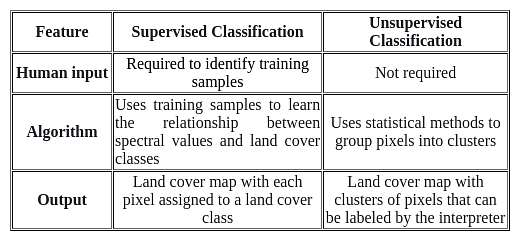
What is the difference between supervised and unsupervised classification in remote sensing image interpretation?
(a) Monsoon break is the phenomenon which means monsoon rainfall stops for a couple of days.
(b) Western Ghats receive orographic rain during the monsoon.
(c) First rain in a place is called as monsoon burst.
(d) The El Nino current decreases the temperature of water.
Select the correct option:
Variable Y regresses with variable X with the conditions that 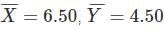 and b = 2.50 in the linear regression model (Y = a + bX), where
and b = 2.50 in the linear regression model (Y = a + bX), where 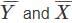 are means of the respective variables and b refers to gradient of line of Y w. r. t X. Which one of the following values of parameter 'a' of the model is correct?
are means of the respective variables and b refers to gradient of line of Y w. r. t X. Which one of the following values of parameter 'a' of the model is correct?
a) balanced regional development
b) Eradication of poverty
c) Increasing trend in life expectancy
d) Technological development
Choose the correct option:-
i. Dualism means difference in views.
ii. Dualism lies in methodology.
iii. It includes content of study, approach of study and method of study.
Choose the correct option from below:
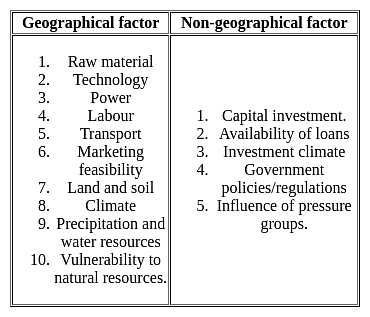
Which one of the following is not a geographical factor favorable for the location of an industry?
Assertion (A): The double-humped camel found in cold desert of Ladakh is called as Bactrian camel.
Reason (R) : Greeks called the area of central Asia as Bactria.
Select the correct answer from options given below:
Choose the correct option for the statements gien below:
(A) Endogenic forces sometimes produce sudden movements
(B) Sudden moments like earthquakes and volcanoes cause mass destruction on the surface of the earth
(a) Ratzel applied organic theory to biogeography.
(b) Humboldt was of the opinion that life of people living in islands, plains and mountains was similar.
(c) Kant described the impact of environment in late 18th century.
(d) Darwin’s theory of origin of species is dependent on the idea that the nature changes with time.
Code:
|
60 tests
|


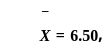 ,
,