MPTET Varg 2 Science Mock Test - 2 - MPTET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test MPTET Varg 2 Mock Test Series 2024 - MPTET Varg 2 Science Mock Test - 2
गद्यांश के अनुसार, कोकून के अंदर तितली स्वयं को सप्रयास मरोड़ती है ताकि:
कवि ने सूर्य की तुलना प्रभात के ग्वाले से क्यों की है?
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
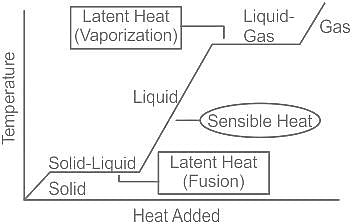
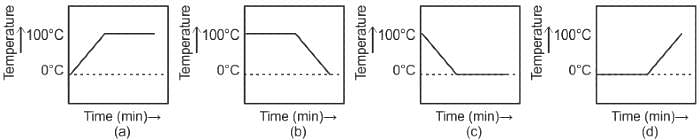
A student heats a beaker containing ice and water. He measures the temperature of the content of the beaker as a function of time. Which of the following would correctly represent the result?
The main source of energy in deep sea water can be -
Which of the following a type of simple tissue that has long, narrow cells with thick and lignified cell walls?
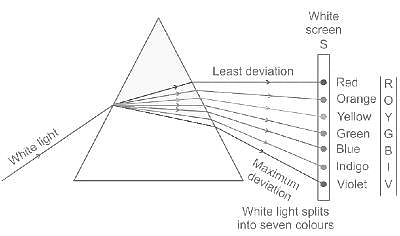
Write the given four colors in the ascending order of their wavelength.
Yellow, Red, Green, And Violet
Which of the following can be the best way to teach the concept of "physical and chemical change" to class Vth students?
The disproportionation redox reaction among the following is :
Which of the following steps is not related to the project method?
While teaching the topic 'Motion' in class VIII, the teacher starts from a story as "Once Newton was sitting under the apple tree and an apple falls down on him, then a question was confusing him that why the apple fell down why not upward".
What do you understand by this type of activity by the teacher?
The buoyant force is greater if volume of an object submerged in liquid is _______
A science teacher asks students to give examples of solid, liquid and gas. Here giving examples is related to –