SEBI Grade A (General Stream) Mock Test - 7 - Bank Exams MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test Mock Test Series for SEBI Grade A Exam 2024 - SEBI Grade A (General Stream) Mock Test - 7
In March 2024, Name the Insurance Company that has recently launched a comprehensive women's health insurance plan 'Health PowHER'.
In March 2024, Prime Minister (PM) Narendra Modi launched the 'Pradhan Mantri Samajik Utthan evam Rozgar Adharit Jankalyan' (PM-SURAJ) national portal to disadvantaged communities by the _____________ (Ministry).
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
In March 2024, a high-level committee (HLC) on 'One Nation, One Election', headed by ____________ presented the report to President Droupadi Murmu, recommending simultaneous polls for all three tiers of governance.
What is the central theme of the passage?
Which of the following should be the SECOND sentence after rearrangement?
Directions: In the following question, a sentence is given with four words marked as (A), (B), (C) and (D). These words may or may not be placed in their correct order. Four options with different arrangements of these words have been provided. Mark the option with the correct arrangement as the answer. If no rearrangement is required, mark option (5) as your answer.
In the following number series, a wrong number is given. Find out the wrong number.
3, 3, 12, 108, 1728, 43300
A and B together do some work in 10 days, B and C together do the same work in 25 days and C and A together do the same work in 50 days, then, In how many days will the three of them together complete same the work?
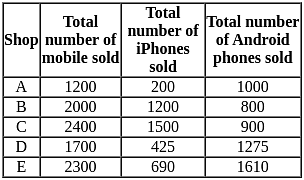
Among all of the stores which store sold the maximum number of iphones?
A swimmer swims in still water at the speed of 15 km/hour. He takes thrice as much time to reach the destination when he swims up in the river as it takes when he swims down in the river. At what speed the river is flowing?
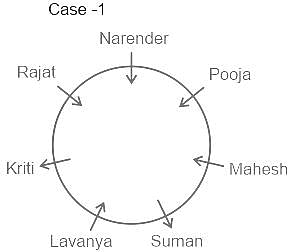
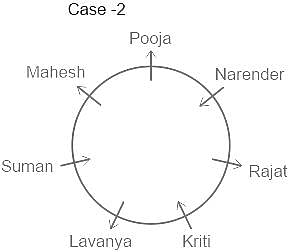
Who is sitting just between Kriti and Narender ?
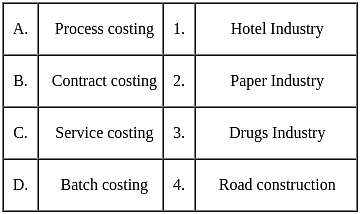
Match the following and choose the correct option
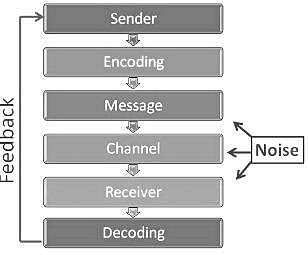
The right order of elements in a successful communication is:
Leadership style which takes decisions with subordinate is
Which of the following is NOT a type of ledger prepared under self-balancing leger system?