Test: Alpha-carbon Chemistry - MCAT MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test Organic Chemistry for MCAT - Test: Alpha-carbon Chemistry
Which of the following resonance structures would be the most stable hybrid of the base catalyzed enolate of this molecule?
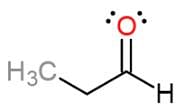

What is the proper IUPAC name for the following molecule?

| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Which of the following are true statements regarding enolate formation?
I. Overall the more substituted a double bond on an enolate, the less stable the molecule is.
II. Low temperature reactions favor a more rapidly formed enolate
III. Thermodynamic enolates are favored in reactions with strong, sterically hindered bases.
I. Overall the more substituted a double bond on an enolate, the less stable the molecule is.
II. Low temperature reactions favor a more rapidly formed enolate
III. Thermodynamic enolates are favored in reactions with strong, sterically hindered bases.
In the presence of a base, which carbon acts as the electrophilic site for this reaction of this molecule?
Which of the following ring structures will result in an equilibrium that favors the enol form?
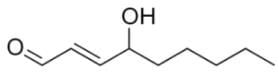
Which of the following are correct products of a retro-aldol reaction on the following molecule?
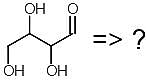
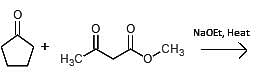
Which of the following could undergo an aldol condensation to form the following molecule?
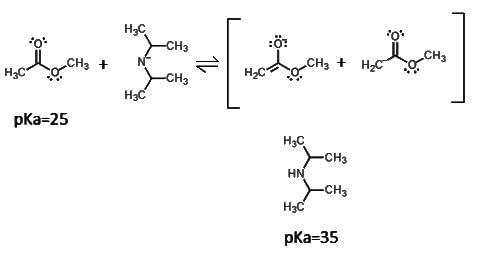
Given the following reaction, are the products or reactants favored?
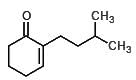
Which of the following would be the proper products of an aldol condensation of this molecule?
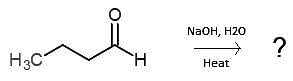
|
140 videos|5 docs|15 tests
|
|
140 videos|5 docs|15 tests
|