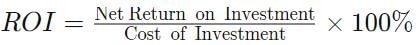Test: Business Arithmetic- 1 - Commerce MCQ
12 Questions MCQ Test Entrepreneurship Class 12 - Test: Business Arithmetic- 1
Joseph invested ₹ 1,000 in a pizza restaurant in 2018 and sold the shares for a total of ₹ 1,200 one year later. While looking at the accounts, he wanted to calculate the return on investment for his restaurant. To calculate it, he divided the net profits by the investment cost. Calculate and confirm how much would be the return on investment for Joseph’s restaurant.
In a sugar mill in UP, jaggery is produced using cane. The mill owner is unable to decide whether to continue with his subsidiary or not. The monthly output of the subsidiary is 2,500/kg. Sale price ₹ 100/ kg, Variable cost ₹ 30/kg, Fixed expenses ₹ 70,000. The mill owner is trying to find out the break-even point in units. It will be?
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Harshdeep is the stock keeper of Neha Textiles Ltd. The company is into converting cotton yarn into fabric and then further computerised printing on the same to add value to the fabric. He wants to know the ideal quantity of yarn to be ordered so that the production process does not stop. How can he know the correct time to place an order?
Pintu runs a company that sells ball pens. They first determined the fixed costs, which included Property tax, salaries, etc, which sums up to 1,00,000. The variable cost for manufacturing a pen is ₹ 2 per unit. Hence, they sell the pen at a price of ₹ 10. If one has to determine the break-even point, that would come up to:
How is ‘Unit of Sale’ determined in a restaurant providing dinner?
Which of the following is an example of variable cost?
Which of the following statement is false with respect to ABC analysis?
Which of the following is an examples of carrying costs for inventories?
A company uses 30 units of an item per day and the order lead time is 5 days. What is the re-order point?
A company uses 300 units of an item per day and the order lead time is 5 days. What should be the level of inventory when a new order is to be placed?
Annual quantity of jeans sold by a shop is 1,200 at the rate of ₹ 100/- per month. Cost of placing an order and receiving goods is ₹ 500/- per order. Inventory holding cost is ₹ 30/- per annum. What is the economic order quantity for the shopkeeper?
|
19 videos|62 docs|12 tests
|
|
19 videos|62 docs|12 tests
|