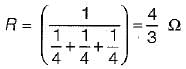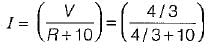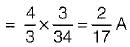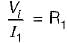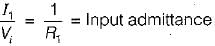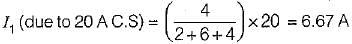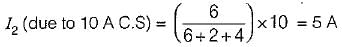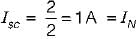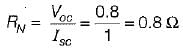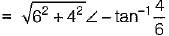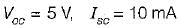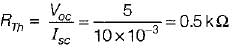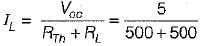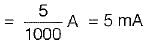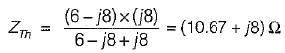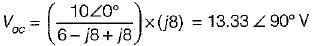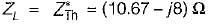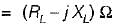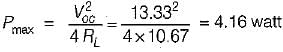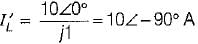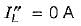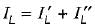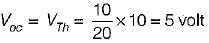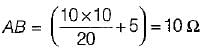Test: Circuit Theorems- 3 - Electrical Engineering (EE) MCQ
20 Questions MCQ Test Topicwise Question Bank for Electrical Engineering - Test: Circuit Theorems- 3
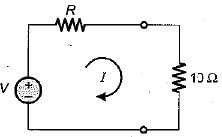
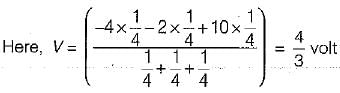
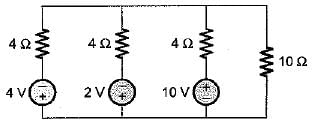
The current flowing through the resistance of 10 Ω for the circuit shown below is

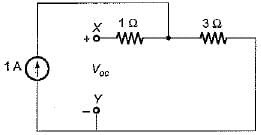
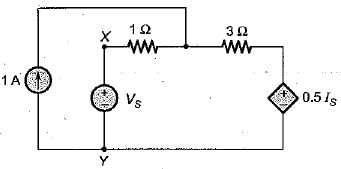
The Thevenin’s equivalent voltage source across the terminals X-Y shown below is

| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
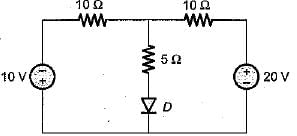
The Norton’s equivalent resistance across the diode in the given circuit is

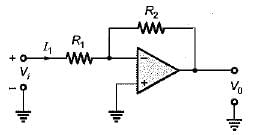
Assuming the op-amp to be ideal, the input admittance of the op-amp shown below is
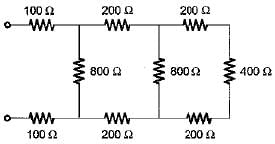
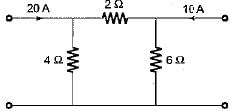
In the π-circuit shown below, the current through the 2 Ω, resistor is
Match List-I (Elements) with List-ll (Type) and select the correct answer using the codes given below the lists:
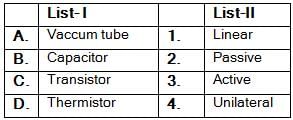
Codes:
The maximum power that a 12 V d.c. source with an interna! resistance of 2 Ω can supply toa resistive load is
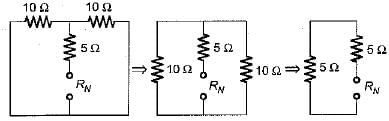
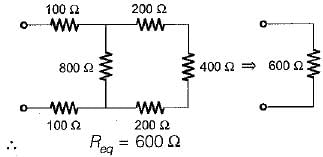
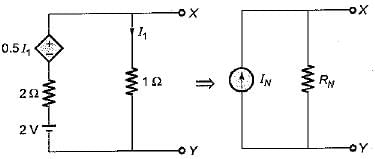
The Norton’s equivalent circuit for the circuit shown below across the terminals X-Y can be represented as a current source (IN) connected across a resistance (RN). The value of IN and RN are respectively
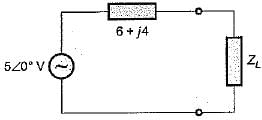
To effect maximum power transfer to the load, ZL (W) for the circuit shown below should be
In order to apply superposition theorem, it is necessary that the network be only
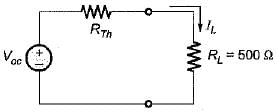
A network N is to be connected to a load of 500 ohms. If the Thevenin’s equivalent voltage and Norton’s equivalent current of N are 5 volts and 10 mA respectively, the current through the load will be
If all the elements in a particular network are linear, then the superposition theorem would hold, when the excitation is
The maximum value of power transferred to the load ZL shown in figure below is
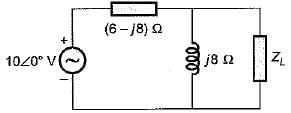
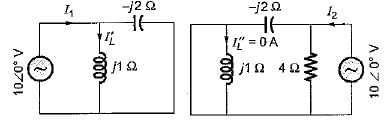
In the circuit shown below, the current through the inductive reactance is
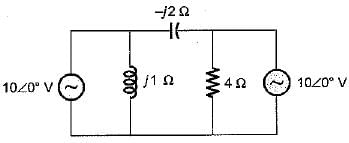
Which of the following theorems is applicable for both linear and non-linear circuits?
While determining RTh of a circuit
1. voltage and current sources should be left as they are.
2. all independent current and voltage sources are short-circuited.
3. all sources should be replaced by their source resistances.
4. all dependent sources remain as they are.
Q. Which of the statements is/are true in relation of RTh?
For the circuit given in figure below, the Thevenin’s voltage and resistance as seen at “AB" are respectively
Consider the following statements about Norton’s equivalent of a circuit across a given two load terminals:
1. Norton’s equivalent resistance is the same as Thevenin’s equivalent resistance RTh.
2. Norton’s equivalent is the voltage equivalent of the network.
3. The load is connected in parallel to the Norton’s equivalent resistance.
Out of the above statements, which statements hold true?
When the power transferred to the load is maximum, the efficiency is