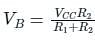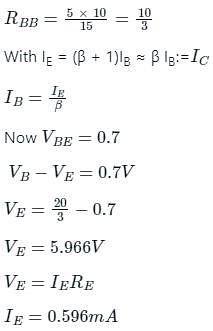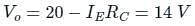Test: Common Emitter Configuration - Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test Electronic Devices - Test: Common Emitter Configuration
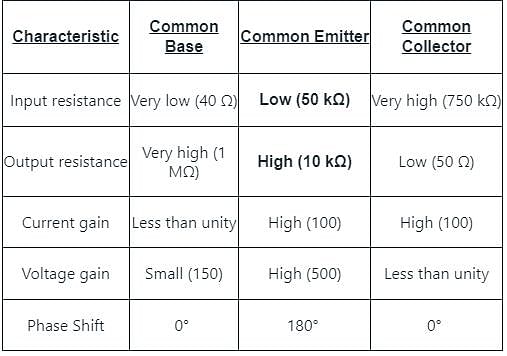
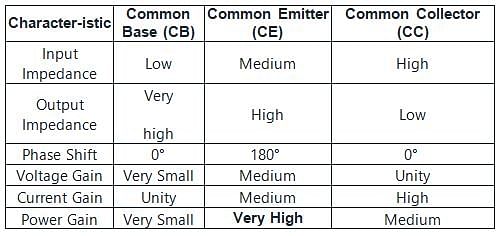
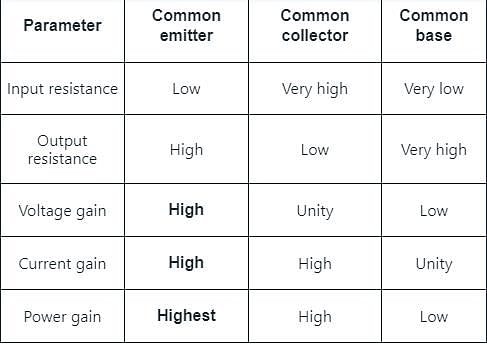
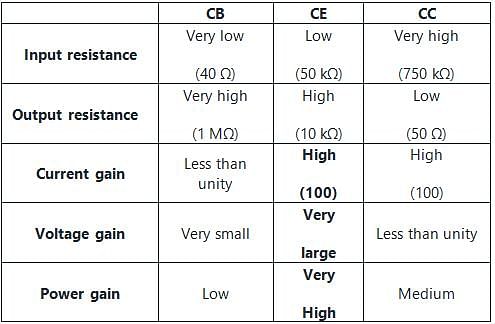
Input resistance of a common emitter transistor of the order of
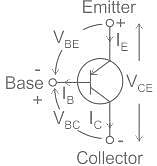
In a common-emitter amplifier, the input AC signal to be amplified is applied across:
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
How many degree phases have been shifted from input to output in common emitter configuration?
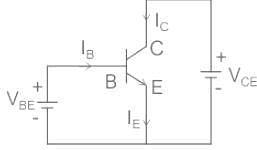
Which type of configuration has high output impedance but low input impedance?
Which of the following BJT configuration has highest Power Gain?
In which of the following amplifier configurations, the power gain is the largest?
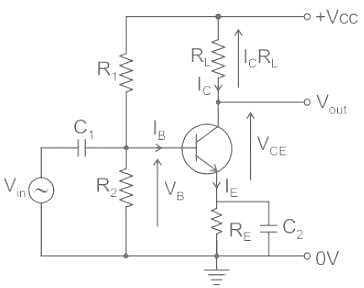
In a CE amplifier, collector load is 4 kΩ and quiescent current is 1 mA. Find the operating point if VCC = 10 V.
For highest power gain, what configuration is used?
The most widely used amplifier configuration is
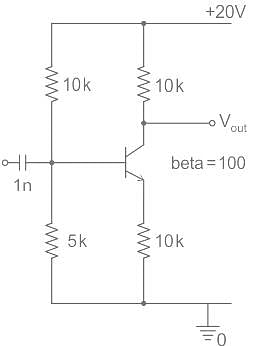
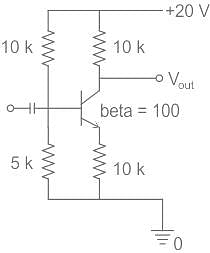
Given figure shows a silicon transistor connected as a common emitter amplifier. The quiescent collector voltage of the circuit is approximately.
|
21 docs|29 tests
|
|
21 docs|29 tests
|