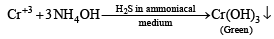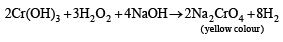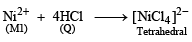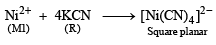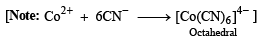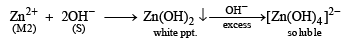Test: Comprehension Based Questions: Analytical Chemistry - JEE MCQ
7 Questions MCQ Test 35 Years Chapter wise Previous Year Solved Papers for JEE - Test: Comprehension Based Questions: Analytical Chemistry
PASSAGE-1
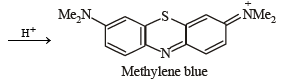
p-Amino-N, N-dimethylaniline is added to a strongly acidic solution of X. The resulting solution is treated with a few drops of aqueous solution of Y to yield blue coloration due to the formation of methylene blue. Treatment of the aqueous solution of Y with the reagent potassium hexacyanoferrate(II) leads to the formation of an intense blue precipitate. The precipitate dissolves on excess addition of the reagent. Similarly, treatment of the solution of Y with the solution of potassium hexacyanoferrate (III) leads to a brown coloration due to the formation of Z. (2009)
Q. The compound X is
p-Amino-N, N-dimethylaniline is added to a strongly acidic solution of X. The resulting solution is treated with a few drops of aqueous solution of Y to yield blue coloration due to the formation of methylene blue. Treatment of the aqueous solution of Y with the reagent potassium hexacyanoferrate(II) leads to the formation of an intense blue precipitate. The precipitate dissolves on excess addition of the reagent. Similarly, treatment of the solution of Y with the solution of potassium hexacyanoferrate (III) leads to a brown coloration due to the formation of Z. (2009)
PASSAGE-1
p-Amino-N, N-dimethylaniline is added to a strongly acidic solution of X. The resulting solution is treated with a few drops of aqueous solution of Y to yield blue coloration due to the formation of methylene blue. Treatment of the aqueous solution of Y with the reagent potassium hexacyanoferrate(II) leads to the formation of an intense blue precipitate. The precipitate dissolves on excess addition of the reagent. Similarly, treatment of the solution of Y with the solution of potassium hexacyanoferrate (III) leads to a brown coloration due to the formation of Z. (2009)
Q. The compound Y is
p-Amino-N, N-dimethylaniline is added to a strongly acidic solution of X. The resulting solution is treated with a few drops of aqueous solution of Y to yield blue coloration due to the formation of methylene blue. Treatment of the aqueous solution of Y with the reagent potassium hexacyanoferrate(II) leads to the formation of an intense blue precipitate. The precipitate dissolves on excess addition of the reagent. Similarly, treatment of the solution of Y with the solution of potassium hexacyanoferrate (III) leads to a brown coloration due to the formation of Z. (2009)
PASSAGE-1
p-Amino-N, N-dimethylaniline is added to a strongly acidic solution of X. The resulting solution is treated with a few drops of aqueous solution of Y to yield blue coloration due to the formation of methylene blue. Treatment of the aqueous solution of Y with the reagent potassium hexacyanoferrate(II) leads to the formation of an intense blue precipitate. The precipitate dissolves on excess addition of the reagent. Similarly, treatment of the solution of Y with the solution of potassium hexacyanoferrate (III) leads to a brown coloration due to the formation of Z. (2009)
Q. The compound Z is
p-Amino-N, N-dimethylaniline is added to a strongly acidic solution of X. The resulting solution is treated with a few drops of aqueous solution of Y to yield blue coloration due to the formation of methylene blue. Treatment of the aqueous solution of Y with the reagent potassium hexacyanoferrate(II) leads to the formation of an intense blue precipitate. The precipitate dissolves on excess addition of the reagent. Similarly, treatment of the solution of Y with the solution of potassium hexacyanoferrate (III) leads to a brown coloration due to the formation of Z. (2009)
PASSAGE-2
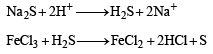
An aqueous solution of a mixture of two inorganic salts, when treated with dilute HCl, gave a precipitate (P) and a filtrate (Q).
The precipitate P was found to dissolve in hot water. The filtrate (Q) remained unchanged, when treated with H2S in a dilute mineral acid medium. However, it gave a precipitate (R) with H2S in an ammoniacal medium. The precipitate R gave a coloured solution (S), when treated with H2O2 in an aqueous NaOH medium. (JEE Adv. 2013-II)
Q. The precipitate P contains
PASSAGE-2
An aqueous solution of a mixture of two inorganic salts, when treated with dilute HCl, gave a precipitate (P) and a filtrate (Q).
The precipitate P was found to dissolve in hot water. The filtrate (Q) remained unchanged, when treated with H2S in a dilute mineral acid medium. However, it gave a precipitate (R) with H2S in an ammoniacal medium. The precipitate R gave a coloured solution (S), when treated with H2O2 in an aqueous NaOH medium. (JEE Adv. 2013-II)
Q. The coloured solution S contains
PASSAGE-3
An aqueous solution of metal ion M1 reacts separately with reagents Q and R in excess to give tetrahedral and square planar complexes, respectively. An aqueous solution of another metal ion M2 always forms tetrahedral complexes with these reagents.
Aqueous solution of M2 on reaction with reagent S gives white precipitate which dissolves in excess of S. The reactions are summarized in the scheme given below:
Scheme:
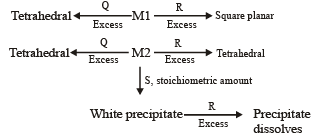
6. M1, Q and R, respectively are (JEE Adv. 2014)
PASSAGE-3
An aqueous solution of metal ion M1 reacts separately with reagents Q and R in excess to give tetrahedral and square planar complexes, respectively. An aqueous solution of another metal ion M2 always forms tetrahedral complexes with these reagents.
Aqueous solution of M2 on reaction with reagent S gives white precipitate which dissolves in excess of S. The reactions are summarized in the scheme given below:
Scheme:

Q. Reagent S is (JEE Adv. 2014)
|
347 docs|185 tests
|
|
347 docs|185 tests
|


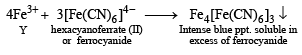
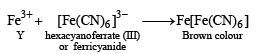
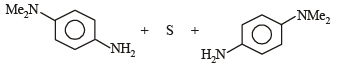

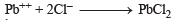 (White ppt) soluble in hot water.
(White ppt) soluble in hot water.