Test: Electrostatics - MCAT MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test Physics for MCAT - Test: Electrostatics
After MgCl2 dissolves in a neutrally charged solvent, what is the net charge of the solution?
If one sphere has a mass of 2 kg and an electric charge of +4 μC while another sphere, 3 meters away, has a mass of 1 kg and an electric charge of +5 μC, what is the acceleration of the more massive sphere?
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
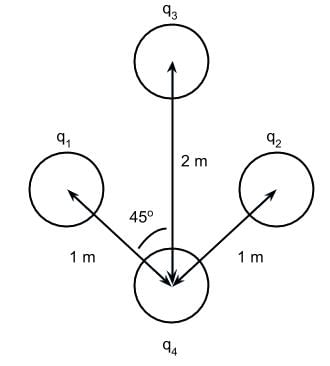
In the figure below, spheres q1 ,q2 , and q3 have the same positive charge magnitude. Which of the following is a possible direction for the net electric field vector on q4?

The magnitude of electric field experienced by a charge at a certain distance from a source charge is equal to 64 N/C. What will be the magnitude of the electric field at four times that distance and with a source charge half as strong?
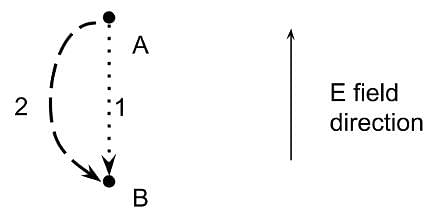
In five seconds, a point charge moves from position A to position B as shown in the diagram below. Which one of the following two paths require the most energy?
A constant electric field moves a positive point charge from one position to another position so that the change in electric potential is −450 V. Which of the following must increase during this movement?
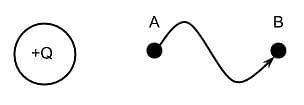
The figure below shows a source charge Q. Which of the following can best describe the electric potential difference as a positive point charge is moved from position A to position B through the indicated path?
The magnitude of the electric force experienced by a point charge a distance d away from a source charge is affected by which of the following?
Sphere A and B have the same mass and charge magnitudes. They are placed a distance r away from each other so that gravitational forces and electrostatic forces allow both spheres to be in equilibrium. What would occur if sphere A doubled in charge?
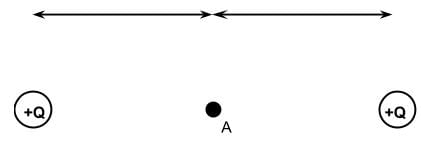
In the diagram below, which of the following statements is true about a point charge in position A, which is midway between two positive source charges of equal magnitude?
|
158 videos|9 docs|21 tests
|


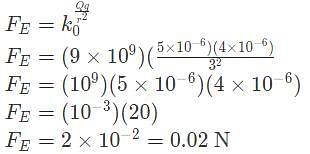
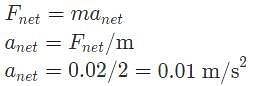
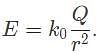 Where r is the distance between the charges, Q is the source charge, and k0 is Coulomb's constant.
Where r is the distance between the charges, Q is the source charge, and k0 is Coulomb's constant.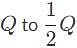 we obtain:
we obtain: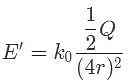
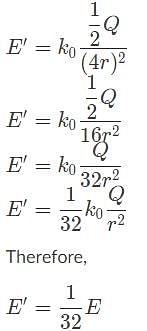
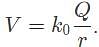 Where Q is the value of a source charge and r is the distance between the source charge and the point charge.
Where Q is the value of a source charge and r is the distance between the source charge and the point charge.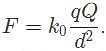 The signs of both charges will only affect the overall sign on the force value. The distance d is the only answer choice that affects the magnitude of the electric force.
The signs of both charges will only affect the overall sign on the force value. The distance d is the only answer choice that affects the magnitude of the electric force.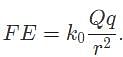 Doubling the charge of sphere A will double the repulsive electrostatic force but not change the attractive gravitational force measurably since the added charge would have such a small mass.
Doubling the charge of sphere A will double the repulsive electrostatic force but not change the attractive gravitational force measurably since the added charge would have such a small mass.














