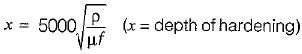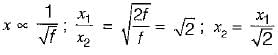Test: Heat Treatment of Steels - 3 - Mechanical Engineering MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test Topicwise Question Bank for Mechanical Engineering - Test: Heat Treatment of Steels - 3
Which of the following is a case hardening process
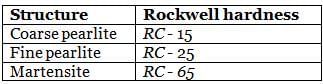
During heat treatment of steel, the hardness of various structure in increasing order is
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Carburized machine components have high endurance limit because carburization
Tempering temperature of most of the material is of the order of
Case hardening is the only method suitable for hardening
Which of the following materials cannot be heat treated
The Iron-carbon diagram and the TTT curves are determined under
TTT diagram indicates time, temperature and transformation of
When the temperature of a solid metal increases
The main purpose of spheroidising treatment is to improve
The essential constituent of a hardened steel is
Which of the following is defined as the ability of the structure to transform into martensite?
The heat treatment process used for hardening of steel is
Microstructure of annealed hypereutectoid plain carbon steel consists of
Which one of the following cooling methods is best suited for converting Austenite steel into very fine Peariite steel?
Doubling the frequency of current in an induction hardening process
“Matching Exercise”. Choose the correct one out of the alternatives A, B, C, D.
Heat treatment process
P. Annealing
Q. Normalising
R. Martempering sizes
S. Nitriding
Application
1. Surface hardening
2. Relieving stress
3. Refining grain
4. Reducing warping and cracking
Match List-I (Heat Treatment) with List-ll (Effect on the properties) and select the correct answer using the codes given below the lists:
List-I
A. Annealing
B. Nitriding
C. Martempering
D. Normalizing
List-ll
1. Refined grain structure
2. Improves the hardness of the whole mass
3. Increases surface hardness
4. Improves ductility
Codes:
A B C D
(a) 4 3 2 1
(b) 1 3 4 2
(c) 4 2 1 3
(d) 2 1 3 4
Match List-I (Name of treatment) with List-ll (Media used) and select the correct answer using the codes given below the lists:
List-I
A. Pack carburising
B. Gas carburising
C. Cyaniding
D. Nitriding
List-ll
1. Ammonia gas
2. Sodium cyanide
3. Carburising compound
4. Ethane
Codes:
A B C D
(a) 3 4 2 1
(b) 2 1 3 4
(c) 3 1 2 4
(d) 2 4 3 1
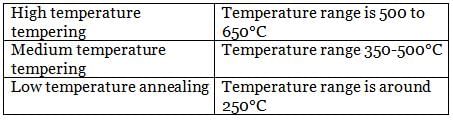
Match List-I (Temperature) with List-ll (Tempering) and select the correct answer using the codes given below the lists:
List-I
A. Low temperature tempering
B. Medium temperature tempering
C. High temperature tempering
List-ll
1. 150°C to 250°C
2. 250°C to 350°C
3. 350°C to 450°C
4. 500°C to 650°C
Codes:
A B C
(a) 1 2 3
(b) 1 2 4
(c) 2 3 4
(d) 4 3 1
Which one of the following advantage of cyaniding is incorrect?
Globular form of cementite is the structure of steel is obtained through
|
45 videos|314 tests
|
|
45 videos|314 tests
|