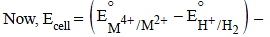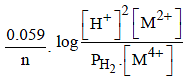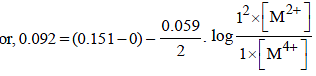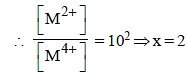Test: MCQs (One or More Correct Option): Electrochemistry | JEE Advanced - JEE MCQ
24 Questions MCQ Test 35 Years Chapter wise Previous Year Solved Papers for JEE - Test: MCQs (One or More Correct Option): Electrochemistry | JEE Advanced
The standard reduction potentials at 298 K for the following half reactions are given against each (1981 - 1 Mark)
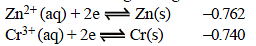
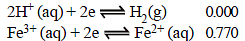
which is the strongest reducing agent?
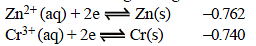
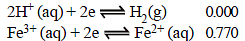
Faraday’s laws of electrolysis are related to the (1983 - 1 Mark)
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
A solution containing one mole per litre of each Cu(NO3)2; AgNO3; Hg2(NO3)2; is being electrolysed by using inert
electrodes. The values of standard electrode potentials in volts (reduction potentials) are : (1984 - 1 Mark)
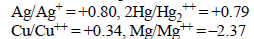
With increasing voltage, the sequence of deposition of metalson the cathode will be :
electrodes. The values of standard electrode potentials in volts (reduction potentials) are : (1984 - 1 Mark)
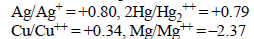
The electric charge for electrode deposition of one gramequivalent of a substance is : (1984 - 1 Mark)
The reaction :
½ Hg2(g) + AgCl(s) → H+(aq) + Cl–(aq) + Ag(s) occurs in the galvanic cell
A solution of sodium sulphate in water is electrolysed usinginert electrodes. The products at the cathode and anode arerespectively (1987 - 1 Mark)
The standard oxidation potentials, Eº, for the half reactions are as (1988 - 1 Mark)
Zn = Zn2+ + 2e–; Eº = +0.76 V
Fe = Fe2+ + 2e–; Eº = +0.41 V
The EMF for the cell reaction :
Fe2+ + Zn → Zn2+ + Fe
A dilute aqueous solution of Na2SO4 is electrolyzed using platinum electrodes.The products at the anode and cathode
are:
The standard reduction potentials of Cu2+ | Cu and Cu2+|Cu+ are 0.337 V and 0.153 respectively. The standardelectrode potential of Cu+ |Cu half cell is (1997 - 1 Mark)
A gas X at 1 atm is bubbled through a solution containing amixture of 1 M Y– and M Z– at 25°C. If the reduction potentialof Z > Y > X, then, (1999 - 2 Marks)
For the electrochemical cell, M|M+ || X- | X,E°M+/M =0.44V and E°(X/X–) = 0.33V.From this data one can deduce that (2000S)
Saturated solution of KNO3 is used to make ‘salt-bridge’because (2001S)
The correct order of equivalent conductance at infinitedilution of LiCl, NaCl and KCl is (2001S)
Standard electrode potential data are useful for understanding the suitability of an oxidant in a redox titration. Some half cell reactions and their standard potentials are given below : (2002S)
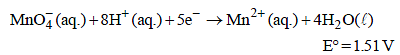
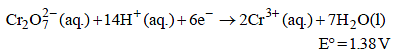
Fe3+ (aq.) + e- → Fe2+ (aq.) E° = 0.77 V
Cl2(g) + 2e- → 2Cl- (aq.) E° = 1.40 V
Identify the only incorrect statement regarding the quantitative estimation of aqueous Fe(NO3)2
In the electrolytic cell, flow of electrons is from (2003S)
The emf of the cell Zn | Zn2+ (0.01 M) | | Fe2+ (0.001 M) | Fe at 298 K is 0.2905 then the value of equilibrium constant for
the cell reaction is (2004S)
The rusting of iron takes place as follows (2005S)
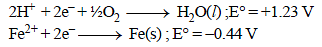
Calculate ΔG° for the net process
Electrolysis of dilute aqueous NaCl solution was carriedout by passing 10 milli ampere current. The time required toliberate 0.01 mol of H2 gas at the cathode is (1 Faraday =96500 C mol–1) (2008S)
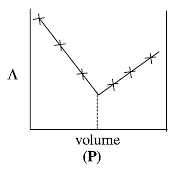
AgNO3(aq.) was added to an aqueous KCl solution gradually and the conductivity of the solution was measured.
The plot of conductance 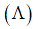 versus the volume of AgNO3 is (2011)
versus the volume of AgNO3 is (2011)
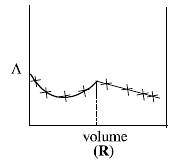
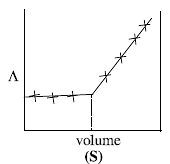
Consider the following cell reaction: (2011)
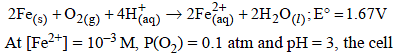
potential at 25ºC is
For the following electrochemical cell at 298 K, Pt(s)|H2(g, 1 bar)| H+ (aq, 1 M) || M4+ (aq), M2+ (aq)|Pt(s)
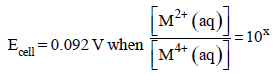
Given : 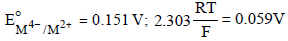
The value of x is (JEE Adv. 2016)
The standard reduction potential values of three metalliccations, X, Y and Z are 0.52,– 3.03 and – 1.18 V respectively.The order of reducing power of the corresponding metals is (1998 - 2 Marks)
For the reduction of  ion in an aqueous solution, E° is + 0.96V. Values of E° for some metal ions are given below
ion in an aqueous solution, E° is + 0.96V. Values of E° for some metal ions are given below
V2+ (aq) + 2e– → V E° = – 1.19 V
Fe3+ (aq) + 3e– → Fe E° = – 0.04 V
Au3+ (aq) + 3e– → Au E° = + 1.40 V
Hg2+ (aq) + 2e– →Hg E° = + 0.86 V
The pair(s) of metals that is(are) oxidized by  inaqueous solution is(are) (2009)
inaqueous solution is(are) (2009)
In a galvanic cell, the salt bridge (JEE Adv. 2014)
|
347 docs|185 tests
|
|
347 docs|185 tests
|


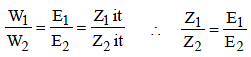
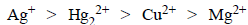
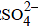
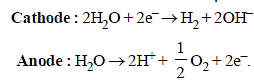
 . Hence, the electrode reactions are
. Hence, the electrode reactions are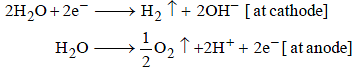
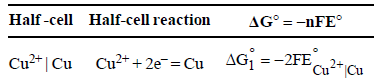
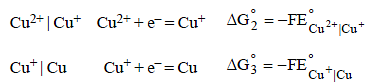
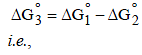
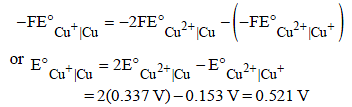
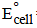 = 0.44 – 0.33 = 0.11V is positive, hence reaction is spontaneous
= 0.44 – 0.33 = 0.11V is positive, hence reaction is spontaneous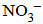 ions are nearly same
ions are nearly same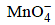 will oxidise Cl– ion according to the following equation
will oxidise Cl– ion according to the following equation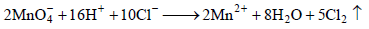
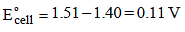
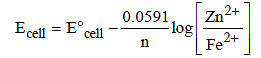
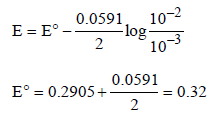
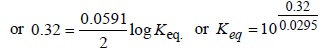
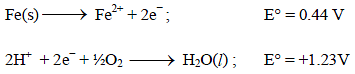
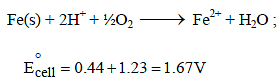
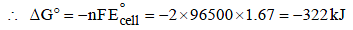
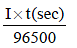
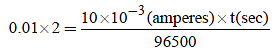
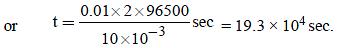
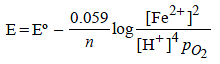
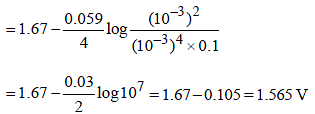
 2H+ (aq) + 2e–
2H+ (aq) + 2e–