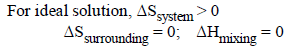Test: MCQs (One or More Correct Option): Solutions | JEE Advanced - JEE MCQ
17 Questions MCQ Test 35 Years Chapter wise Previous Year Solved Papers for JEE - Test: MCQs (One or More Correct Option): Solutions | JEE Advanced
An azeotropic solution of two liquids has boiling point lowerthan either of them when it (1981 - 1 Mark)
For a dilute solution, Raoult’s law states that :(1985 - 1 Mark)
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
When mercuric iodide is added to the aqueous solution ofpotassium iodide then (1987 - 1 Mark)
Which of the following 0.1 M aqueous solutions will havethe lowest freezing point? (1989 - 1 Mark)
The freezing point of equimolal aqueous solutions will behighest for : (1990 - 1 Mark)
0.2 molal acid HX is 20% ionised in solution. Kf = 1.86 Kmolality–1. The freezing point of the solution is : (1995S)
The molecular weight of benzoic acid in benzene asdetermined by depression in freezing point methodcorresponds to : (1996 - 1 Mark)
During depression of freezing point in a solution thefollowing are in equililbrium (2003S)
The elevation in boiling point of a solution of 13.44 g ofCuCl2 in 1 kg of water using the following information will be(Molecular weight of CuCl2 = 134.4 and Kb = 0.52 K molal-1) (2005S)
When 20 g of naphthoic acid (C11H8O2) is dissolved in 50g of benzene (Kf = 1.72 K kg mol–1), a freezing pointdepression of 2K is observed. The Van't Hoff factor (i) is (2007)
The Henry’s law constant for the solubility of N2 gas inwater at 298 K is 1.0 × 105 atm. The mole fraction of N2 in airis 0.8. The number of moles of N2 from air dissolved in10 moles of water at 298 K and 5 atm pressure is (2009)
Dissolving 120 g of urea (mol. wt. 60) in 1000 g of water gavea solution of density 1.15 g/mL. The molarity of the solutionis (2011)
The freezing point (in °C) of a solution containing 0.1 gof K3[Fe(CN)6] (Mol. wt. 329) in 100 g of water (Kf = 1.86 Kkg mol–1) is (2011)
For a dilute solution containing 2.5 g of a non-volatile nonelectrolytesolute in 100 g of water, the elevationin boiling point at 1 atm pressure is 2°C. Assumingconcentration of solute is much lower than the concentrationof solvent, the vapour pressure (mm of Hg) of the solutionis (take Kb = 0.76 K kg mol–1) (2012)
In the depression of freezing point experiment, it is foundthat the (1999 - 3 Marks)
Benzene and naphthalene form an ideal solution at roomtemperature. For this process, the true statement(s) is(are) (JEE Adv. 2013)
Mixture(s) showing positive deviation from Raoult’s law at35 °C is (are) (JEE Adv. 2016)
|
347 docs|185 tests
|
|
347 docs|185 tests
|


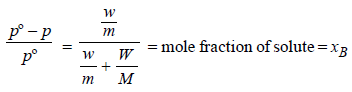
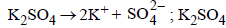 gives highest number of particles (2 + 1 = 3).
gives highest number of particles (2 + 1 = 3).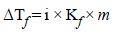
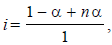 where n = no. of ions
where n = no. of ions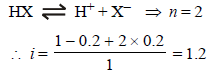
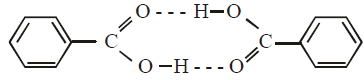
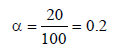

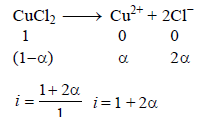
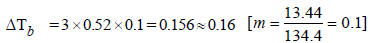
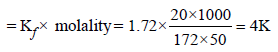
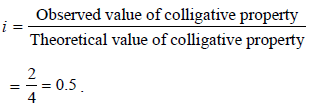
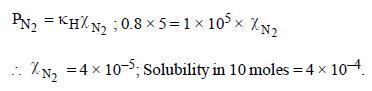
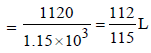
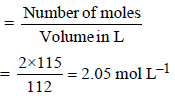
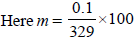
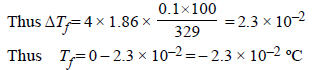
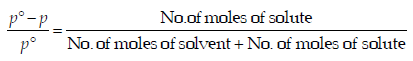
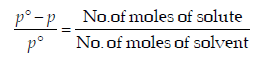
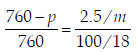 .... (i)
.... (i)