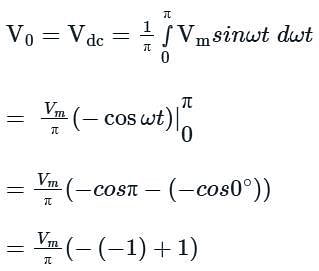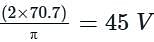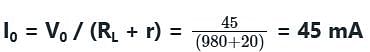Test: Power Electronics - 1 - Electrical Engineering (EE) MCQ
25 Questions MCQ Test Power Electronics - Test: Power Electronics - 1
In the below figure the average load current is 15 A. The rms value of transformer secondary current is

| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
In a 3 phase fully controlled converter the firing frequency is
The amount of dielectric heating is inversely proportional to frequency.
The phenomenon of overlap in converter operation due to
A thyristor has a maximum allowable junction temperature of 120ºC and the ambient temperature is 40ºC. If thermal resistance is 1.6º C/W, the maximum allowable internal power dissipation is
For a 12 pulse operation, the two 6 pulse units are fed by
In a single phase full wave converter (M - 2 connection) feeding a highly inductive load, the firing angle for each thyristor is a in the respective half cycle. The period of conduction of each thyristor is
An SCR is triggered at 40ºin the positive half cycle only. The average anode current is 50 A. If the firing angle is changed to 80º, the average anode current is likely to be
The characteristics of a non-linear resistance is i = kv4. If i becomes 100 times, v becomes
In a step down chopper using pulse width modulation, Ton = 3 x 10-3 and Toff = 1 x 10-3 s. The chopping frequency is
Thyristors are suitable for dc circuit breakers but not for ac circuit breakers.
Assertion (A): Inverters and choppers use fast switching thyristors
Reason (R): Fast switching SCR has low turn off time.
The value of capacitor C for dynamic equalising circuit of series connected thyristors is determined by
Assertion (A): If the duty cycle of chopper is low the current would not become discontinuous
Reason (R): If the time constant L/R of the load in chopper is low the current may become discontinuous.
An electric heater is controlled by thyristors through on-off control. If a = 0.4, the heating is
A two winding transformer is feeding a single phase half wave rectifier circuit. The load is purely resistive. The rms value of transformer secondary current is Is and rms value of load current in Irms. Then
In single phase half wave regulator, the average current over one full cycle
The dynamic equalising circuit consists of a series combination of capacitor C and resistor RC across each thyristor. This resistance RC (along with parallel connected diode)
A single phase semiconverter is feeding a highly inductive load and has freewheeling diode across the load. The waveshapes of output voltage and output current
A full-wave rectifier uses 2 diodes. The internal resistance of each diode is 20 Ω. The transformer RMS secondary voltage from centre tap to each end of the secondary is 50 V and the load resistance is 980 Ω. Mean load current will be
|
5 videos|50 docs|46 tests
|
|
5 videos|50 docs|46 tests
|


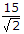 = 15/1.414 = 10.608 A.
= 15/1.414 = 10.608 A.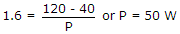 .
.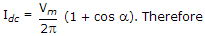
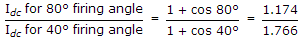 .
.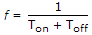 .
.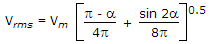 .
.