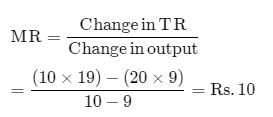Test: Price Determination In Different Markets - 1 - CA Foundation MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test Business Economics for CA Foundation - Test: Price Determination In Different Markets - 1
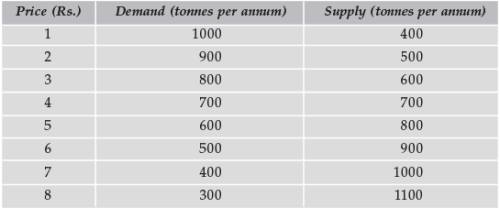
In the table below what will be equilibrium market price?
Assume that when price is Rs. 20, quantity demanded is 9 units, and when price is Rs. 19, quantity demanded is 10 units. Based on this information, what is the marginal revenue resulting from an increase in output from 9 units to 10 units.
Assume that when price is Rs.20, quantity demanded is 15 units, and when price is Rs.18, quantity demanded is 16 units. Based on this information, what is the marginal revenue resulting from an increase in output from 15 units to 16 units?
Suppose a firm is producing a level of output such that MR > MC. What should be firm do to maximize its profits?
Suppose that a sole proprietorship is earning total revenues of Rs. 1,00,000 and is incurring explicit costs of Rs. 75,000. If the owner could work for another company for Rs. 30,000 a year, we would conclude that :
Which of the following is not an essential condition of pure competition?
What is the shape of the demand curve faced by a firm under perfect competition?
Which is the first order condition for the profit of a firm to be maximum?
Which of the following is not a characteristic of a “price taker”?
Which of the following statements is false?
With a given supply curve, a decrease in demand causes
It is assumed in economic theory that
Assume that consumers’ incomes and the number of sellers in the market for good A both decrease. Based upon this information we can conclude, with certainty, that equilibrium :
Suppose that the supply of cameras increases due to an increase in foreign imports. Which of the following will most likely occur?
Assume that in the market for good Z there is a simultaneous increase in demand and the quantity supplied. The result will be :
Suppose the technology for producing personal computers improves and, at the same time, individuals discover new uses for personal computers so that there is greater utilisation of personal computers. Which of the following will happen to equilibrium price and equilibrium quantity?
Which of the following is not a condition of perfect competition?
Which of the following is not a characteristic of a perfectly competitive market?
Which of the following is not a characteristic of monopolistic competition?
All of the following are characteristics of a monopoly except :
Oligopolistic industries are characterized by :
Price-taking firms, i.e., firms that operate in a perfectly competitive market, are said to be “small” relative to the market. Which of the following best describes this smallness?
Monopolistic competition differs from perfect competition primarily because
The long-run equilibrium outcomes in monopolistic competition and perfect competition are similar, because in both market structures
A monopolist is able to maximise his profits when :
In which form of the market structure is the degree of control over the price of its product by a firm very large?
Which is the other name that is given to the average revenue curve?
Under which of the following forms of market structure does a firm have no control over the price of its product?
|
86 videos|255 docs|58 tests
|