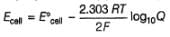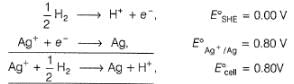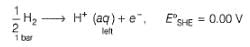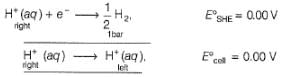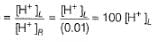Test: Reference Half Cells & Nernst Equations - JEE MCQ
29 Questions MCQ Test Chemistry for JEE Main & Advanced - Test: Reference Half Cells & Nernst Equations
Only One Option Correct Type
This section contains 18 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE is correct.
Q.
Which cell will measure the standard electrode potential of zinc electrode?
For the following cell with hydrogen electrodes at two different pressure p1 and p2 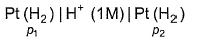
emf is given by
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
A solution of Fe2+ is titrated potentiometrically using Ce4+ solution.
Fe2+ → Fe3+ + e- , E0 = -0.77 V
emf of the Pt | Fe2+ , Fe3+ pair at 50% and 90% titration of Fe2+ are
Two half-cells are given
Ag | AgCl | KCl (0.2 M), Ag | AgBr | KBr (0.001 M),
Ksp(AgCl) = 2.8 x 10-10, Ksp (AgBr) = 3.3 x 10 -13
For a spontaneous cell reaction, cell set up is
In the following cell at 298 K,two weak acids (HA) and (HB) with pKa (HA) = 3 and pKa (HB) = 5 of equal molarity have been used as shown.
Thus, emf of the cell is
A concentration cell reversible to anion (Cl-) is set up
cell reaction is spontaneous ,if
Which has the maximum potential at 298 K (numerical value) for the half-cell reaction?
2H+ + 2e- → H2 (1 bar)
For the cell, and for the cell Pt(H2) | H+ (1M)| Ag,
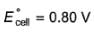
Thus Ecell for the
Ag|Ag+ (0.1M) || Zn2+ (0.1M) | Zn is ....................and cell reaction is...............
Consider the following cell reaction,
2Fe(s) + O2(g) + 4H+ (aq) →2Fe2+ (aq) + 2H2O(l) , E°= 1.67 V
At [Fe2+] = 1 x 10-3 M. and pH = 3,the cell potential at 298 K is
For the following cell with gas electrodes at p1 and p2 as shown:
Cell reaction is spontaneous , if
For the half-cell, Cl-|Hg2Cl2, Hg(l), E = 0.280V at 298K electrode potential has maximum value when KCl used is
Given at 298 K standard oxidation potential of quinhydrone electrode = -0.699 V Standard oxidation potential of calomel electrode = -0.268 V
Thus, emf of the cell at 298 K is
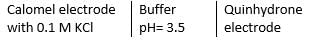
E°red (standard reduction electrode potentials) of different half-cell are given
In which cell , is ΔG° most negative?
Given the following half-cell reactions and corresponding reduction potentials:
Which combination of two half-cell would result in a cell with largest (E°cell > 0)?
Following half-cell, Pt (H2)|H2O behaves as SHE at a pressure of
Electrode potential of the following half-cell is dependent on
Hg, HgO |OH-(aq)
One or More than One Options Correct Type
This section contains 4 multiple type questions. Each question has 4 choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONE or MORE THAN ONE are correct.
Q.
Select the correct statement(s).
In the following electrochemical cell.
Zn cell Zn2+ ||H+ | Pt (H2)
Ecell = E°cell if
For Daniell cell E°cell = 1.10 V. If state of equilibrium is attained, then
Select the half-cell for the half-cell reaction(s) to be spontaneous
Comprehension Type
This section contains a passage describing theory, experiments, data, etc. Two questions related to the paragraph have been given. Each question has only one correct answer out of the given 4 options (a), (b), (c) and (d)
Passage I
1.05 g of lead ore containing impurity of Ag was dissolved in HNO3 and the volume was made 350 mL. A silver electrode was dipped in the solution and Ecell of Pt(H2) | H+ (1M)|| Ag+| Ag was 0.500 V at 298 K. E°Ag+/Ag = 0.80 V
Q.
Pure [Ag+] in the ore is
Passage I
1.05 g of lead ore containing impurity of Ag was dissolved in HNO3 and the volume was made 350 mL. A silver electrode was dipped in the solution and Ecell of Pt(H2) | H+ (1M)|| Ag+| Ag was 0.500 V at 298 K. E°Ag+/Ag = 0.80 V
Q.
Percentage of silver in the sample is
Passage II
For the following,
Q.
pH of the solution in the half-cell containing 0.02 HA is(HA is a weak monobasic acid)
Passage II
For the following,
Q.
pKa of the weak monobasic acid is
One Integer Value Correct Type
This section contains 3 questions, when worked out will result in an integer value from 0 to 9 (both inclusive)
Q.
For the following cell with metal X electrodes,
Ecell = -0.028 V at 298 K, if there is no liquid juncton potential,valency of X is.......
Osmatic pressure of a 0.001 M weak monobasic acid (HA) at 300 K is 2.5 x 10-2 atm.Thus,emf of the follwing in decivolt is| 0.001 M HA........
pH of the solution in the anode compartment of the follwoing cell at 298 K is x
when Ecell - E°cell = 0.0591 V , Pt (H2) | pH = x|| Ni2+ (1M)| Ni.
Derive the value of x.
|
352 videos|596 docs|309 tests
|
|
352 videos|596 docs|309 tests
|


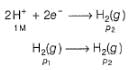
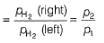
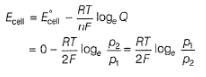
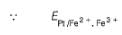 =
=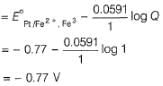
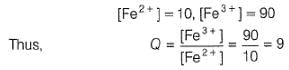
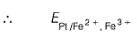
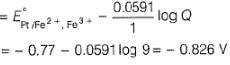

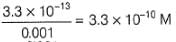
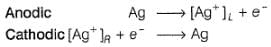
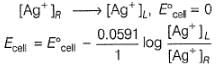
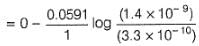
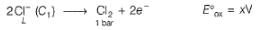
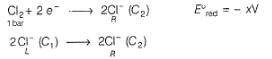
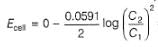
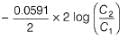
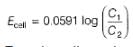

 Cu(s) + Zn2+ (1M),
Cu(s) + Zn2+ (1M),