Test: Sensory Perception - 1 - MCAT MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test Psychology and Sociology for MCAT - Test: Sensory Perception - 1
Clinicians will see large amounts of data (labs results, patient symptoms, etc) over the course of their practice, and their brains will subconsciously group that data along certain established principles. Awareness of this underlying mechanism will help clinicians identify potential bias and provide better care. Which of the following best explains the Gestalt principles of grouping?
Which of the following best exemplifies the Gestalt principles of grouping?
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Meningitis and the flu share many early symptoms. Which of the following could explain why a doctor could misdiagnose meningitis as the flu during flu season?
Repeated administration of some drugs will lead to a decrease in their effectiveness, an occurrence known as drug tolerance. When this occurs, doctors may need to increase the dosage in order to continue therapy. What is true of this increase?
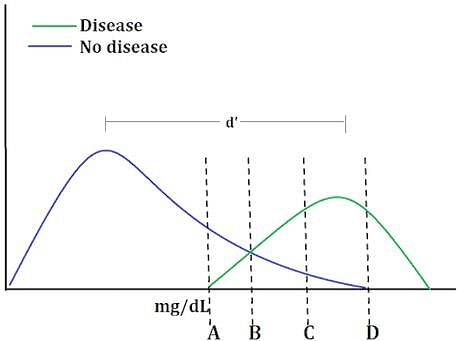
A diagnostic test is developed for a potentially fatal disease. In order to effectively treat the disease, those diagnosed with it must immediately be placed on a costly and poorly tolerated medication. Which threshold should be used for this test?
Diplopia is the scientific term for double vision, a condition in which the patient perceives two images of the same entity, usually displaced horizontally or vertically. Which of the following perceptual cues is most affected by diplopia?
Which of the following is an example of sensory desensitization?
A patient is experiencing chest pain and sees several specialists. The cardiologist is worried about a heart attack and orders an echocardiogram, while the pulmonologist orders a lung capacity test. What perceptual organization principles are these doctors exhibiting?
Which of the following would trigger high frequency firing from a non-adapting mechanoreceptor?
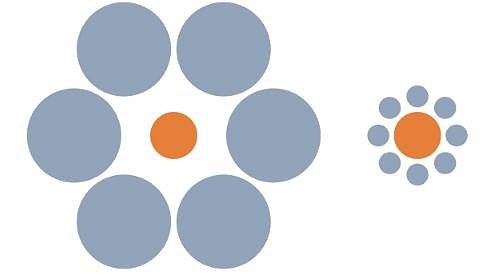
This image best demonstrates what idea about perception?
|
339 videos|14 docs|42 tests
|
|
339 videos|14 docs|42 tests
|

















