Test: Tariff and Non- Tariff Barriers - UGC NET MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test UGC NET Commerce Preparation Course - Test: Tariff and Non- Tariff Barriers
What do tariffs primarily aim to achieve in international trade?
Assertion (A): Trade barriers limit the benefits of trade based on comparative advantage, leading to reduced specialization and lower productivity and economic growth.
Reason (R): Consumers face higher prices and fewer choices due to limited competition from imports, which especially impacts lower-income individuals who spend a significant portion of their income on protected goods.
Assertion (A): Exporters in countries with trade barriers may also face retaliation from other nations, affecting their competitiveness.
Reason (R): Overall, if the most efficient producers are restricted from supplying goods and services globally, global living standards can decline.
What type of non-tariff barrier can lead to higher costs for consumers who lose access to banned products?
What do non-tariff barriers entail of international trade?
What is the primary purpose of imposing tariffs on imported goods by governments?
Assertion (A): Imposition of tariffs on imported goods can lead to increased prices for consumers within the country.
Reason (R): Tariffs are designed to protect domestic industries by making foreign goods relatively more expensive.
Assertion (A): Negotiating trade agreements to lower trade barriers is a more sustainable approach compared to imposing tariffs.
Reason (R): Trade agreements aim to enhance the benefits of international trade through open trade policies.
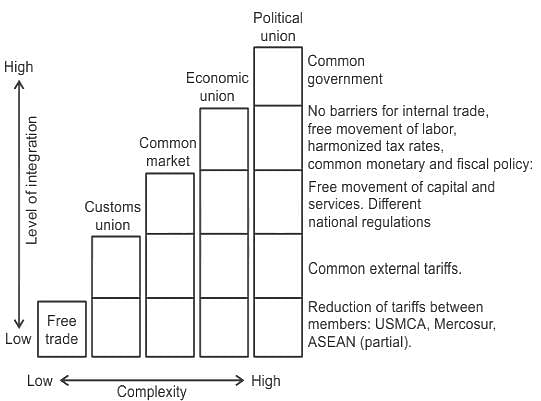
In theory, several levels of economic integration are possible. Arrange the following from the least to the most integrated:
A. Common Market
B. Free Trade Area
C. Economic Union
D. Political Union
E. Customs Union
Choose the correct answer from the options given below
Consider the following
1. Tariff binding
2. Tariffication
3. Tariff cuts
4. Reduction in subsidies and domestic support
Which of the above are aspects of the Uruguay Round Agreement on agriculture?
|
235 docs|166 tests
|