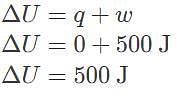Test: Thermodynamics - MCAT MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test General Chemistry for MCAT - Test: Thermodynamics
When heating a solution, a scientist detects a temperature increase in the solution during a period of time. Which of the following statements accurately characterizes the solution during this period?
Equal amounts of heat are absorbed by 100 g, samples of various solid metals with differing specific heat values. Which of the following statements is true regarding metals and their specific heat values?
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
In a system undergoing adiabatic compression, what are the values of internal energy and heat if work done on the system is 500 J?
Additional gas is pumped inside a rigid container that stores compressed gas. Which of the following is a true statement about this system?
Which of the following scenarios violates the first law of thermodynamics, “the conservation of energy?"
A hot object is placed next to a cold object so that they are touching. Which of the following statements is true?
I. Heat will transfer from the hot object to the cold object because the hot object has a higher temperature.
II. The two objects are in thermal equilibrium
III. Internal energy will transfer from the hot object to the cold object because the hot object has greater internal energy.
Atmospheric gases absorb more energy than they emit. If we consider a gas to be a closed system, which of the following is true?
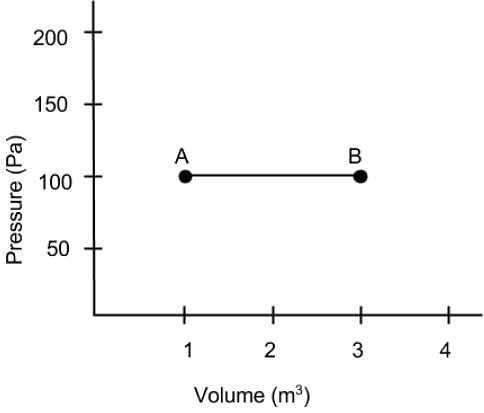
What is the net work done on the gas as it goes from point A to B on the Pressure vs Volume diagram?
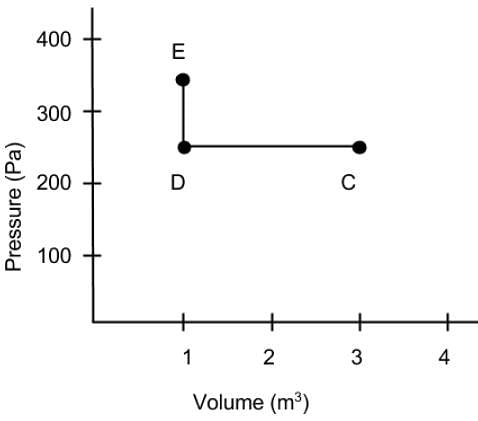
What is the net work done on the gas as it goes from point C to D and then to E on the Pressure vs Volume diagram?
|
164 videos|11 docs|16 tests
|
|
164 videos|11 docs|16 tests
|