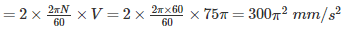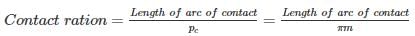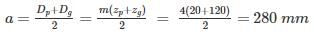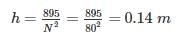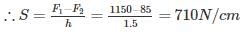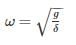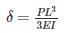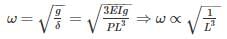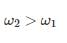Theory of Machines - 1 - Mechanical Engineering MCQ
20 Questions MCQ Test SSC JE Mechanical Mock Test Series 2025 - Theory of Machines - 1
Coriolis acceleration component of a slider moving at 75π mm/s on a link rotating at 60 rpm will be
Critical or whirling speed is the speed at which the shaft tends to vibrate violently in ________.
Which of the following statement is TRUE about the contact ratio?
A pair of spur gears consists of a 20 teeth pinion meshing with a 120 teeth gear. The module is 4 mm. Calculate the centre distance (in mm).
When one of the links of a kinematic chain is fixed, then the chain is called _______.
A cam in which the follower reciprocates or oscillates in a plane parallel to the axis of the cam is known as
What will be the vertical height (m) of a watt governor, if the speed of rotation is 80 rpm?
For a Hartnell governor, the loads on the spring at the lowest and highest equilibrium speeds are 1150 N and 85 N, respectively. If the lift of the governor is 1.5 cm, then spring stiffness would be
What is the radial distance of a tooth from the pitch circle to the top of the tooth known as?
Elliptical gear train used in differential gear of automobile helps in:
The mass of flywheel of a steam engine is 3250 kg with the radius of gyration of 1 m. The starting torque of the engine is 4500 N - m. What is the angular acceleration (rad/s2) of the flywheel?
________ gear train is used to connect minute hand to hour hand, in a clock mechanism.
A cantilever beam of cross section area ‘A’, moment of Inertia I and length ‘L’ is having natural frequency ω1. If the beam is accidentally broken into two halves, the natural frequency of the remaining cantilever beam ω2will be such that
In case of cam, the maximum value of the pressure angle is kept as-
________ mechanism produces mathematically an exact straight line motion.
|
3 videos|1 docs|55 tests
|