UGC NET Paper 2 Geography Mock Test - 6 - UGC NET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test UGC NET Mock Test Series 2024 - UGC NET Paper 2 Geography Mock Test - 6
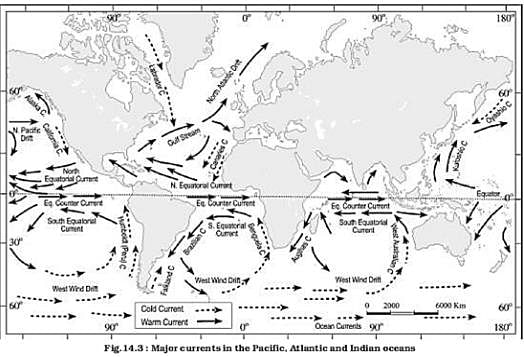
Which one of the following is NOT a current of the Atlantic Ocean?
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Arrange the following continents in descending order of size:
South America, Africa, Antarctica, Europe, North America
Choose the correct option.
Any industry located in a rural area which produces any goods, renders any service with or without the use of power is known as ________
Which among the following state of India is best known for Saffron Cultivation?
Match the following ocean currents with which they are named :
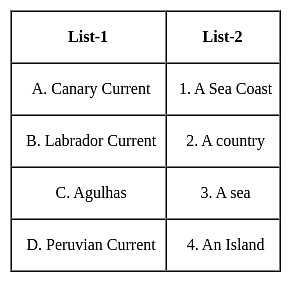
Select the correct code :
Choose the correct statement from below:
Statement I:The concentration of the economy in the core city begins as a result of innovation. capital accumulation and industrial growth.
Statement II: The pre-industrial (agricultural) society, with localized economies and a small-scale settlement structure.
What is the significance of understanding landscape evolution according to the passage?
Given below are two statements, one is labelled as Assertion (A) and the other as Reason (R).
Assertion (A): Rainfall occurs in the winter season in a Mediterranean climate.
Reason (R): In summer these regions remain under the influence of dry terrestrial winds.
Select the correct answer from the code given below :
Match List - I with List - II and select the correct answer from the code given below the lists.
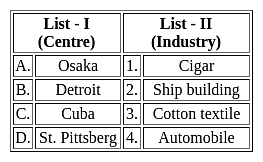
Consider the following statements and choose the correct answer from the options given below.
Statement I: Integration of the national economy with the world economy encourages the free flow of goods and services.
Statement II: Liberalisation aims to unlock the economic potential of the country by encouraging the private sector and multinational corporations to invest and expand
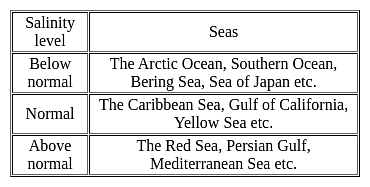
Which among the following factors influence the salinity of ocean water?
1. Precipitation
2. Evaporation
3. Ocean Currents
4. Temperature
Select the correct code from the options given below:Which of the following is/are the ideal conditions for temperature inversion to occur?
A. Cloudy skies
B. Calm and stable air
C. Long summer days
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
(a) With shift in technology, there has been a shift in the structure of industries.
(b) The globalization has caused a new international division of labour.
(c) The high tech industrial regions have very little to no place for blue collar jobs.
(d) R&D is the most important feature of traditional large scale industrial regions.
Choose the correct option from below:
(a) The laterite soils are used as building material.
(b) The forest soils are rich in humus.
(c) The forest soils are deficient in potash, phosphorus, and lime.
(d) Kari is a type of soil found in Kerala.
Given below are two statements. One is labelled as Assertion (A) and the other is labelled as Reason (R).
Assertion (A): India is the second largest irrigated country in the world.
Reason (R): The whole country of India is fully irrigated.
Select the correct answer from options given below:
(a) High drainage density means that the flood risk is minimal.
(b) If the drainage density is high, the bifurcation ratio too is high.
(c) Drainage density is dependent upon climate and physical characteristics of drainage basin.
(d) Drainage density is total length of river multiplied by the total area of the drainage basin.
Code:
Which one of the following is the junction point of the Eastern Ghats and Western Ghats?
The demographic transition model was developed primarily to explain the:
|
16 docs|120 tests
|