UPPSC Prelims (GS I) Mock Test - 6 - UPPSC (UP) MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test UPPSC Mock Test Series 2025 - UPPSC Prelims (GS I) Mock Test - 6
With reference to palaeolithic age in Uttar Pradesh, which of the following material was used to make tools?
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Consider the following statements regarding the effect of the devaluation of the Indian rupee
- make exports less competitive and cheaper for foreigners
- discourages exports
- reduces trade deficits
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
Who is not a member of the Committee constituted for recommendations of appointment of Chairperson and other Members of National Human Rights Commission?
To review the annual statement of accounts and annual progress report of the panchayat is the main function of:
If the temperature of a place increases suddenly the relative humidity:
Who took the leadership of the revolt of 1857 from Mathura?
Uttar Pradesh government will establish its first ‘Turtle Conservation Reserve’ in which river?
Consider the following statements with respect to Zero Budget Natural Farming (ZBNF):
- It is a farming practice that believes in the natural growth of crops with the help of fertilizers and pesticides.
- It is water-efficient but requires more tilling.
- Subash Palekar is considered the father of ZBNF.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
Which of the following revolutionary groups was involved in Kakori Conspiracy Case?
Which international organization has agreed to fund Odisha to increase social protection?
Which British India Act laid down a provision that there could be open competition for ICS?
Golden rice is genetically modified to produce ß carotene to solve the problem of:
Which of the following are the fiscal policy measures taken by the government to control inflation?
- Reduction in public expenditure and public borrowing.
- Increasing taxes on private businesses.
- Increasing interest rates in the economy.
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
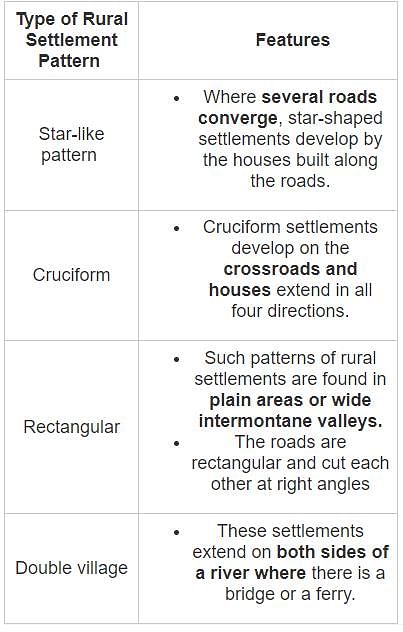
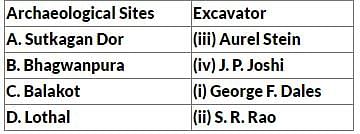
Match List I with List II
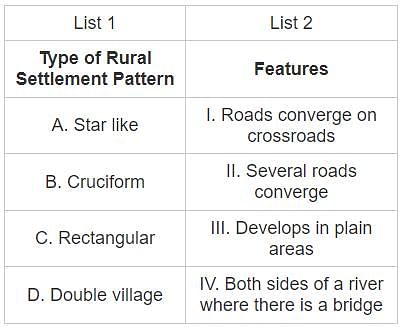
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
Which one of the following glasses is used in bulletproof screens?
Which of the following river rises in the Indian Himalayan?
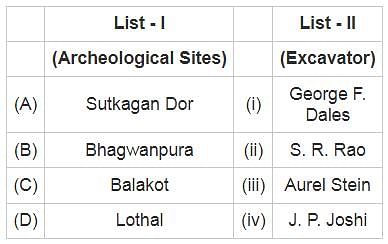
Match List - I with List - II and select the correct answer using code given below:
Read the following sentences about transpiration in plants :
(A) Transpiration creates suction pull which causes water to reach great heights in tall trees.
(B) Transpiration helps in maintaining optimum body temperature in plants.
(C) Transpiration helps in absorption of water by the roots.
Which of the following statements is/are correct ?
Consider the following facts of the First Lok Sabha elections of 1952 and choose the correct answer :
(A) The Congress obtained 45 percent of the total votes but it managed to win 74 percent of the seats.
(B) The Socialist Party secured more than 10 percent of the votes all over the country but it could not even win 3 percent of the seats.
Which of the following may be called as fiscal deficit?
According to Census 2011 of India, what is the population density per square kilometer of Uttar Pradesh?
Which states are identified as having safe groundwater zones according to the recent assessments in Uttar Pradesh?
What initiative has the Uttar Pradesh government taken to connect agriculture startups with e-commerce platforms?
What is the maximum penalty established by the Uttar Pradesh Public Examination (Prevention of Unfair Means) Ordinance for those involved in question paper leaks?
|
2 docs|37 tests
|