UPPSC Prelims (GS I) Mock Test - 7 - UPPSC (UP) MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test UPPSC Mock Test Series 2025 - UPPSC Prelims (GS I) Mock Test - 7
In the context of biodiversity, 'The Evil Quartet' refers to the set of four:
A layer in the Earth's atmosphere called Ionosphere facilitates radio communication. Why?
- The presence of ozone cause the reflection of radio waves to Earth.
- Radio waves have a very long wavelength.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
A sandy and saline area is the natural habitat of an Indian animal species. The animal has no predators in that area but its existence is threatened due to the destruction of its habitat. Which one of the following could be that animal?
Which institution launched India's largest drone pilot training institute?
The rise in water level in oceans and seas due to the melted ice sheets and glaciers causes:
Cryopreservation of gametes of threatened species in viable and fertile condition can be referred to as:
Which one of the following is not a 'Sustainable Development Goal' (SDG) target to be achieved by 2030?
Which district of Uttar Pradesh receives the lowest rainfall?
Which among the following option is incorrect Location of India’s Biosphere Reserves?
Which of the following statements is correct about socialism mentioned in the Preamble of the Indian Constitution?
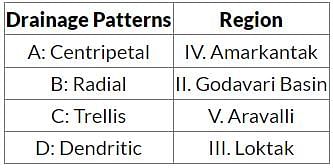
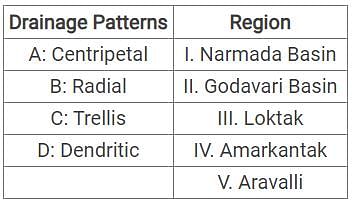
Geological structure, physiography and precipitation regimes influence evolution of drainage patterns. India with it’s diversity in the above mentioned attributes showcases a variety of drainage patterns across regions. Match the following drainage patterns found in the regions given below:
Which platform is being used for the digitization of the Urban Frame Survey (UFS) by the National Sample Survey Office (NSSO) and the National Remote Sensing Centre (NRSC)?
Which of the following is a characteristic of root system?
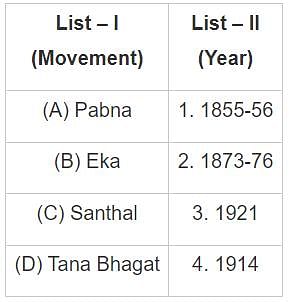
Match List-I with List-II and select the correct answer using the codes given below the lists:
Which one of the following is NOT correctly matched?

Which of the following Gupta rulers destroyed the Saka chieftain Rudrasena III and annexed his kingdom?
Which of the following is the correct description of Lex Loci Act, 1850?
Consider the following statements:
- Money Multiplier is the amount of Broad money that banks generate with each rupee of reserves or base money available with them.
- Broad money is the most liquid part of the money supply.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
Consider the following statements regarding Carbon Capture, Utilisation, and Storage (CCUS):
1. The utilization of captured carbon dioxide could lead to the development of more sustainable fuels and raw materials for various industries.
2. The storage of captured carbon dioxide may pose significant geological and safety risks, particularly due to the potential of leakage.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct ?
With reference to Anti-defection law in India, consider the following statements:
1. It provides that a member of a House belonging to a political party can be disqualified if he/she votes against the party whip.
2. It mandates that the presiding officer of the House has to decide a defection case within 3 months from the date on which such a petition is referred to him/her.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
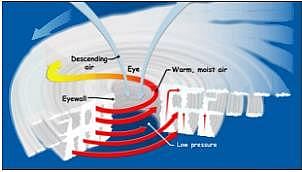
Tropical cyclone in general accompanied by
- Strong winds
- Exceptional rain
- Storm surge
Choose the correct answer from the codes given below.
In the early Vedic period, society was classified on the basis of ______.
Who among the following composed the poem, 'Veeron Ka Kaisa Ho Basant'?
In nature, which of the following is/are most likely to be found in brackish water?
1. Ebony
2. Kelp
3. Rhizophora
4. Cattail
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
The outer layers of the Sun, extending to thousands of km above the disc (photosphere) is termed as:
Read the given statements and select the correct option.
Assertion (A) : There is a close relationship between height of land and the character of vegetation.
Reason (R) : The growth of vegetation depends on slope and thickness of soil.
Who was the then ruler of that place where Somnath Temple was attacked?
With reference to Balance of Payments, which of the following constitutes/constitute the Current Account?
1. Balance of trade
2. Foreign assets
3. Balance of Invisibles
4. Special Drawing Rights
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
What significant change was observed in the black carbon levels in Varanasi according to recent studies?
|
2 docs|37 tests
|