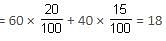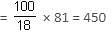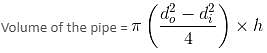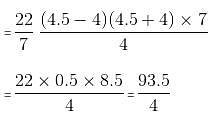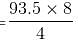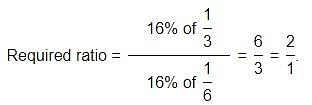Uttarakhand D.El.Ed Mock Test - 9 - UTET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test Uttarakhand D.El.Ed Mock Test Series 2024 - Uttarakhand D.El.Ed Mock Test - 9
What is the fixed honorarium proposed by the Uttarakhand government for residents who adopt destitute bovine animals?
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
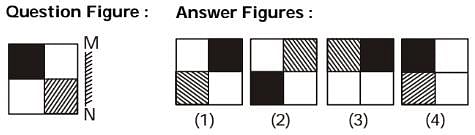
If a mirror is placed on the line MN, then which of the answer figures is the right image of the given figure?

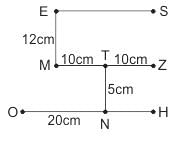
Direction: Study the following information and answer the given questions carefully.
Eight books S, E, M, T, N, O, H and Z are lying on the table such that E is 12cm north of M, which is 10cm to the west of T. Z is 10cm east of T. S is to the north of Z. H is to the south of Z. O is 20cm west of N, which is 5cm south of T. S is to the east of E. N is to the west of H.
Q. In which direction is O with respect to E?
Jenny walked 2.5 km towards North and turned towards West. After covering 2 km’s he turned to South and walked 1.5 km’s. He then turned to East and covered 2 km’s. How far is Jenny from original point?
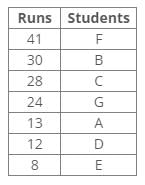
Directions: Read the given information carefully and answer the questions given below:
Seven players A, B, C, D, E, F and G did a different number of runs in the match – 8, 12, 13, 24, 28, 30 and 41 but not necessarily in the same order.
C scored 16 runs more than D. F scored more runs than B. Runs of B are more than 28. The score of A is not a multiple of 4. The difference between the score of B and G is 6.
Q. Who among the following scored 28 runs in the match?
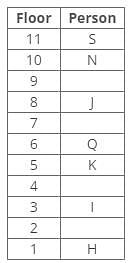
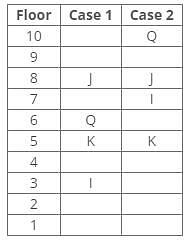
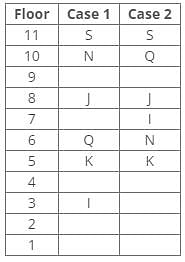
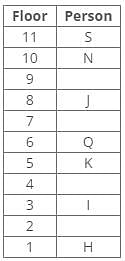
Direction: Study the following information and answer the given questions carefully.
A certain number of people live on different floors of a building, where the bottommost floor is numbered 1 and the floor above it is 2 and so on. There is no vacant floor in the building.
J lives three floors above K. One person lives between J and N. The number of persons living between Q and K is equal to the number of persons living between N and S. The number of persons living below H is equal to the number of persons living above S. Q lives three floors above I. The number of persons living between I and N is one less than the number of persons living below J. K lives on the 5th floor. S doesn’t live on a perfect square-numbered floor. One person lives between I and H. One person lives between Q and J.
Q. How many persons live below the person who lives three floors below J?
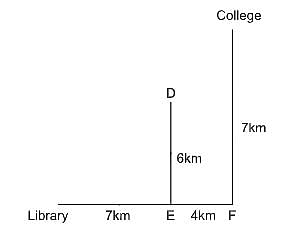
Directions: Each of the following consists of a question and two statements numbered I and II given below it. You have to decide whether the data provided in the statements are sufficient to answer the question:
In which direction is Library with respect to the college?
I. Point A is 3km North of Library. Point C is 3km North of point B. Point D is 3km East of point C.
II. College is 7km North of point F. Point D is 6km North of point E. Library is 7km west of point E. Point F is 4km East of point E.
Directions: In this type of questions, some particular words are assigned certain substituted names. Then a question is asked that is to be answered in the substituted code language.
If 'sand' is called 'air', 'air' is called 'plateau', 'plateau' ia called 'well', 'well' is called 'island' and 'island' is called 'sky', then from where will a woman draw water?
Amit Said, "this girl is the wife of the grandsom of my Mother." Who is Amit to the Girl?
In this following questions, various terms of the letter series are given with one term missing as shown by (?). Choose the missing term out of the given alternative.
Z, S, W, O, T, K, Q, G, ?, ?
Srini wrote his class 10th board examination this year. When the result came out he searched for his hall ticket to see his roll number but could not trace it. He could remember only the first three digits of the 6 digit number as 267. His father, however, remembered that the number was divisible by 11. His mother gave the information that the number was also divisible by 13. They tried to recollect the number when all of a sudden Srini told that the number was a multiple of 7. What was the unit digits of the number?
At Infosys, 60% of the employees are males and the rest are females. Further, 20% of the males and 15% of the females are getting bonus. If the number of employees getting bonus is 81, then find the total number of employees who are not getting bonus.
Set A contains 10 consecutive numbers starting from x and set B contains 8 consecutive even numbers starting from y. The ratio of the average of set A elements to that of set B elements is 9 : 14. What is the ratio of x to y?
What is the difference between the simple interest on a principal of Rs. 500 being calculated at 5% per annum for 3 years and 4% per annum for 4 years?
A piece of metal pipe is 7 cm long with inner diameter of the cross section as 4 cm. If the outer diameter is 4.5 cm and the metal weighs 8 gm/cu cm, the weight of the pipe is
Study the following pie-diagrams carefully and answer the questions given below it:
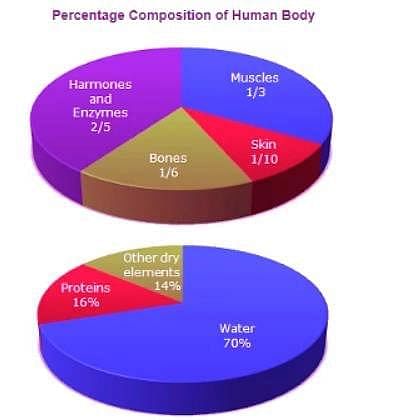
Q. What is the ratio of the distribution of proteins in the muscles to that of the distribution of proteins in the bones?
Which among the following types of intelligence would be most used when trying to navigate through traffic?
What different methods can teachers use to help children remember new things all the time?
I. Estimate
II. Classification
III. Retribution
Which of the following factors affecting the differences in an individual?
Which test is done to assess the learning outcome measured in terms of skill and knowledge developed from a learning event?
The most rapid and significant socialization occurs in: