Test: Digestion & Absorption - 1 (Old NCERT) - JAMB MCQ
25 Questions MCQ Test Biology for JAMB - Test: Digestion & Absorption - 1 (Old NCERT)
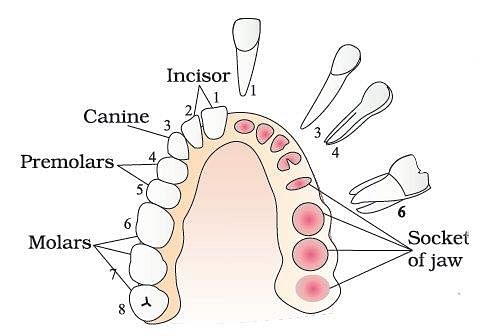
The teeth that occur in human beings are:
The enzyme which hydrolyze the starch is:
In the Enteric nervous system:
I. Neurons of the Myenteric plexus regulate glandular secretions in GI tract.
II. Neurons of Meissner’s plexus regulates peristaltic waves.
I. Neurons of the Myenteric plexus regulate glandular secretions in GI tract.
II. Neurons of Meissner’s plexus regulates peristaltic waves.
Complete the following reaction and mark the correct answer in the options for i, ii, iii
- Maltose ( in presence of Maltase) → Glucose + i
- Lactose ( in presence of Lactase) → Glucose + ii
- Sucrose (in presence of Sucrase) → Glucose + iii
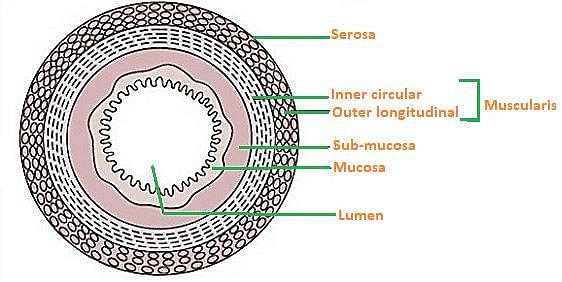
Which layer of alimentary canal is formed of loose connective tissues?
Every cell contains DNA and when we consume plant /animal material , the DNA which reaches our digestive tract is digested by:
A patient is generally advised to specially consume more meat, lentils, milk and eggs in diet only when he suffers from
What should be filled in to replace question mark in the following sequence:
? → Trypsinogen → Trypsin
The process by which small electrolytes are absorbed
Bacteria responsible for chronic gastritis is :
The major site of absorption in alimentary canal is
Regurgitation is more common in infants than in adults. The reason will be:
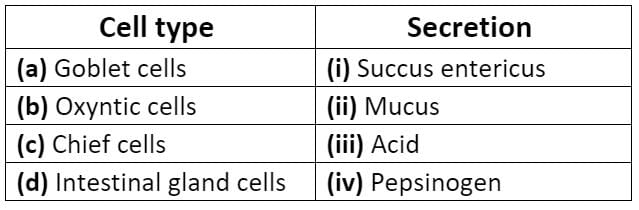
Match the cells and their secretions:
The secretions released into small intestine are
Read the following statements and select the correct option.
Statement 1 : The human small intestine is the longest portion in the alimentary canal.
Statement 2 : Absorption of digested food requires a very large surface area.
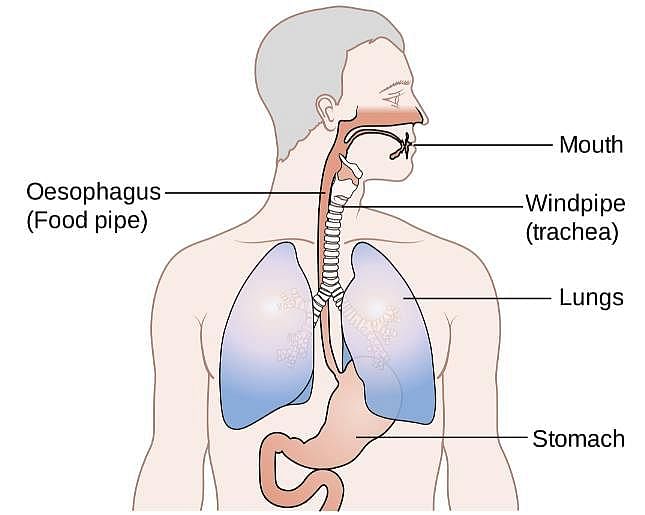
_____ from pharynx is conveyed into oesophagus by _____ .
The part which is common passage for both digestive and respiratory tracts :
Which layer of alimentary canal forms crypts in between the base of villi?
Absorption of fats takes place through:
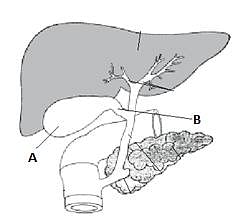
Read the following statements about CCK (cholecystokinin) :
i. This hormone stimulates gastrointestinal motility and pancreatic endocrine function.
ii. This hormone stimulates the release of bile from the gall bladder.
|
224 videos|175 docs|151 tests
|