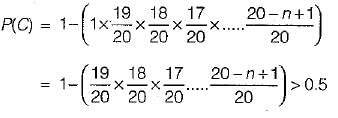Test: Graphs & Hashing- 1 - Computer Science Engineering (CSE) MCQ
15 Questions MCQ Test GATE Computer Science Engineering(CSE) 2025 Mock Test Series - Test: Graphs & Hashing- 1
Consider the following graph:
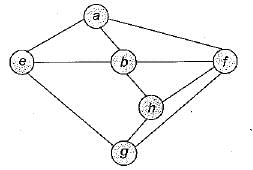
Among the following sequences
1. a b e g h f
2. a b f e h g
3. a b f h g e
4. a f g h b e
Which are depth first traversals of the above graph?

1. a b e g h f
2. a b f e h g
3. a b f h g e
4. a f g h b e
In a depth-first traversal of a graph G with n vertices, k edges are marked as tree edges. The number of connected components in G is
Let G be a directed graph whose vertex set is the set of numbers from 1 to 100. There is an edge from a vertex i to a vertex j iff either j = i + 1 or j = 3i. The minimum number of edges in a path in G from vertex 1 to vertex 100 is .
What is the largest integer m such that every simple connected graph with n vertices and n edges contains at least m different spanning trees?
The most efficient algorithm for finding the number of connected components in an undirected graph on n vertices and m edges has time complexity,
The Breadth First Search algorithm has been implemented using the queue data structure. One possible order of visiting the nodes of the following graph is
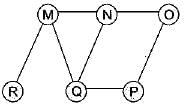
Let G of be a graph with n vertices and m edges. What is the tightest upper bound on the running time of Depth First Search on G, when G is represented as an adjacency matrix?
An advantage of chained hash table (external hashing) over the open addressing scheme is
Given the following input (4322,1334,1471,9679, 1989, 6171,6173, 4199) and the hash function x mod 10, which of the following statements are true?
1. 9679,1989,4199 hash to the same value
2. 1471,6171 hash to the same value
3. All elements hash to the same value
4. Each element hashes to a different value
A hash table contains 10 buckets and uses linear probing to resolve collisions. The key values are integers and the hash function used is key % 10. If the values 43,165,62,123,142 are inserted in the table, in what location would the key value 142 be inserted?
Which of the following statement(s) is TRUE?
I. A hash function takes a message of arbitrary length and generates a fixed length code.
II. A hash function takes a message of fixed length and generates a code of variable length.
III. A hash function may give the same hash value for distinct messages.
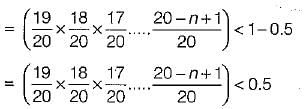
Consider a hash function that distributes keys uniformly. The hash table size is 20. After hashing of how many keys will the probability that any new key hashed collides with an existing one exceed 0.5.
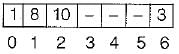
Consider the hash table of size seven, with starting index zero, and a hash function (3x + 4) mod 7. Assuming the has table is initially empty, which of the following is the contents of the table when the sequence 1, 3, 8, 10 is inserted into the table using dosed hashing?
Note that - denotes an empty location in the table
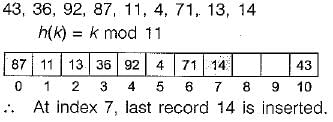
Consider a hash table of size 11 that uses open addressing with linear probing. Let h(k) = kmod 11 be the hash function used. A sequence of records with keys 43 36 92 87 11 4 71 13 14 is inserted into an initially empty hash table, the bins of which are indexed from zero to ten. What is the index of the bin into which the last record is inserted?
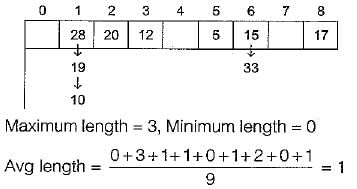
Consider a hash table with 9 slots. The hash function is h(k) = k mod 9. The collisions are resolved by chaining. The following 9 keys are inserted in the order:
5, 28, 19, 15, 20, 33, 12, 17, 10
The maximum, minimum, and average chain lengths in the hash table, respectively, are
|
55 docs|215 tests
|
|
55 docs|215 tests
|