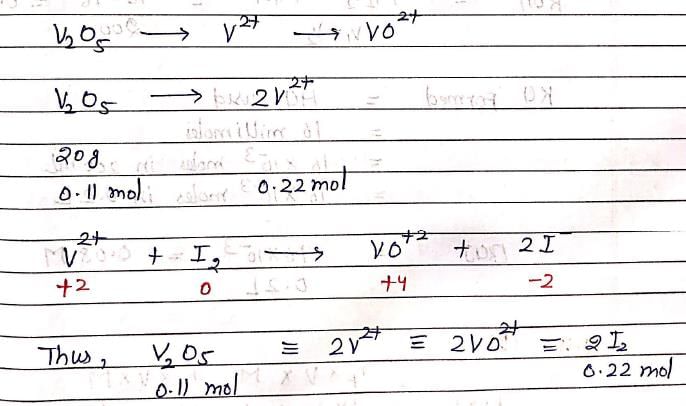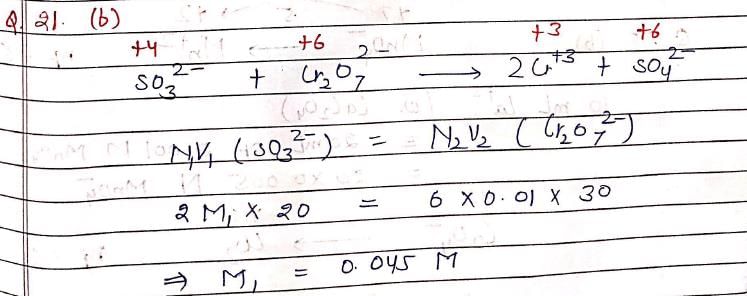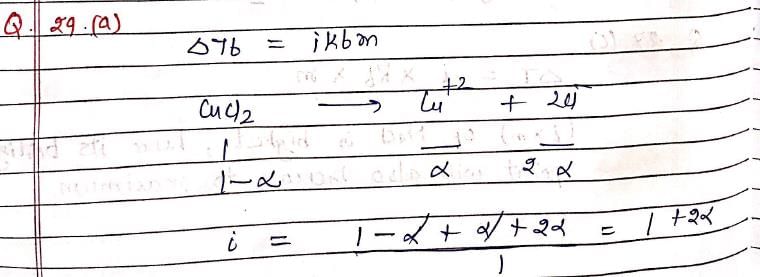Mole - Volumetry - Redox - Colligative Properties - Chemistry MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test Mock Test Series for IIT JAM Chemistry - Mole - Volumetry - Redox - Colligative Properties
Consider a titration of Potassium dichromate solution with acidified Mohr’s salt solution using diphenylamine as indicator. The number of moles of Mohr’s salt required per mole of dichromate is:
Number of moles of NH3 formed when 0.535g of NH4Cl is completely decomposed by NaOH, is:
NH4Cl + NaOH → NH3 + NaCl + H2O
NH4Cl + NaOH → NH3 + NaCl + H2O
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
2KClO3 →2KCl + 3O2. 5g of KClO3 gave 0.03 mole of O2. The percentage purity of KClO3 is:
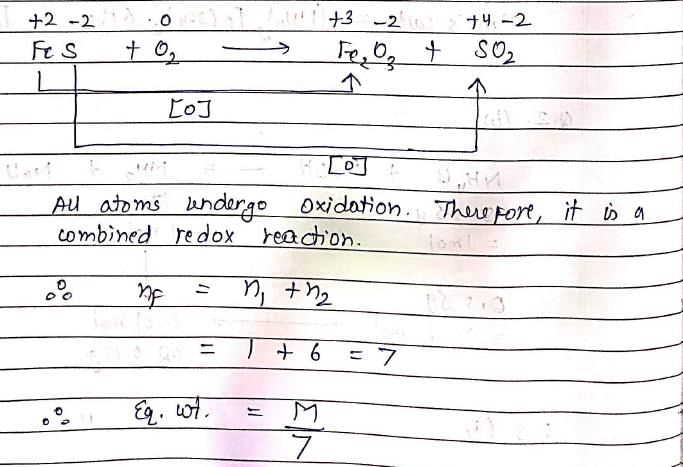
Calculate the equivalent Mass of FeS in the following reaction ?
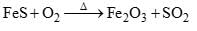
Which of the following acts as an oxidizing agent ?
Vapor pressure of CHCl3 and CH2Cl2 at 250C are 200 mmHg and 41.5 mmHg resp. Vapor pressure of solution obtained by mixing 25.5g of CHCl3 and 40g of CH2Cl2 at same temp will be? (M.Wt. of CH2Cl2 = 85u and M.Wt. of CHCl3 = 119.5u)
The relationship been Osmotic pressure at 273K when 10g Glucose (P1), 10g Urea (P2), 10g Sucrose (P3) are dissolved in 250 mL of water:
Average osmotic pressure of human blood is 7.8 bar at 370C. What is the concentration of an aqueous NaCl solution that could be used in blood stream? [R = 0.0821 JK-1mol-1]
The value of Kf for water is 1.86, calculated from glucose solution. The value of Kf for water, calculated from NaCl solution will be (M.Wt of NaCl = 58.5 g/mol):
At temp 3270C and concentration C, Osmotic pressure of a solution is P. The same solution at concentration C/2 and temp 4270C shows Osmotic pressure 2atm. Value of P will be:
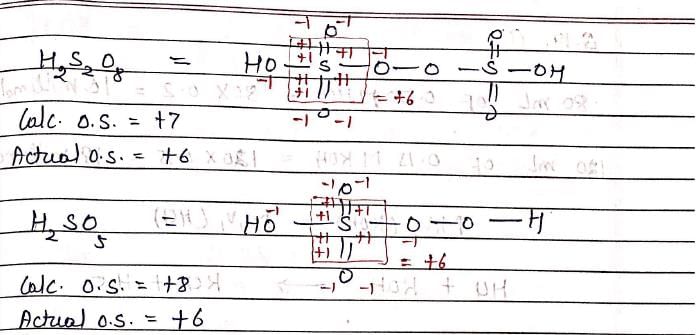
H2S2O8 and H2SO5 both have +6 oxidation state of sulfur. This is due to:
In an experiment, 20g of Vanadium oxide (molar mass 182 g/mol) was reduced by excess of Zinc dust in acidic solution to Vanadium (II) ions. The required number of moles of Iodine to re-oxidize Vanadium (II) to VO2+ is:
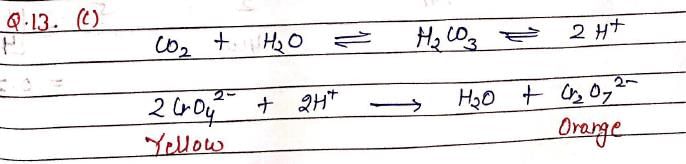
If CO2 is passed into waste water containing CrO4–2 (yellow), then, solution turns:
When 80 mL of 0.20 M HCl is mixed with 120 mL of 0.15 MKOH, the resulting solution is same as a solution of:
200 ml M/2 HNO3, 100 ml M/1 NaOH, 200 ml M/5 HCl are mixed together. The normality and the nature of mixture is:
A 5.25% solution of a substance is isotonic with a 1.5 % solution of Urea in the same solvent. If density of both the solutions are assumed to be equal to 1.0g cm–3, molar mass of substance will be:
Which of the following condition is not satisfied by an ideal solution ?
At a suitable pressure near the freezing point of water, there exists:
0.1 M NaCl and 0.05 M BaCl2 solutions are separated by a semi-permeable membrane in a container. For this system, choose the correct alternative:
Normal boiling point of water is 373K (at 760mm). Vapor pressure of water at 298K is 23mm. If enthalpy of evaporation is 40656 J/mol, boiling point of water 23mm pressure will be:
[R = 8.314821 JK-1mol-1]
A 20 mL solution of Na2SO3 required 30 mL of 0.01 M Potassium dichromate solution for oxidation to Na2SO4. Hence, Molarity of Na2SO3 solution is:
In [Cr(O2)(NH3)4(H2O)]Cl2, oxidation number of Cr is +3, the, O2 will be in form:
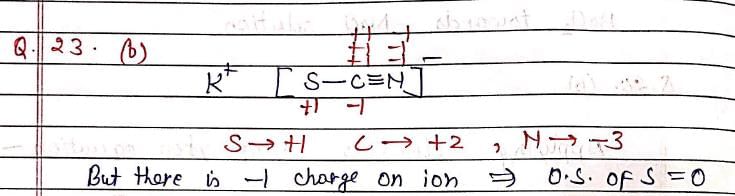
Oxidation state of sulfur in KSCN is (assume there is triple bond between C and N):
Starch paper is used to test the presence of:
10 mL of a blood sample (containing Calcium oxalate) is dissolved in an acid. It required 20 mL of 0.001 M KMnO4 (which oxidizes oxalate to CO2). Hence, Ca2+ ion in 10 mL blood is:
0.01 M solution of KCl and BaCl2 are prepared in water. The freezing point of KCl is found to be –20C. What is freezing point of BaCl2 solution when it is completely ionized?
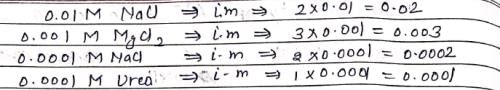
The correct order of increasing boiling points of the following aqueous solutions:
(I). 0.0001 M NaCl
(II). 0.0001 M Urea
(III). 0.001 MgCl2
(IV). 0.01 M NaCl
58.5 g of NaCl and 180 g of Glucose were separately dissolved in 1000 mL of water. Identify the correct statement regarding elevation of boiling point of resulting solutions:
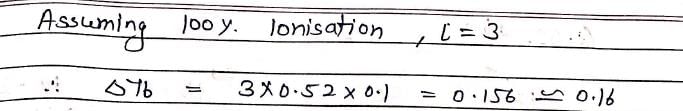
The elevation in boiling point of a solution of 13.44g of CuCl2 in 1Kg of water using following information will be ?
(M.Wt of CuCl2 = 134.4, Kb = 0.52 K molal–1, assume CuCl2 as a strong electrolyte):
Consider separate solutions of 0.5M C2H5OH (aq), 0.1 M Mg3(PO4)2 (aq), 0.25 M KBr (aq), 0.125 M Na3PO4 (aq). Which statement is true about these solutions, assuming all salts to be strong electrolytes ?
|
2 docs|25 tests
|