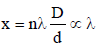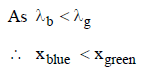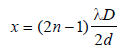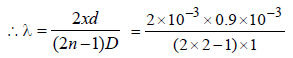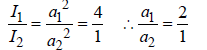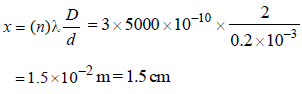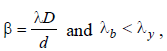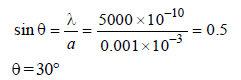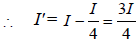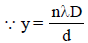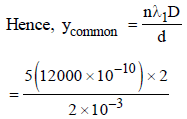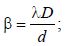31 Year NEET Previous Year Questions: Wave Optics - NEET MCQ
21 Questions MCQ Test Physics Class 12 - 31 Year NEET Previous Year Questions: Wave Optics
Which one of the following phenomena is notexplained by Huygen’s construction ofwavefront? [1988]
Which of the following phenomenon is notcommon to sound and light waves ? [1988]
Interference is possible in [1989]
The Young’s double slit experiment is performed with blue and with green light of wavelengths 4360Å and 5460Å respectively. If x is the distance of 4th maxima from the central one, then [1990]
In Young’s double slit experiment, the fringe width is found to be 0.4 mm. If the whole apparatus is immersed in water of refrative index 4/3, without disturbing the geometrical arrangement, the new fringe width will be [1990]
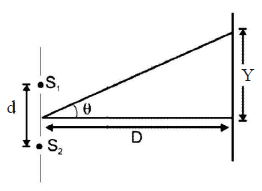
In Young’s experiment, two coherent sources areplaced 0.90 mm apart and fringe are observedone metre away. If it produces second dark fringeat a distance of 1 mm from central fringe, thewavelength of monochromatic light used wouldbe [1991, 1992]
Ratio of intensities of two waves are given by 4 : 1. Then the ratio of the amplitudes of the twowaves is [1991]
In Young’s double slit experiment carried out withlight of wavelength (λ) = 5000Å, the distancebetween the slits is 0.2 mm and the screen is at 200 cm from the slits. The central maximum is at x = 0. The third maximum (taking the central maximum as zero th maximum) will be at x equal to [1992]
If yellow light emitted by sodium lamp in Young’s double slit experiment is replaced by a monochromatic blue light of the same intensity [1992]
Interference was observed in interferencechamber where air was present, now the chamberis evacuated, and if the same light is used, acareful observer will see [1993]
A parallel beam of monochromatic light ofwavelength 5000Å is incident normally on asingle narrow slit of width 0.001 mm. The light isfocussed by a convex lens on a screen placed infocal plane. The first minimum will be formed forthe angle of diffraction equal to [1993]
In a Fresnel biprism experiment, the two positionsof lens give separation between the slits as 16cm and 9 cm respectively. What is the actualdistance of separation? [1996]
Colours appear on a thin soap film and on soapbubbles due to the phenomenon of [1999]
Which of the following shows particle nature oflight? [2001]
A paper, with two marks having separation d, isheld normal to the line of sight of an observer ata distance of 50m. The diameter of the eye-lensof the observer is 2 mm. Which of the followingis the least value of d, so that the marks can beseen as separate ? The mean wavelength ofvisible light may be taken as 5000 Å. [2002]
The periodic waves of intensities I1 and I2 pass through a region at the same time in the same direction. The sum of the maximum and minimum intensities is:
A lens having focal length f and aperture of diameter d forms an image of intensity I. Aperture of diameter
2/d in central region of lens is covered by a black paper. Focal length of lens and intensity of image now will be
respectively:
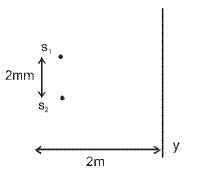
In Young’s double slit experiment, the slits are 2 mmapart and are illuminated by photons of twowavelengths λ1 = 12000Å and λ2 = 10000Å. Atwhat minimum distance from the common centralbright fringe on the screen 2 m from the slit will abright fringe from one interference patterncoincide with a bright fringe from the other ? [NEET 2013]
A parallel beam of fast moving electrons isincident normally on a narrow slit. A fluorescentscreen is placed at a large distance from the slit.If the speed of the electrons is increased, whichof the following statements is correct ? [NEET 2013]
In Young’s double slit experiment the distancebetween the slits and the screen is doubled. Theseparation between the slits is reduced to half.As a result the fringe width [NEET Kar. 2013]
A parallel beam of light of wavelength λ is incident normally on a narrow slit. A diffraction pattern is formed on a screen placed perpendicular to the direction of the incident beam. At the second minimum of the diffraction pattern, the phase difference between the rays coming from the two edges of slit is [NEET Kar. 2013]
|
98 videos|334 docs|102 tests
|