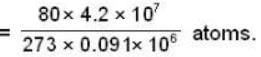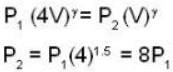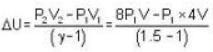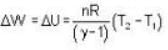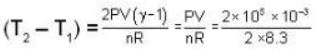IIT JAM Physics MCQ Test 7 - Physics MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test IIT JAM Physics Mock Test Series 2025 - IIT JAM Physics MCQ Test 7
Vessel A is filled with hydrogen while vessel B, whose volume is twice that of A, is filled with the same mass of oxygen at the same temperature. The ratio of the mean kinetic energies of hydrogen and oxygen is
At what temperature will the r.m.s. velocity of gas be half its value at 0°C ?
A gas has molar heat capacity C = 37.35J mol-1 k-1 in the process PT = constant. Find the number of degrees of freedom of molecules in the gas.
Calculate the difference of heat capacities of He 4 if the specific volume of it at 6 K and at a pressure of 19.7atm be 2.64* 10-2 m3 k mol-1. Given KT = 9.42* 10-8 m2N-1 and α = 5.35*10-2 K-1.
If 250 g of Ni at 120° C is dropped into 200 g of water at 100C contained by a calorimeter of 20 cal/0C heat capacity, what will be the final temperature of the mixture? (Given CNi = .106k cal/0C)
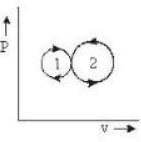
In the following indicator diagram, the net amount of work done will be
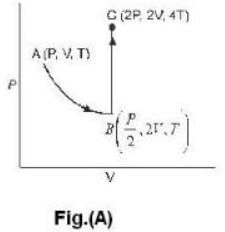

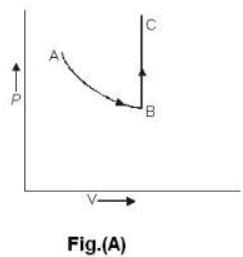
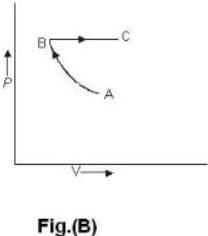
One mole of an ideal gas is takes from an initial state (P. V. T) to a final state (2P. 2V, 4T) by two different paths as shown in the Fig.A and B given above. If the changes in internal energy between the final and the initial states of the gas along the paths I and II are denoted by  respectively, then :
respectively, then :
A carnot engine accepts 1000 calorie heat at 500K and give back 400 calorie heat to sink. What temperature is of sink?
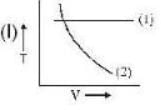
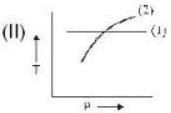
If (1) represents isothermal and (2) represents adiabatic, which of the graphs given above in respect of an ideal gas are correct?
Consider a reversible isothermal expansion of a photon gas. Determine the entropy S for this gas at temperature T and volume V
The Joule-Thomson coefficient and change in temperature during Joule- Thomson effect is given by
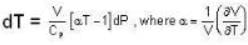
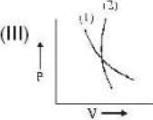
which one is correct about αT to produce cooling and heating effect respectively?
A system of N localized, non-interacting spin 1/2 ions of magnetic moment μ each is kept in an external magnetic field H. If the system is in equilibrium at temperature T, then Helmholtz free energy of the system is
For a system comprising a very large number of particles N of similar subsystem . and each having partition function Z. if the system is to be considered non-interacting, then the partition function for the composite system is given by
The change in vapour pressure of water as the boiling temperature changes from 100oC to 103oC. Given latent heat of steam = 540 cal./gm. and specific volume of steam = 1670 c.c./gm.
The diameter of 4He atom is 1  . One mole of the gas occupies 20 litres at 20 K. Given R = 8.4 J mol-1 K-1 and NA = 6 x 1023 mol-1 Then
. One mole of the gas occupies 20 litres at 20 K. Given R = 8.4 J mol-1 K-1 and NA = 6 x 1023 mol-1 Then
There are two vessels; each of them contains one mole of a monatomic ideal gas. Initial volume of the gas in each vessel is 8.3 * 10-3 m3 at 27oC. Equal amount of heat is supplied to each vessel. In one of the vessels the volume of the gas is doubled without change in internal energy, whereas the volume of the gas is held constant in the second vessel. The vessels are now connected to allow free mixing of the gas. (R = 8.3 J/mol K.) Then
One gram of water (1 cm3) becomes 1671 cm3 of steam when boiled at a constant pressure of 1 atm (1.013 * 105 Pa). The heat of vaporization at this pressure is Ly= 2.256 x 106 J/kg. Then
At what temperature (in Kelvin) will the average speed of hydrogen molecules be the same as that of nitrogen molecules kept at 35oC. Molecular weights of nitrogen and hydrogen are 28 and 2 atomic mass units respectively. Given Boltzmann’s constraint = 1.38 * 10-23 joule per degree.
At what temperature (in Kelvin) is the root mean square velocity equal to the escape velocity from the surface of the earth for hydrogen and for oxygen?
Two glass bulbs of equal volumes are connected by a narrow tube and are filled with a gas at OoC and a pressure of 76 cm of Hg. One of the bulbs is then placed in a water bath maintained at 62oC . What is the new value of pressure (in cm) inside the bulbs in terms of Hg? The volume of connecting tube is negligible.
A vessel of volume V = 30 litre contains an ideal gas at temperature. T = 0°C. Keeping temperature constant, a part of the gas is allowed to escape from the vessel causing the pressure to fall down by ΔP = 0.78 atm. Find the mass of the gas released. Its density under normal conditions is p= 1.3 g/it
A vertical hollow cylinder contains an ideal gas. The gas is enclosed by a 5 kg movable piston with area of cross section 5x10-3m2. Now the gas is heated from 300 K to 350K and the piston rises by 0.1 m. The piston is now clamped at this position and the gas is cooled back to 300K. Find the difference between the heat energy added during the heating process and the energy lost during the cooling process. (1 atm = 105 N/m2)
During an integral number of complete cycles, a reversible engine (shown by a circle) absorbs 1200 joules from reservoir at 400 K and performs 200 joules of mechanical work, find the sum of quantities of heat (in Joules) exchanged with the other two reservoirs.
Suppose 1.00 kg of water at 1000C is placed in thermal contact with 1.00 kg of water at O0C. What is the total change in entropy (in J/K)? Assume that the specific heat of water is constant at 4190 J/kgk over this temperature range.
Calculate the critical temperature (in °C) of a gas for which the Vander Waal’s constants are a = 0.00374. b = 0.0023 and the gas constant is given by 273 R = 1.00646.
Calculate the pressure (in atmospheres) required to make water freeze at - 10C. Change of specific volume when 1 gm of water freezes into ice = .091 cc.,J =4.2 x 107 ergs/cal..1 atmosphere 106 dynes / cm2 and the latent heat of ice = 80 cal./ gm.
A weightless piston divides a thermally insulated cylinder into two parts of volumes V and 3V. 2 moles of an ideal gas at pressure P = 2 atmosphere are confined to the part with volume V = 1 litre. The remainder of the cylinder is evacuated. Initially the gas is at room temperature. The piston is now released and the gas expands to fill the entire space of the cylinder. The piston is then pressed back to the initial position. Find the increase of internal energy (in Joule) in the process. The ratio of the specific heat of the gas γ = 1.5.
|
4 docs|21 tests
|


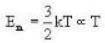
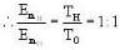
 we have
we have 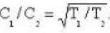
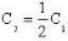 So. we have,
So. we have, 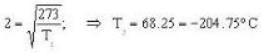

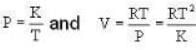
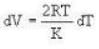
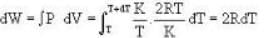

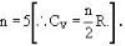
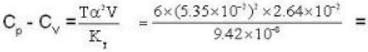 4813 J.k mol-1 K-1
4813 J.k mol-1 K-1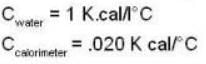
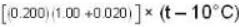

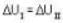


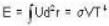
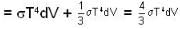
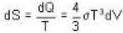
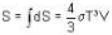
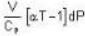
 or heating is produced.
or heating is produced.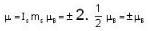 ...(i)
...(i)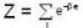
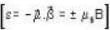 ...(ii)
...(ii)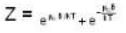

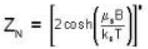
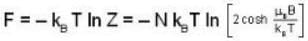
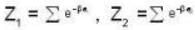
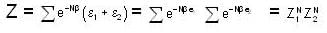 Given Z1 = Z2
Given Z1 = Z2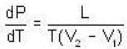
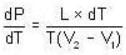
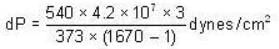
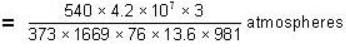
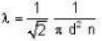
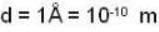
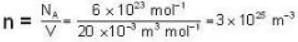
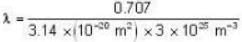

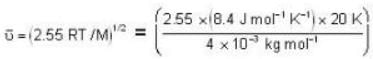
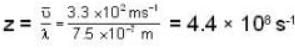
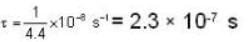

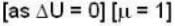
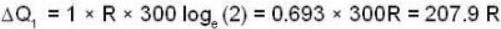
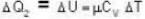
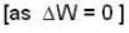
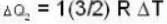
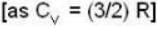
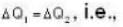
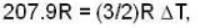
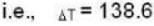
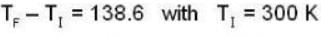

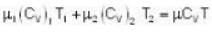 With
With 
 and
and 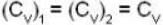
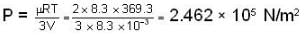
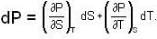
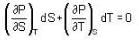
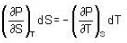

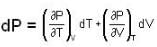
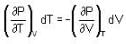
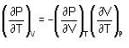
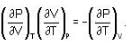
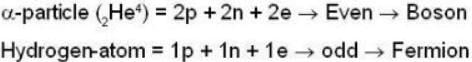


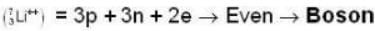
 are the average speeds of hydrogen and nitrogen molecules at temperatures T1K and T2K respectively, we have
are the average speeds of hydrogen and nitrogen molecules at temperatures T1K and T2K respectively, we have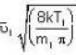 ...(i)
...(i)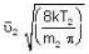 ...(ii)
...(ii)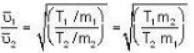 ...(iii)
...(iii)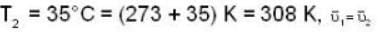
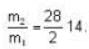
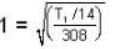
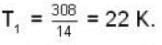
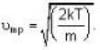


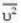
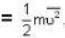
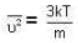
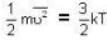
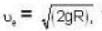 where R is the radius of the earth.
where R is the radius of the earth. 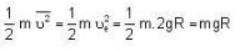
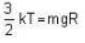
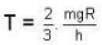
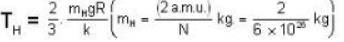
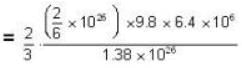
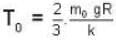
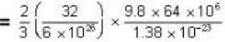
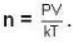
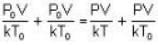
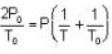
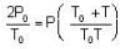
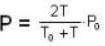
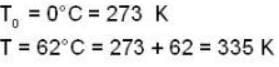
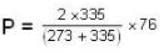
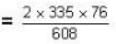 = 83.75 cm of Hg
= 83.75 cm of Hg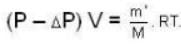 ...(ii)
...(ii)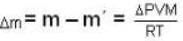
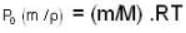
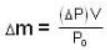

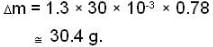
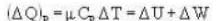 ...(i)
...(i)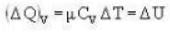 ..(ii)
..(ii)

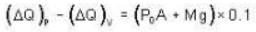
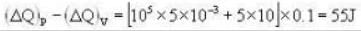 Ans.
Ans.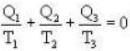 i.e.
i.e. 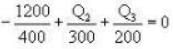
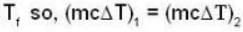
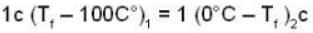
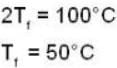

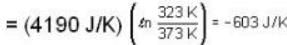
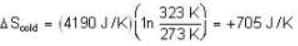


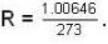

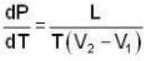
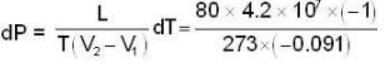 dynes/cm2.
dynes/cm2.