Test: Fibre to Fabric - Class 6 MCQ
5 Questions MCQ Test Science Olympiad Class 6 - Test: Fibre to Fabric
Refer to the given figures, X and Y and select the correct statement regarding them.


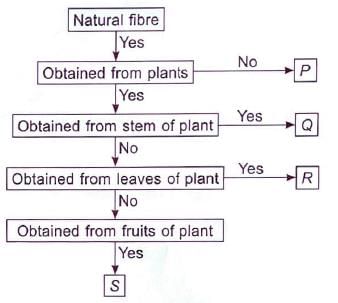
Refer to the given flow chart and select the incorrect statement regarding P, Q, R and S.

| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Different steps involved in processing of fibres are given below.
(i) Spinning
(ii) Weaving
(iii) Ginning
(iv) Scouring
(v) Retting
Select the option that correctly identifies the steps that are involved in processing of cotton.
(i) Spinning
(ii) Weaving
(iii) Ginning
(iv) Scouring
(v) Retting
Refer to the given dichotomous key and select the incorrect statement regarding P , Q, R, S and T.
(i) (a) It is a natural fibre. - Go to (ii)
(ii) (b) It is a man-made fibre. - P
(ii) (a) Fibre is obtained from plants.- Go to (iii)
(b) Fibre is obtained from animals.- Go to (iv)
(iii) (a) Fibre obtained from stem. - Q
(b) Fibre obtained from fruit. - R
(iv) Fibre obtained by killing of source organism. - S
(b) Fibre obtained by killing source organism. - T
Read the following characteristics of a fibre and identify it.
(i) It is a natural breathable fabric, i.e., the air can pass in and out through its fibres.
(ii) Each fibre is made up of 20-30 layers of coiled cellulose springs.
(iii) It has moisture absorbing quality and is used to make good quality clothes.
(iv) It has natural twist that makes it suitable for spinning.
|
49 videos|108 docs|105 tests
|
|
49 videos|108 docs|105 tests
|

















