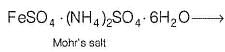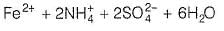Test: Introduction to Coordination Compounds - NEET MCQ
25 Questions MCQ Test Chemistry Class 12 - Test: Introduction to Coordination Compounds
Only One Option Correct Type
Direction (Q. Nos. 1-10) This section contains 10 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE is correct.
Q.
Primary and secondary valency of Pt in [Pt(en)2CI2] are
If zeise’s salt has the formula [Pt(C2H4)CI3]-. In this, platinum primary and secondary valency are
The two complexes PtCI4 . 2NH3 and PtCI4 . 2KCI do not give precipitate of AgCI when treate with AgNO3. The structures of these complexes are
A cobaltamine has the formula CoCI3 . xNH3. This when reacted with AgNO3 solution, one third of the chloride is precipitated. It can have the structure
The spin only magnetic moment value (in Bohr magneton units) of Cr(CO)6 is
The anion acetylacetonate (acac) forms chelate with Co3+, The ring of the chelate is
Oxidation states of iron in the complexes [Fe(H2O)5NO]2+ are
Complexes in which the oxidation number of a metal is zero is/are
An example for bidentate and negatively charged ligand is
One or More than One Options Correct Type
Direction (Q. Nos. 11-15) This section contains 5 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONE or MORE THAN ONE are correct.
Q.
An example of double salt is/a
Type of bonding in K4 [Fe(CN)6] is/a
The effective atomic number of Fe in Fe(CO)5 is
Which of the following statements is/are correct?
A freshly prepared aqueous solution of Pd(NH3)2CI2 does not conduct electricity, it suggests that
Comprehension Type
Direction (Q. Nos. 16 and 17) This section contains a paragraph, describing theory, experiments, data, etc. Two questions related to the paragraph have been given. Each question has only one correct answer among the four given options (a), (b), (c) and (d).
Passage
Complex compounds are addition compounds formed by the stoichiometric combination of two or more simple salts but do not decompose into constituent ions completely. The first such complex prepared by Tassaert is hexamine cobalt (III) chloride. Later many such compounds were prepared and their properties were studied. The chloramines complexes of cobalt (III) chromium (III) not only exhibit a spectrum of colours but also differ in the reactivity of their chlorides. Moreover, greater the number of ions produced by a complex in solution, greater is the electrical conductivity. This type of information was obtained for several series of complexes.
Q.
Coordination number of Co in CoCl3 . 5H2O is six. The volume of 0.1 N AgNO3 needed to precipitate the chlorine in 200 mL of 0.01 M solution of complex is
Complex compounds are addition compounds formed by the stoichiometric combination of two or more simple salts but do not decompose into constituent ions completely. The first such complex prepared by Tassaert is hexamine cobalt (III) chloride. Later many such compounds were prepared and their properties were studied. The chloramines complexes of cobalt (III) chromium (III) not only exhibit a spectrum of colours but also differ in the reactivity of their chlorides. Moreover, greater the number of ions produced by a complex in solution, greater is the electrical conductivity. This type of information was obtained for several series of complexes.
Q.
The number of ions per mole of the complex CoCI3 . 5NH3 in aqueous solution will be
Matching List Type
Direction (Q. No. 18) Choices for the correct combination of elements from Column I and Column II are given as options (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which one is correct.
Q.
'Match the Column I with Column II and mark the correct option from the codes given below.
One Integer Value Correct Type
Direction (Q. Nos. 19-23) This section contains 5 questions. When worked out will result in an integer from 0 to 9 (both inclusive).
Q.
Formula of Mohr’s salt is FeSO4 . (NH4)2SO4 . xH2O. Here x value is
When AgNO3 solution is added in excess to 1 M solution of CoCI3 . xNH3, one mole of AgCI is formed. The value of x is
The volume (in mL) of 0.1 M AgNO3 required for complex precipitation of chloride ions present in 30 mL of 0.01 M solution of [Cr(H2O)5Cl]Cl2, as silver chloride is close to
Oxidation state of cobalt in Co(CO)6 is
In the complex PtCl4 . 5NH3 if coordination number of platinum is 6, number of chloride ions precipitated by adding AgNO3 are
Statement Type
Direction (Q. Nos. 24 and 25) This section is based on Statement I and Statement II. Select the correct answer from the codes given below.
Q.
Statement I : Oxidation state of Fe in Fe(CO)5 is zero.
Statement II : EAN of Fe in this complex is 36.
Statement I : The oxidation num ber of platinum in Zeise’s salt is +4.
Statement II : Zeise’s salt is ionic complex.
|
108 videos|286 docs|123 tests
|