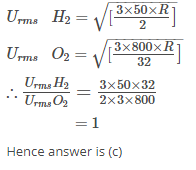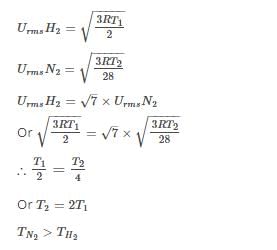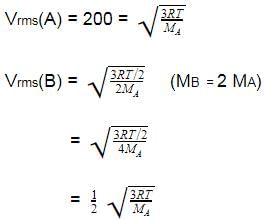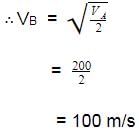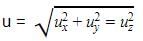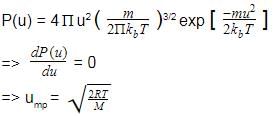Test: Molecular Velocity (Old NCERT) - JEE MCQ
20 Questions MCQ Test Chemistry for JEE Main & Advanced - Test: Molecular Velocity (Old NCERT)
Direction (Q. Nos. 1-15) This section contains 15 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE option is correct.
Q. Pressure and temperature needed to confine 1.0 x 1025 gas molecules, each with a mass of 1.0x 1025 kg and root mean square velocity of 1.0x 103ms-1 in a 1.0 m3 container are

At 298 K, which of the following gases has the lowest average molecular speed?
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
By what ratio will the average velocity of the molecules in a gas change when the temperature is raised from 50°C to 200°C?
The root mean square velocity of a monoatomic gas (molar mass = m g mol-1) is u. Its kinetic energy per mole (E) is related to u by equation
Root mean square velocity (u) is dependent on temperature. Value of is
The pressure needed to confine 1.00 mole of N2 molecules to 24.8 L flask is 1.0 bar. Thus, root mean square velocity of the gas assuming ideal behaviour is
The ratio between the root mean square speed of H2 gas at 50 K and that of O2 gas at 800 K is
[IIT JEEE 1996]
The rms velocity of hydrogen gas is √7 times of the rms velocity of nitrogen gas. If T is the temperature of the gas, then
[IIT JEE 2000]
For CO2, given that average velocity at T, is equal to most probable velocity at T2.
Thus, T1/T2 is
For gaseous state, if most probable speed is denoted by C*, average speed by and mean square speed by C, then for a large number of molecules, the ratios of these speeds are
[JEE Main 2013]
Molar mass of a certain gas B is double that of A.
Also RMS velocity of gas A is 200 ms -1 at a certain temperature. RMS velocity of gas B at the temperature half that of A is
A vessei of capacity 1 dm3 contains 1.03 x 1023 H2 molecules exerting a pressure of 101.325 kPa. Calculate RMS speed and average speed.
The molecular velocity of any gas is
[AlEEE 2011]
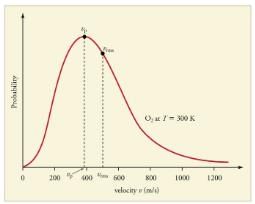
Distribution of molecules with velocity is represented by the curve as shown Select the correct statement(s).
Direction (Q. Nos. 16 and 17) This section contains 2 questions. when worked out will result in an integer from 0 to 9 (both inclusive).
Q. Temperature of an ideal gas is changed from -173°C to 127°C. Thus average velocity changes by .......... times.
At what temperature (in °C) root mean square velocity of O2 gas at 300 K is equal to most probable velocity of Ne(20 g mol-1)?
Direction (Q. Nos. 18-20) This section contains a paragraph, wach describing theory, experiments, data etc. three Questions related to paragraph have been given.Each question have only one correct answer among the four given options (a),(b),(c),(d).
Distribution of molecular velocities was studied by Maxwell and is given by
is also called probability P.
Q.
Based on following curves, arrange temperatures T1 , T2 and T3 in increasing order,
Distribution of molecular velocities was studied by Maxwell and is given by
is also called probability P.
Q. Following is the distribution of molecules at 300 K for gases X, Y and Z
Thus,
Distribution of molecular velocities was studied by Maxwell and is given by
is also called probability P.
Q.
As velocity increases, probability also increases. It is maximum at a particular velocity. This is called most probable velocity. At this point, variation of probability P with velocity u is
Thus, based on this, velocity is
|
352 videos|596 docs|309 tests
|
|
352 videos|596 docs|309 tests
|


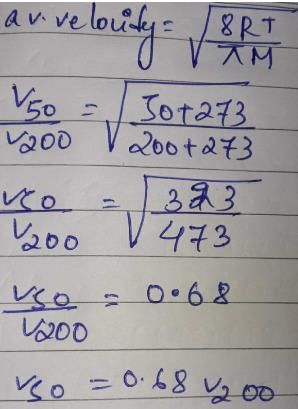
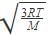 /DT
/DT