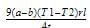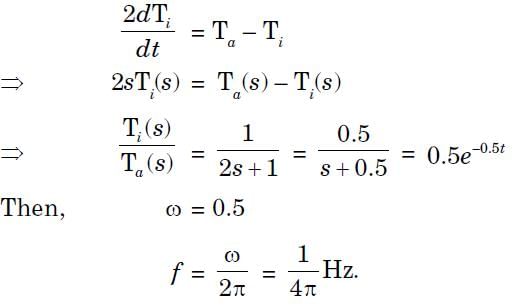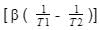Test: Measurement of Temperature - Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) MCQ
20 Questions MCQ Test Sensor & Industrial Instrumentation - Test: Measurement of Temperature
A straight bimetallic strip 25 cm long and 1.4 mm thick is made of copper and invar and has one end fixed. How much will the free end of the strip deflect if the temperature changes 18°F?
A 42-cm length of 2.3-mm thick copper-invar bimetallic strip is wound into a spiral
with a radius of 5.2 cm at 70°F. What is the deflection of the strip at 120°F?
What is the resistance of a platinum resistor at 480°C if its resistance at 16°C is 110Ω?
The characteristics of a thermometer measuring ambient temperature are 2 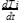 + Ti - Ta = 0 where Ti and Ta are the indicated and ambient temperatures, respectively, both in C, and time is in seconds. The – 3 dB cut-off frequency in the frequency response of the thermometer is
+ Ti - Ta = 0 where Ti and Ta are the indicated and ambient temperatures, respectively, both in C, and time is in seconds. The – 3 dB cut-off frequency in the frequency response of the thermometer is
For a copper-constantan (Type T) thermocouple, the junction potential E (in V) at C is given
by E = 38.74θ + 3.3 x 10– 2 θ 2 + 2.07 x 10– 4 θ 3 – 2.2 x 10– 6 θ 4 +higherorderr terms, assuming the cold junction compensation. The sensitivity of thermocouple at 100C is approximately
The values of the material constants for thermistors P and Q are 4000 K and 3000 K, respectively. The resistance of each thermistor at 298 K is 2 kΩ . At 373 K, the ratio of the resistance of thermistor P to that of thermistor Q will be closest to
A type J (iron-constantan) thermocouple has a voltage sensitivity of 55 μV/C. A digital voltmeter (DVM) is used to measure the voltage under the condition shown in the following
figure.
Given that T1 = 300C, T2 = 100C and T3 = T4 = 20 C, the meter will indicate a voltage of
A thermometer at room temperature 30C is dipped suddenly into a bath of boiling water at 100C. It takes 30 seconds to reach 96.5C. The time required to reach a temperature of 98 C is
A mercury barometer reads h mm Hg with the temperature of the mercury at T C. The barometer reading corrected for the standard temperature 0 C with β denoting the volumetric
The expansion coefficient of mercury in 0 C– 1 is
A temperature-measuring instrument is modeled as a first-order system with a time constant of 5s. The sensor of the instrument is placed inside an oil bath whose temperature has a sinusoidal
variation with an amplitude of 10 0C and a period of 20s around an average temperature of 200 0C.
The sinusoidal component at the output of the instrument will have amplitude.
Data given below should be used for answering questions
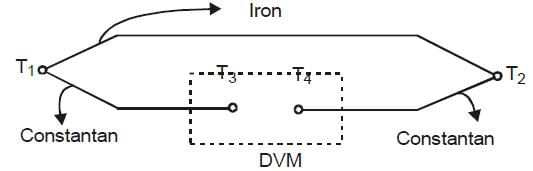
The table provides the thermo-emf sensitivity of five materials concerning platinum around 273 K
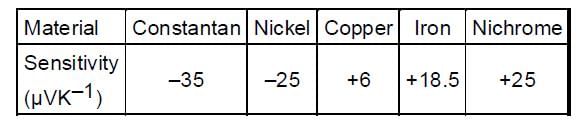
The thermocouple pair that gives the maximum sensitivity around 273 K is
Data given below should be used for answering questions
The table provides the thermo-emf sensitivity of five materials concerning platinum around 273 K
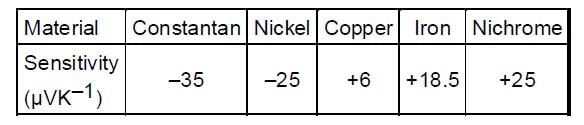
Two copper -constantan thermocouples are connected such that the two constantan wires are joined together. The two copper wires are connected to the input of a low noise chopper stabilized differential amplifier having a gain of 1000. One thermocouple junction is immersed in a flask containing ice and water in equal proportion. The other thermocouple is at a temperature of T.
If the output of the amplifier is 2.050 V, the temperature T is
A thermocouple is suddenly immersed in a medium of high temperature. The approximate
time taken by the thermocouple to reach 98% of the steady-state value is
The sensing element of a thermocouple at its hot junction is provided with a shield while taking measurements in a high-temperature gas. The principal reason for giving the shield is
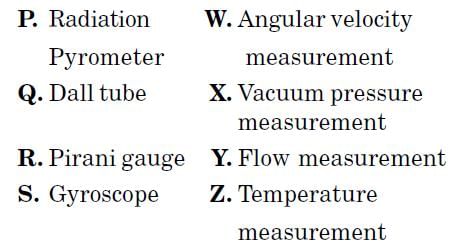
In the context of transducers, identify the correct matches List I with List II :
Which of the following is used as an indication instrument in a liquid expansion system?
When a bimetallic thermometer is heated, curling occurs to the metal side with the least temperature coefficients.
Ratio of the net amount of heat received and stored in the body for a specific time interval is known as
In a steel bulb thermometer, which liquid can be used for measuring temperature up to 60000C?
|
23 videos|24 docs|29 tests
|


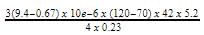 cm = 2.1 cm
cm = 2.1 cm