Assertion & Reason Test: Mineral & Energy Resources - 1 - Class 10 MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test Geography for Class 10 - Assertion & Reason Test: Mineral & Energy Resources - 1
Match the following items given in column A with those in column B:
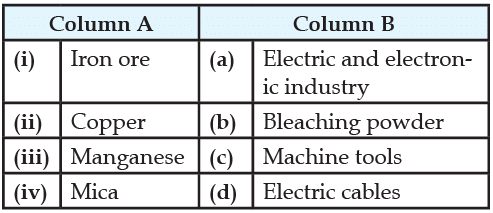

Match the following items given in column A with those in column B:
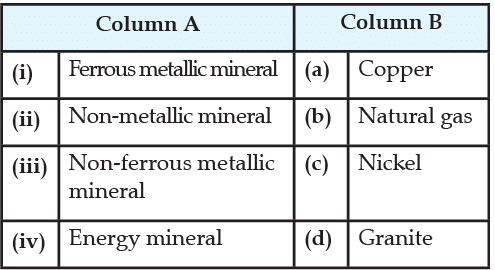

Arrange the following in correct sequence:
Following is the sequence of generating tidal energy:
(i) During high tide water flows into the inlet and gets trapped when the gate is closed.
(ii) Floodgate dams are built across inlets.
(iii) By this method oceanic tides can be used to generate electricity.
(iv) After the tide falls outside the floodgate, the water retained by the floodgate flows back to the sea via pipe that carries it through a power - generating turbine.
Arrange the following in correct sequence:
Following is the sequence of generating geothermal :
(i) It is so hot that when it rises to the earth's surface, it turns into steam.
(ii) Groundwater in such areas (where the geothermal gradient is high) absorbs heat from the rocks and becomes hot.
(iii) This steam is used to drive turbines and generate electricity.
(iv) Geothermal energy exists, because the earth grows progressively hotter with increasing depth.
Analyse the information given below, considering one of the following correct options:
It lies in Chhattisgarh and Maharashtra. Very high grade hematites are found in the famous Bailadila range of hills in the Bastar district of Chhattisgarh. The range of hill comprises 14 deposits of super high grade hematite iron ore. It has the best physical properties needed for steel making. Iron ore from these mines is exported to Japan and South Korea Via Visakhapatnam port.
Analyse the information given below, considering one of the following correct options:
Shrubs, farm waste, animal and human waste are used to produce biogas for domestic consumption in rural areas. Decomposition of organic matter yields gas, which has higher thermal efficiency in comparison to kerosene, dung cake and charcoal. Biogas plants are set up at municipal, cooperative and individual levels. The plants, using cattle dung are known as 'Gobar gas plants' in rural India. These provide twin benefits to the farmer in the form of energy and improved quality of manure. Biogas is by far the most efficient use of cattle dung. It improves the quality of manure and also prevents the loss of trees and manure due to burning of fuel wood and cow dung cakes.
Assertion and Reason Type Questions:
In the questions given below, there are two statements marked as Assertion (A) and Reason (R). Read the statements and choose the correct option:
Assertion (A) : Toothpaste cleans our teeth.
Reason (R) : The sparkle in some toothpastes comes from mica.
Assertion and Reason Type Questions:
In the questions given below, there are two statements marked as Assertion (A) and Reason (R). Read the statements and choose the correct option:
Assertion (A) : India is fortunate to have fairly rich and varied mineral resources.
Reason (R) : These variations exist largely because of the differences in the geological structure, processes and time involved in the formation of minerals.
Find the incorrect option:
Find the incorrect option:
|
22 videos|57 docs|40 tests
|


















